Clonorchis sinensis
advertisement

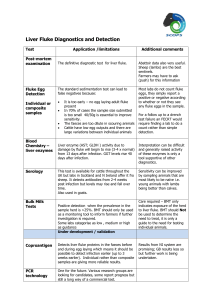
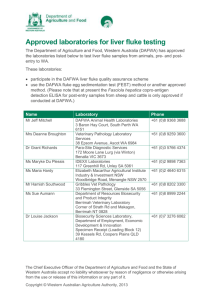
Clonorchis sinensis Iman Diriye & Mikayla Hardy INTRODUCTION Common name is the oriental liver fluke or chinese liver fluke. Disease caused by infection: Clonorchiasis 10-25 mm fluke. Hermaphroditic. They mature in the bile duct of the liver. They can produce 4,000 eggs per day for 6 months. History Documented in 1875 by James McConnell Parasites dated back to 278 B.C. was found in an Asian corpse from the Han dynasty Taxonomy Common Name: Chinese Liver Fluke Scientific Name: Clonorchis sinensis Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Trematoda Order: Opisthorchiida Family: Opisthorchiidae Genus: Clonorchis Species: C. sinensis Hosts Definitive host: human, pigs, and rodents. First Intermediate host: snail Second Intermediate host: specific freshwater fish (example: Grass Carp) or crustaceans Reservoir host: dogs, cats Geographic Distribution Found in China Japan Korea Taiwan Vietnam Can also be found be non-endemic areas from infected immigrants, or eating imported uncooked freshwater fish infected by metacercariae. Map Of Geographic Locations LIFE CYCLE Morphology Eggs Miracidia Sporocysts Rediae Cercariae Metacercariae Adult Fluke Transmission Ingestion of raw or improperly cooked freshwater fish or crustaceans that contain encysted larvae Food or drink contaminated with eggs Not transmitted directly human to human Infected person may pass viable eggs for up to 30 years after initial infection Symptoms Often asymptomatic Fever, chills, stomach pains, digestive problems, bile obstruction, vomiting, enlargement of spleen and liver Severe infestation-Cholangioheptitis, liver failure, cancer of bile ducts Small number of cases experience Jaundice No host immunity after infection Diagnosis Examination of stool samples Characteristic eggs in feces Elisa Blood test Endoscopy Tissue Sample Identify Adult Liver Flukes Video Cannulation of bile duct. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g18B2r m78E4 Treatment Praziquantel-drug of choice; increases cellular membrane permeability resulting in a loss of intra-cellular calcium, paralyzes muscles of fluke. Albendazole-inhibits metabolism in the fluke cells causing them to become immobile Prevention & Control Avoid consuming raw or undercooked freshwater fish and crustaceans Control snail population Control and eliminate night soil usage near fish ponds. Avoid use of contaminated water. Review! What are the definitive, intermediate, and reservoir hosts? Where do the flukes mature? What are some of the symptoms? What are some methods of diagnosis? What are the methods of prevention/control? REFERENCES http://dpd.cdc.gov/dpdx/images/ParasiteImages/AF/Clonorchiasis/Clonorchis_LifeCycle.gif http://www.atlas.or.kr/atlas/alphabet_view.php?my_code Name=Clonorchis%20sinensis http://clonorchiasis.blogspot.com/ http://pioneerunion.ca.schoolwebpages.com/education/c omponents/scrapbook/default.php?sectiondetailid=2769&l inkid=nav-menu-container-4-13026. http://www.stanford.edu/group/parasites/ParaSites2001/cl onorch/ClonorchiasisWebsite.html http://www.antimicrobe.org/history/Clonorchis%20sinensisYeh.asp Roberts,L.Janovy, J.Foundations of Parasitology, 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill,2009