Phylum : Platyhelminthes
advertisement

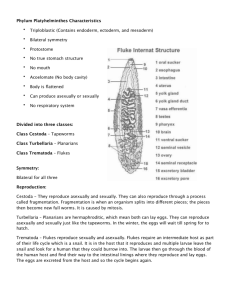
Phylum : Platyhelminthes The Flatworms Acoelomates Classes of Platyhelminthes Class Turbellaria (e.g., Planaria) The Flukes Class Trematoda (e.g., Fascioloaris, Clonorchis) Class Monogenea Class Cestoda (e.g., Taenia) General Characteristics Free-living or parasitic Bilaterally symmetrical, and dorsoventrally flattened First animals with 3 germ layers - triploblastic Ectodermis Mesodermis Endodermis Epidermis has cilia or cuticle Coelom lacking (acoelomate) General Characteristics cont. Digestive system incomplete Excretory system – protonephridia Nervous system – ladder-like Respiratory, circulatory, and skeletal system lacking Most monecious Some have fragmentation and regeneration (Asexual) Figure 14.01 Class Turbellaria Freeliving Flatworms Free-living Ciliated epidermis Mouth ventral Digestive system incomplete Dugesia w.m. Eyespots Auricle Figure 14.02 Freshwater Flatworm Figure 14.co Marine Flatworm Marine Flatworm Trematoda and Monogenea The Flukes Endoparasites Cuticle covering body Oral sucker surrounds mouth Ventral sucker used for attachment Complex life cycles Clonorchis Clonorchis One Intermediate host Shistosoma – Blood Fuke Clonorchis – Chinese liver fluke Two Intermediate hosts Cestoda The Tapeworms Endoparasites Body consists of proglottids and scolex Proglottids snapshots of development Scolex has structures for attachment (Hooks, suckers and rostellum) No digestive system Figure 14.18 Figure 14.19 Taenia scolex Mature Proglottids Figure 14.20 Taenia – can get to 30+ feet long Hydatid Cysts of dog tapeworm in human brain A case of a parasite in the wrong host