ls holt arthropod stu notes
advertisement

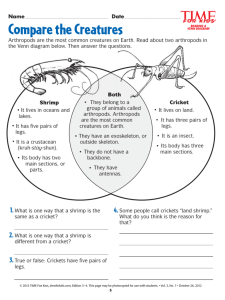
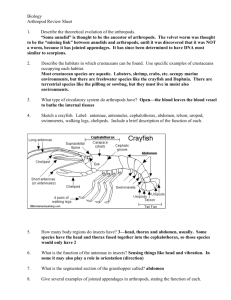
Name: _______________________ Period: ______________________ ARTHROPODS HOLT CH. 29 PG. 701-711 ARTHROPOD CHARACTERISTICS _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ Most have _____________________________________ Many have __________________________ ______________________________ _________________________________________ in larval stage ________________________________________ APPENDAGE-structure that extends form arthropod’s body wall ARTHROPOD=“_______________________________” __________________________-made of carbohydrate CHITIN-thin/flexible ________________________ attach ________________________ attach ___________________________ _____________________________________ REPSIRATION AND CIRCULATION ____________________________-air enters body through these openings _____________________-tubes there air travels from spiracles to bloodstream Aquatic arthropods breath with __________________ _______________ CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Terrestrial arthropods breath with ______________ _________________ FEEDING/DIGESTION/ EXCRETION Many mouthparts/appendages for taking in food ____________________ __________________-excretory system of arthropods Waste leaves through _________________ ___________________________ EYE Composed of thousands of individual visual units SOME also have simple eyes (single lenses)-see only light and dark, not images LIFE CYCLE Most reproduce ___________________ Usually______________________ fertilization Many have specialized reproductive organs _________________________-shedding of exoskeleton to allow for growth GROUPS OF ARTHROPODS 4 main groups (SUBPHYLA of phyla ARTHROPODA) ________________________-insects _________________________-millipeds/centipedes _________________________--lobsters/shrimp _________________________--spiders SEE PG. 705!!! SUCCESS OF ARTHROPODS More arthropods than all other animal groups COMBINED More than ______________________ species identified (and growing) Exoskeleton provides _______________________ (land and water) Wide range of food sources and habitats ARACHNIDS SUBPHYLUM __________________________ (spiders, scorpions, mites, ticks and horseshoe crabs) Have appendages called __________________________________ (1st pair of appendages specialized for feeding) Modified into pincers or fangs ____________________________-2nd pair of appendages-catch and handle prey _____________________________ of WALKING LEGS No antennae _______________________________________ (head chest) ____________________________________ (belly) ________________________________-largest class CLASS ARACHNIDA All (except some mites) are ___________________________________ Most _________________________________ Don’t have jaws (consume only ______________________________) _____________________________ turn prey into liquid (see pg. 710-711) Most do more good than harm (predators of insects) SPIDERS Chelicerae of spiders modified into fangs Poison glands secrete toxins (kills/paralyzes prey) 2 poisonous species in US ______________________________________ ______________________________________ _______________________-appendages at end of abdomen-secrete sticky silk strands SCORIONS/MITES/TICKS ________________________-segmented abdomen ending in venomous stinger Grasping pincers-seizing food and sexual reproduction _______________-head, thorax and abdomen fused into single unsegmented body Most not harmful Can spread viral/fungal infections (ex. ________________________) _____________________________________ Ancient group of invertebrates (400 million years) SUBPHYLUM CRUSTACEA ___________________________, some fresh water __________________________ (head chest) and ABDOMEN Appendages on _____________________ Have _____________________ for feeding and two antennae Breathe with _____________________________ TERRESTRIAL CRUSTACEANS ______________________________ (only PARTIALLY adapted for land-tied to ocean) AQUATIC CRUSTACEANS ___________________________ (most abundant multicelled food source), krill, barnacles (sessile), ___________________-crayfish, crabs, lobsters (_________________ legs) ______________________-’hood’ over cephalothorax LARVA=___________________ (MOLTS several times to allow for growth) FOOD CHAIN-fairy shrimp, water fleas, krill _____________________-barnacles DECAPODS LARGEST GROUP OF CRUSTACEANS Shrimp, crayfish, crab, lobsters _____________________-pinchers _____________________-swimming legs on ventral abdomen ___________________________-flattened tail on posterior end (swim backwards)