Spanish Clothing & Grammar Vocabulary List
advertisement

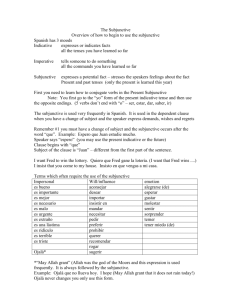
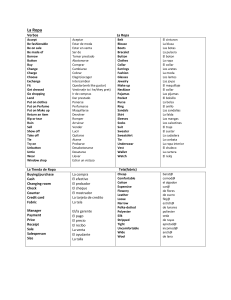
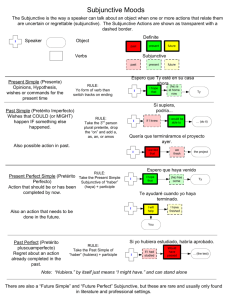
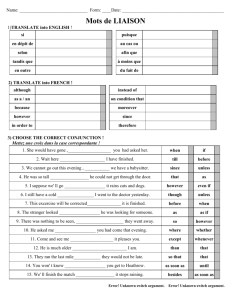
La Ropa Verbos La Ropa Accept Be fashionable Be on sale Be made of Borrow Button Buy Change Charge Choose Exchange Fit Get dressed Go shopping Lend Put on clothes Put on Perfume Put on Make up Return an item Rip or tear Ruin Sell Show off Take off Tie Try on Unbutton Untie Wear Window shop Aceptar Estar de moda Estar en venta Ser de Tomar prestado Abotonorse Comprar Cambiarse Cobrar Elegir/escoger Intercambiar Quedar(verb like gustar) Vestirse(e to i he/they pret) Ir de compras Dar prestado Ponerse Perfumarse Maquillarse Devolver Romper Arruinar Vender Lucir Quitarse Atarse Probarse Desabotonarse Desatarse Llevar Echar un vistazo Belt Blouse Boots Bracelet Button Clothes Collar Earrings Fashion Glasses Jewelry Make up Necklace Pajamas Pocket Purse Ring Sandals Skirt Sleeves Socks Suit Sweater Sweatshirt Tie Underwear Vest Wallet Watch La Tienda de Ropa Buying/purchase Cash Changing room Check Counter Credit card Fabric La compra El efectivo El probador El cheque El mostrador La tarjeta de credito La tela Manager Payment Price Receipt Sale Salesperson Size El/la gerente El pago El precio El recibo La venta El ayudante La talla Cheap Comfortable Cotton Expensive Flowery Leather Loose Narrow Polka-dotted Polyester Silk Stripped Tight Uncomfortable Wide Wool El cinturon La blusa Las botas La pulsera El boton La ropa El collar Los aretes La moda Los lentes Las joyas El maquillaje El collar Las pijamas El bolsillo La bolsa El anillo Las sandalias La falda Las mangas Los calcetines El traje El sueter La sudadera La corbata La ropa interior El chaleco La cartera El reloj Tela(fabric) barat@ comod@ el algodon car@ de flores de cuero floj@ estrch@ de lunares poliester seda de rayas apretad@ incomod@ anch@ de lana Simple future (will/might) a) Will/might---Leave the verb alone (don’t conjugate it)and add the endings!!!!! Ex: yo hablaré Yo é Tú ás Ella á Nosotros emos Ellos án Ex: I will go=iré, You will eat=comerás, he will sleep=dormirá, we will see=veremos, they will drink=beberán Verbs with irregular future stems: (Remember that this same stem is used to form the conditional.) decir haber hacer poder poner querer saber salir tener valer venir to say dirhabr- there to be [impersonal]; to have [helping verb] har- to make, do podr- to be able pondr- to put, place, set querr- to want, love sabr- to know [a fact], know how [+ infinitive] saldr- to leave, go out tendr- to have valdr- to be worth vendr- to come b) Future conditional. Ex: If I see you, I will say “hi”. OR I will say “hi”, if I see you. Si yo te veo, yo diré “hola” Formula: If + present tense conjugation of verb, + will conjugation of verb Conditional a) Reported speech. Ex: She said that she would visit. Ella dijo que visitaría. b) Present conditional. Ex: If I said “hi”, you would be happy. Formula: Si + ellos in preterite drop “ron” add “ra, ras, ra, ramos, ran” , conditional with “ía” Ex: Si yo tuviera dinero, yo compraría una casa grande. c) Verbs with irregular conditional stems: (Remember that this same stem is used to form the conditional.) decir haber hacer poder poner querer saber salir tener valer venir to say dirhabr- there to be [impersonal]; to have [helping verb] har- to make, do podr- to be able pondr- to put, place, set querr- to want, love sabr- to know [a fact], know how [+ infinitive] saldr- to leave, go out tendr- to have valdr- to be worth vendr- to come Present Subjunctive When do we use “subjunctive”? You use the subjunctive when you express wishes/hopes and impersonal expressions. Hopes/Wishes a) Hopes and wishes are expressed with verbs like 1) esperar=hope 2) recomendar 3) sugerir=suggest 4) querer 5) necesitar 6) preferir 7) insistir en b) The hopes/wishes have to be about other people, not referring to oneself. Ex: I hope to go to California.=Not subjunctive because the hope is for myself. I hope you go to California.=subjunctive because the hope is about someone else. c) To express subjunctive the sentences are always set up like this: I hope that you, I recommend that you, I suggest that you, I want that you, I need that you, I prefer that you…… The subjective conjugation will always appear in the part after “que”, the 2nd part of the sentences. Ex: Yo espero que tú vengas. Yo quiero que ellos vengan. Yo sugiero que ella venga. d) How do you get the subjunctive conjugation? For most verbs, the present subjunctive is formed by following these three steps: 1. Start with the yo form of the present indicative. 2. Then drop the -o ending. 3. Finally, add the following endings: -ar verbs: -e, -es, -e, -emos, -éis, en -er and -ir verbs: -a, -as, -a, -amos, -áis, -an Impersonal Expressions a) What are they? They are expressions without a subject mentioned. Ex: It is good that you go. It is bad that you go. It is necessary that you go. b) You would use subjunctive with these types of expressions if the expression is directed at a person. If they are used just as general statements, no subjunctive is used. Ex: It is good to eat well=Es bueno comer bien.=not subjunctive because no one person is mentioned. Ex: It is good that you eat well=Es bueno que tú comas bien.=subjunctive because the statement is aimed at a person. c) Common impersonal expressions are: 1) es bueno que 2) es malo que 3) es necesario que 4) es mejor que 5) es horrible que …many of these expressions start with “es + adjective + que” Verbs like Gustar aburrir=to be boring to bastar=to be enough encantar=to love faltar=to lack/need ir=go (a mi) (a ti) (a él) (a nosotros) (a ellos) me te le nos les molestar/fastidiar=annoy/bug/bother importar=to matter, to care interesar=be interested in/interesting to parecer=to seem quedar=to fit/have left salir=to turn out gusta(1 item) OR gustan(2 or more items) “-ly”--adverb To make an adverb like “slowly”. Take an adjective “rapido” and add “ly” to it. If the adjective ends in “o”, need to change it to an “a” then add “ly”! Example: lento(slow), rápido, constante, inmediato, feliz, triste, claro, perfecto, exacto lentamente, rápidamente, constantemente, inmediatamente, felizmente, tristemente