Financial Statement Forecasting
advertisement

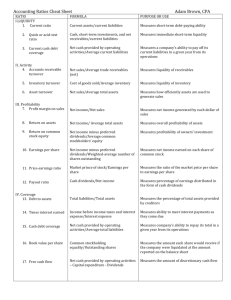
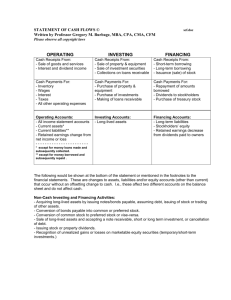
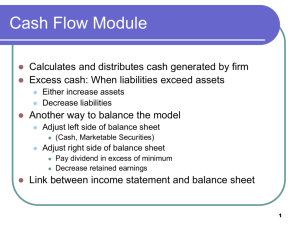
Financial Statements Forecasting 3 Primary Financial Statements Income statement Balance sheet Consolidated statement of cash flows Other decision-making measures: Financial ratios Common size statements Free cash flow projections & valuation Financial Analysis Assess the strengths and weaknesses of the firm’s current condition Ratio analysis Break-even analysis Operating and financial leverage analysis Generate pro forma financial statements to identify strategies to improve the condition and assess future risks Growth and the Need for Financing Growth is frequently associated with cash Faster growth more profits more cash This is incorrect! Growth and profits do not always generate sufficient cash flow to cover the assets needed for growth! Growth needs to be managed and planned Firms often fail when the needs of expansion overwhelm the available resources for expansion 4 Flow of a Sales-Driven Model 5 Sustainable Growth in the Rapid Growth Phase “It takes money to make money" phase Increased sales require more assets of all types Internal sources may not generate enough cash Retained earnings Increase in spontaneous liabilities May need to raise capital externally Debt Equity 6 Calculating the Discretionary Financing Needed Compile changes in assets Left side of balance sheet Cash Current Assets Inventories & Account Receivables Long-term assets Net Fixed Assets Goodwill Subtract forecasted Total Liabilities and Equity from Total Assets to determine Discretionary Funds Needed (DFN) 7 Achieving Equilibrium When Discretionary Funds Needed is Positive Raise external financing Increase debt Issue more stock Reduce cash &/or marketable security stock balances Decrease dividends 8 Achieving Equilibrium When Discretionary Funds Needed is Negative Decrease external capital: Repurchase shares Pay off debt Hold excess cash &/or marketable security balances Increase dividends 9 The “Plug” The balance-sheet items which will “plug” or balance the balance sheet model so that Total Assets equals Total Liabilities & Equity Models the assumption of how the firm finances itself: Cash & marketable securities Debt Equity Dividends Testing the model for perverse effects Questions: Example: Problems associated with using dividends as a plug When assumptions change what happens to the plug values? Does it make sense? May not have adequate cash balances to pay the dividends that are calculated Negative dividends can be calculated when the firm experiences a loss Dividends may not distribute excess cash that the firm wishes to reduce Solution involves using =max(Calculated Dividend,0) 11 Equilibrium checks Balance Sheet Discretionary Funds Needed must equal 0 Statement of Cash Flows Net increase in cash from Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows less changes in cash & marketable securities in Balance Sheet >> must equal 0 12