File
advertisement

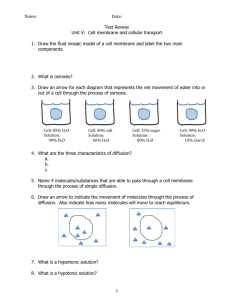
Do Now:
The Cell Membrane
The “bouncer” of the cell
The Cell Membrane –
(Plasma Membrane)
{
The barrier of the Cell
Functions (Jobs) of The Cell
Membrane
Separates cell from outside environment
Protective barrier
Regulates movement in & out of cell
Ex. Windows Screen in spring
Selectively Permeable
Membrane
Selectively permeable: Only certain
molecules can pass through
Small molecules move through easily
Ex: O2, CO2, H2O
Selectively Permeable
Membrane
STARCH
Large molecules
can NOT move
through
Ex: starch
Transport: movement of
materials across the membrane
Three types of transport:
1.
2.
3.
Constant, free movement of small molecules
( glucose, O2, CO2 )
Free movement of water
Movement that requires energy (ATP):
things that are forced through membrane
What happens when you
spray air freshener?
First type: Diffusion
Diffusion: Molecules
move freely from
where there’s the
most, to where
there’s the least of
them
Diffusion is passive
Passive: doesn’t
require energy,
happens freely
10
Diffusion of Liquids
11
Which way will the glucose
move?
Equilibrium
Molecules will move until there’s an equal amount on
both sides- called equilibrium
12
Concentration: how densely
packed something is
Example
Low concentration:
loosely packed
High concentration:
tightly packed
Concentration: how tightly
packed the molecules are
Example
Low concentration:
a little sugar
dissolved
High concentration:
a LOT of sugar
dissolved
Which side is high
concentration?
A)
High Concentration
A) More
tightly
packed
B)
Low Concentration
What is Osmosis?
Diffusion across a membrane
• Diffusion of water
across a membrane
• Moves from HIGH
water concentration
to LOW water
concentration
Semipermeable
membrane
16
Diffusion of H2O Across A
Membrane
High H2O concentration
Low H2O concentration
Which way will water move? When is equilibrium reached?
Where will water move?
10 Glucose
90 H2O
IN to
the CELL
CELL
20 Glucose
80 H2O
Where will water move?
90 Glucose
10 H2O
CELL
Out of
the CELL
80 Glucose
20 H2O
Where will water move?
10 Glucose
90 H2O
CELL
10 GLucose
90 H2O
The water is already balanced!
equilibrium
The cell is at _______________.
What happens when you
pour salt on a slug??
The slug’s cells dehydrate and this kills the slug
Why does popcorn make us thirsty??
Mouth
Cell
WATER
SALT
Huge popcorn =A big scam
Makes you super thirsty!
Dots = salt
Equal amount of
water
NO NET
MOVEMENT OF
H2O (equal amounts
entering & leaving)
More Water
outside,
water moves
in
(Cell Swells)
More
water
inside,
water
moves out
(shrinking of a cell)
Water moves towards where the most dots are
23
Osmosis in Red Blood Cells
Which way did the water move?
24
Which way did the water move?
25
Transport helps to maintain
Homeostasis
•
Homeostasis: A balanced,
steady state
•
Does this by controlling what
enters & leaves the cell
Last type of transport: Active
transport
•
Molecules move from where
there’s the least to where there’s
the most
(the opposite of diffusion)
•
Requires ATP!
Diffusion vs. Active
Transport
-High to Low
concentration
-Low to High
concentration
-Uses ATP
Exit card...
Many poisons work by inhibiting ATP
production. Which type of transport would be
most affected?
a. osmosis
b. diffusion
c. active transport
Lets Review…
1. Define Diffusion
2. Is diffusion an active or passive process? Does it
use energy?
3. How is active transport different from passive
transport?
4. True or False: Osmosis is a type of diffusion
30
Describe what is happening: