Arthropods
advertisement

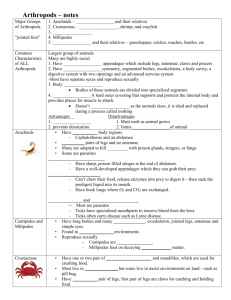
Arthropods Chapter 10 Arthropods • 1. What phylum do spiders, grasshoppers, lobsters and centipedes all belong to? ARTHROPODA Arthropods • 2. “arthros” mean “jointed” • 3. “podos” means “foot” or “leg” Molting • Molting: Shedding of the exoskeleton –Insects shed their outer skeleton to grow –Skin not flexible like ours Characteristics of Arthropods 4. Arthropods share four main characteristics: A. Exoskeleton (or outer shell) i. Prevents evaporation of water ii. Used for protection Characteristics of Arthropods 4. Arthropods share four main characteristics: B. Segmented Bodies i. Arthropods can have up to three sections ii. Head, Thorax and Abdomen Characteristics of Arthropods 4. Arthropods share four main characteristics: C. Jointed Appendages i. Examples: Legs, wings and arms. ii. Give animal flexibility Characteristics of Arthropods 4. Arthropods share four main characteristics: D. Diversity i. Scientists have discovered over one million species Crustaceans 5. Crustaceans share three main body structure features: a. Two or three body sections b. Five or more pairs of legs c. Two pairs of antennae Crustaceans 6. What are chelipeds used for? Used to capture prey and to defend itself Obtaining Food and Oxygen 7. Crustaceans obtain oxygen by gills. Located beneath the shell of the crustacean Obtaining Food and Oxygen 8. Crustaceans obtain food by: a. Scavengers: Eats dead plant and animals b. Herbivores: Eating plants c. Predators: Eating animals they have killed Crustacean Life Cycle 9. Most crustaceans begin theirs lives as microscopic, swimming larvae. Metamorphosis 10. The change in shape and habits of an insect as it grows into an adult. Arachnids 11. Arachnids are arthropods with: a. Two body sections b. Four pairs of legs c. No Antennae Arachnids 12. Some examples of arachnids include ticks, mites and spiders. 13. All spiders are carnivores. Centipedes & Millipedes 14. All centipedes and millipedes have: a. Two body sections b. One pair of antennae c. Long abdomen Centipedes & Millipedes 15. What’s with the names? - “millipede” means “thousand feet” - “centipede” means “hundred feet” NO SIGNIFIGANCE! Insects 16. Body Structure: All insects… a. Three body sections b. Six legs (3 pairs) c. One pair of antennae d. Usually one or two pairs of wings 17. Three sections of insect body: a. Head b. Thorax c. Abdomen 18. What’s being described? a. b. c. d. e. Internal organs found in Where legs are attached Includes sense organs Small holes for breathing Where wings are attached Insects 19. An insect’s mouthparts are adapted for a highly specific way of getting food. 20. Examples: 1. Coiled up tube 2. Sponge like tongue Insects 21. Chewing mouth parts can be found on: Grasshoppers, dragonflies and ant. The change in shape and habits of an insect as it grows into an adult. Insect is COMPLETELY changed Step #4: Insect Fully developed Step #1: Egg laid Step #3: Pupa formed Step #2: Egg hatches into larva Insect looks like miniature adult Step #1: Eggs laid Step #4: Insect Fully equiped Step #3: Nymph grows and sheds exoskeleton Step #2: nymph hatches and grows Metamorphosis 24. Nymph: Young form of adult with incomplete metamorphosis; miniature adult 25. Larva: The young form of an insect with complete metamorphosis Metamorphosis 26. Nymph’s typically eat the same food as adult because they look just like the adult. Same mouthparts just smaller