Muscular System
advertisement

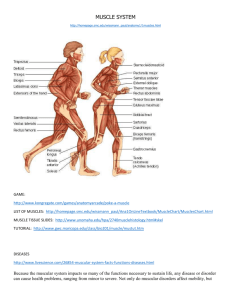
Indiana Standard: 5 Osteocyte The Muscular System Functions of the 640 Muscles in our Body • Move bones and joints • Push substances such as food, fluid and blood through the body • Help regulate body temperature by releasing heat when energy is used, and by shivering when we are cold. Osteocyte The Muscular System Three Types of Muscle Smooth Muscle Cardiac Muscle Skeletal Muscle Muscle Cells are Called Muscle Fibers Osteocyte The Muscular System Smooth Muscle • Involuntary muscle (doesn’t require thought to move) • Smooth without striations or stripes • Lines many organs, examples: • Moves food through digestive system • Empties the bladder • Pushes baby out during birth • Regulates width of blood vessels Osteocyte The Muscular System Cardiac Muscle • Involuntary muscle (doesn’t require though to move) • Striated or striped • Makes up most of the heart • Pumps blood through the body • Cells are connected with intercalated discs that allow impulses to travel from cell to cell triggering contractions Osteocyte The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle • Voluntary (requires thought to move) • Striated or striped • Attached to joints with tendons at points of origin (immovable end) and insertion (moveable end) • Made up of fast twitch and slow twitch muscle fibers Osteocyte The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Point of Origin •Point of attachment that does not move. Point of Insertion •Point of attachment that moves. The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Fast Twitch Muscle Fibers • Contribute to speed • Anaerobic respiration provides energy via glycolysis • Less mitochondria The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Slow Twitch Muscle Fibers • Contribute to endurance • Aerobic respiration provides energy via the citric acid cycle and electron transport chain which yield 36 ATP • More mitochondria The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Fiber Muscle Fiber • Muscle cell The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Fiber Myofibril • Long strands of protein within muscle fibers • Contain actin and myosin filaments The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Fiber Sarcomere • Section of a myofibril • Contain the actin and myosin needed to make the muscle contract The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Fiber Actin • Thin protein fibers • Attached to the ends of the sarcomere which are called Z lines • Pulling on actin filaments causes the sarcomere to contract The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Fiber Myosin • Thick protein fibers • Attached to the center of the sarcomere which is called the M line • Myosin fibers are responsible for the pulling action that causes the sarcomere to contract The Muscular System Increase or Loss of Muscle Tissue Hypertrophy • Muscles grow when they are exposed to physical stress causing microscopic damage • The body releases cytokines to activating the immune system to repair damage • The repetitive process of damage and repair eventually makes muscles bigger and stronger • This increase in mass and strength is hypertrophy The Muscular System Increase or Loss of Muscle Tissue Hypertrophy • The body’s ability to repair muscle affected by: • Diet • Rest • Genetics Atrophy • When muscles are not exposed to resistance or physical stress they shrink • This is known as atrophy The Muscular System Isotonic and Isometric Contractions Isotonic Contractions • There IS movement with isotonic exercise • Isotonic exercise builds muscle Isometric Contractions • Isometric exercises are static exercise • There is NO movement with isometric exercise • Isometric exercise builds muscle KAHOOT