Diabetes Basics
advertisement

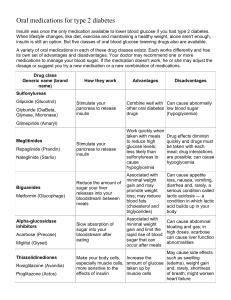
DIABETES Body does not make or properly use insulin: – – – no insulin production insufficient insulin production resistance to insulin’s effects Insulin is the key that opens the door of each cell to allow glucose (sugar) inside No insulin to move glucose from bloodstream into cells causes high blood glucose fuel loss. cells starve short and long-term complications 1 TYPE 1 DIABETES auto immune disorder insulin-producing cells destroyed daily insulin replacement necessary age of onset: usually childhoodyoung adulthood most prevalent type of Diabetes in children and adolescents 2 Diabetes Management 24/7 Constant Juggling: Insulin/medication with: Exercise BG BG & BG Food intake 3 Blood Glucose Monitors INSULIN various ways to administer Diabetes is Managed, But it Does Not Go Away. GOAL: To maintain target blood glucose 6 Assistance in Diabetes Management Routine Care: – Many students will be able to handle all or almost all routine diabetes care by themselves – Some students, because of age, developmental level, or inexperience, will need help from school staff. Urgent Care: – Any student with diabetes may need help with emergency medical care. The student’s Individualized Health Care Plan will provide student specific instructions 7 HYPOGLYCEMIA low blood sugar Caused by: Too much insulin Missed or delayed food Exercise Onset: sudden may progress to unconsciousness if not treated can result in brain damage or death 8 Hypoglycemia(low blood sugar) Possible signs and symptoms Mild Moderate Hunger, Paleness, Dizziness, Crying, Weakness, Irritability Sweating, Anxiety Poor concentration Drowsiness Shakiness Personality changes Blurry vision Confusion Weakness Headache Behavior changes Slurred speech Poor concentration Severe Inability to swallow Loss of consciousness Seizures Treatment for Mild to Moderate Hypoglycemia Quick acting source of glucose, 15 gm Carbohydrate • 4 oz. fruit juice • 15 gm glucose tablets (2-3 tablets) • 1 tube of glucose gel • 4-6 small hard candies • 1-2 tablespoons of honey • 6 oz. regular (not diet) soda (about half a can) Repeat in 15 minutes if symptoms persist 10 Basic Rule for Unclear Symptoms • If in doubt, give quick acting sugar (juice/snack) • If symptoms are hypoglycemia - it will treat symptoms • If symptoms are hyperglycemia - it will not hurt or cause a diabetic coma 11 Treatment for severe Hypoglycemia Glucagon If included in the Individualized HealthCare Plan, use when student exhibits: Unconsciousness, unresponsiveness Convulsions or seizures Inability to safely eat or drink 12 What is Glucagon? • Naturally occurring hormone made in the pancreas • A life-saving, injectable hormone that raises blood glucose level, tells liver to immediately dump it’s emergency reserve of sugar • Treatment for severe hypoglycemia • Can save a life • Cannot harm a student 13 Emergency Kit Contents: 1 mg of freeze-dried glucagon (Vial) 1 ml of water for reconstitution (Syringe) Combine immediately before use Administration of Glucagon1 1 2 3 4 Act Immediately • Position student safely on side for comfort and protection from injury • Call 911 • Call parents as per DMMP (Health Care Plan) 16 After Injection • May take 15-20 minutes for student to regain consciousness. EMS will likely arrive before student regains consciousness • Side effects - vomiting, • If conscious, check blood sugar • Give sips of fruit juice or regular soda, once student is awake and able to drink • Document. Contact nurse. 17 HYPERGLYCEMIA High Blood Sugar Too much sugar in the blood-but cells are starving Onset: Severe hyperglycemia is usually slow to develop Caused by: Too much food Too little insulin Decreased physical activity Illness or infection Injury Stress Hormones Any combination of the above 18 Hyperglycemia Possible signs and symptoms Mild Moderate Severe Thirst Frequent urination Fatigue Hunger Lack of concentration Weight loss Stomach pain Flushed skin Blurred vision Sweet fruity breath Mild symptoms plus: Stomach cramps Dry mouth Nausea Vomiting Mild and Moderate symptoms plus: Labored breathing Confusion Very weak Unconscious Hyperglycemia What to do Goal: Lower the blood glucose to target range. Student tests blood glucose, takes insulin as ordered Encourage student to drink water or sugar free drinks Call parents per care plan. Call 911 for severe symptoms • Extreme weakness (collapsing) • Very confused • Unconsciousness 20