Terms - De Anza College
advertisement

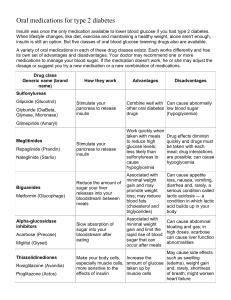
What’s a Concept map? Example: Photosynthesis Terms: solar energy, food energy, CO2, H2O, O2, green plants solar energy CO2 green plants H2O glucose + O2 food energy Concept Map: carbohydrates Objective: to help see the link between terms and ideas learned in class Terms: simple carb, fiber, fructose, added sugar, glucose, complex carb, natural sugar, sucrose, glycogen, lactose, starch, grains, honey, plain yogurt, pears, liver and muscle stores. Practice: Draw a diagram logically linking all of the terms. Concept Map: carbohydrates Objective: to help see the link between terms and ideas learned in class Terms: simple carb, fiber, fructose, added sugar, glucose, complex carb, natural sugar, sucrose, glycogen, lactose, starch, grains, honey, plain yogurt, pears, liver and muscle stores. NOW add blood sugar Practice: Draw a diagram logically linking all of the terms. Blood Sugar Lows and Highs Tools for Control-Overview Insulin (I) Protein based, pancreas produced hormone Attaches to cells-Allows glucose inside cell Result blood glucose (sugar) level decreases Glucagon (G) raises blood sugar level (BSL) Goal BSL ~80-100 mg % Too high or too low= TROUBLE To: TREAT ACUTE SYMPTOMS: simple carb (sugars) To: PREVENT SYPTOMS: restrict simple carb (sugars) sweaty, rapid heart rate dizzy, confused grouchy, anxious Hypoglycemia (Low BSL) Acute danger but uncommon condition RBC’s and brain need glucose 24/7 Basic Cause: I:G out of balance low BSL Prevention (different than treatment) No meal skipping Include healthy complex carb/protein at meals Limit simple and avoid ‘added’ sugar Focus naturally high fiber foods What happens….??? >126 mg% Diabetes Projections: 2000 to 2030 Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Hyperglycemia (high fasting BSL) Cause: not enough or ineffective Insulin Not caused by consuming too much sugar! Result: too much sugar in blood-not enough in cell Consequence: cells/tissues are glucose starved chronic inflammation occurs blood lipids, blood pressure rise, arteries harden tissue/cell function declines DM: A chronic, progressive disease Common consequences Vascular disease (#1 cause-diabetic deaths) Blindness Amputations Kidney disease Renal Dialysis Classifications of Diabetes Type I pancreas fails to make insulin early onset in life Rx: requires insulin. Monitor diet, regular exercise. Classifications of Diabetes Type 2 90-95% of all cases Insulin is ineffective Most adult DM Increasingly common in kids Treatment: Medical pills/injections Lifestyle diet/exercise/stress mgt. Self-Check BSL Helps gauge day to day management success Fasting BSL ✓ morning, bedtime and/or exercise Long term ✓of BSL = hemoglobin A1C Check List: Managing BSL Achieve a healthy weight Quit smoking Daily exercise Trickle in healthy carbs over the day No meal skipping Foods/beverages without added sugar Replace saturated (animal) with unsat (plant) fats Monitor BSL Concept Map: Blood Sugar Level Terms: blood sugar (glucose), hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, glucagon, insulin, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, ineffective insulin, inadequate insulin Draw a diagram logically linking all of the terms. Optional slides Concept Map: Controlling BSL Blood Sugar Level Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia Insulin released Inadequate Ineffective Glucagon released Insulin insulin DM Type 1 DM Type 2 Blood glucose Release liver glycogen Blood glucose Concept Map of Diabetes No insulin (not enough) insulin deficiency 1 cells no longer sensitive to insulin cells can’t absorb sugar 2 Too much sugar in blood vessels (hyperglycemia) Not enough sugar IN cells 1 cells burn fat and protein only ketones build up 2 glycosuria polyuria polydipsia kidneys 3 kidneys can’t handle excess sugar dialysis shock 5 kidney transplant coma death 6 heart retina nerves heart disease retinal damage Neuropathy kidney failure dehydration blood becomes acidic 4 vessel damage numbness heart attack gangrene blindnes s amputation