1. Name 5 Arthropods
advertisement

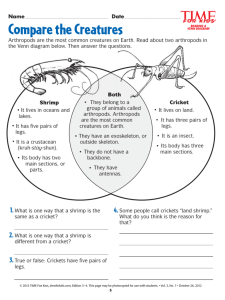
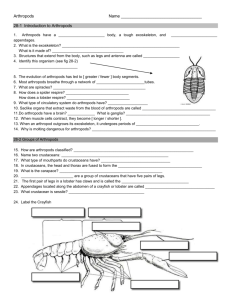
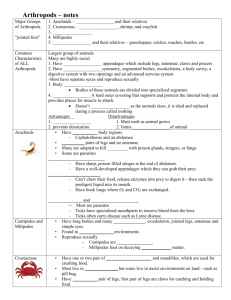
1. Name 5 Arthropods Arthropods and Echinoderms 2. Without opening your book: • Name two ways they are alike. • Name three ways they are different. Arthropods and Mollusks 3. Without opening your book: • Name two ways they are alike. • Name three ways they are different Phylum Arthropoda • There are about 125,000,000 (one hundred, twenty-five million) species of animals on Earth. Over one million of these are in the Phylum Arthropoda. • The name Arthropod means "jointed foot.“ 4. Why are animals in this group called Arthropods? Characteristics of Arthropods • Segmented bodies • Jointed appendages – legs and claws, wings, antennae, mouth parts Characteristics of Arthropods • Bilateral symmetry • Exoskeleton of jointed protective armor Characteristics of Arthropods • Compound eye – they are made up of repeating units with a lens, and visual cells. It is excellent for detecting motion. • Found in all habitats – land, water and air 5. Name FIVE characteristics of arthropods. Characteristics of Arthropods Systems: Circulatory system with gills to obtain oxygen if aquatic Excretory system Complete digestive system Reproduction is sexual 3 Groups of Arthropods • Insects – the most numerous • Chelicerates – horse shoe crabs, scorpions, ticks and mites • Crustaceans – crabs, lobsters, crawfish and shrimp 6. Name the 3 groups Of Arthropods and examples Of each. Insects • 3 pairs of legs • Metamorphosis • 3 body sections • Most species can fly Chelicerates Horse shoe crabs, Spiders, Scorpions, ticks and mites • No antennae • Two body sections • Feeding appendages called chelicerae 7. Do spiders have antennae? How do get their food? Chelicerates: Horse Shoe Crab • They live in coastal waters like The Gulf of Mexico. • They burrow in soft mud looking for worms, clams and • • other mollusks. The hard carapace of the exoskeleton is shaped like a horse shoe and offers protection. The pointed telson or tail is not used for defense or offense and they can be handled safely. 8. Name and describe a marine chelicerate. Crustaceans: crabs, barnacles, lobsters, crawfish and shrimp • 2 pairs of antennae • Chelipeds – claws that are chewing mouth parts Crustaceans: crabs, barnacles, lobsters, crawfish and shrimp • Two body sections: 1) cephalothorax includes the head and chest fused together. 2) abdomen includes the tail. This is the part you eat! . 9. How is a crustacean crab different from a chelicerate horse shoe crab? Crustaceans: sex identification in crabs • Identify the sex of the Crab by looking at the abdomen. • Females have wider abdomens to carry the eggs. • Males have narrower (triangular) abdomen. Crustaceans: reproduction • Sexual reproduction occurs often during the molting of the exoskeleton. 10. What does the larva ( hatched egg) look like? Crustaceans: reproduction • Barnacles may be hermaphroditic, but sex is more common. A barnacle¹s penis will stretch quite a distance to fertilize a neighbor’s eggs. 11. What does “hermaphroditic” mean? Crustaceans: decapods Deca means 10 Lobsters Shrimp Crabs Crayfish 12. How many legs do crabs and crayfish have? • • • • • • • • • PLATES: includes fries and onion rings Clam $10.95 Shrimp $10.95 Scallop $10.95 Calamari (squid)$6.95 Fried Lobster $16.95 Crab cakes $11.00 Crawfish bisque $8.00 Oysters on the half shell $12.00 13. Classify the items on the seafood menu as Mollusks or Crustaceans