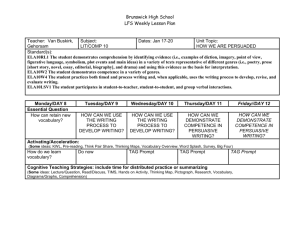
Eng. I Grammar PPt Notes
advertisement

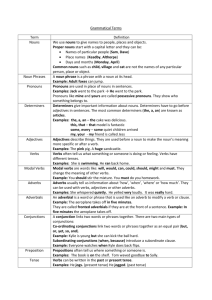
The Eight Parts of Speech The classification of words 8 Parts of Speech 1. Nouns 2. Pronouns 3. Verbs 4. Adjectives 5. Adverbs 6. Prepositions 7. Conjunctions 8. Interjections 1. Noun A noun is a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns Some nouns we can perceive with our five senses. These are persons, places, and things. Some nouns cannot be perceived by the senses. They are ideas, thoughts, emotions, and beliefs. Examples Persons: - Thomas Jefferson - architect - girl Places - Salem - library - continent Examples Things: - desk - barn - boot Ideas: - curiosity - health - eternity Common Nouns Common nouns are a name common to a whole group. It does not specify a member of the group. (frog) Proper Nouns A proper noun is the name of an individual person, place, or thing. It is capitalized. (Blue Dart Frog) Examples Common: - singer - river - building Proper - Mariah Carey - Mississippi River - GlenOak High School 2. Pronouns Pronouns are words used in place of nouns to avoid awkward repetition. Pronouns The word that the pronoun stands for or refers to is its antecedent. Ex: Kim said she would call the airport. (Kim is the antecedent of she.) 6 kinds of pronouns 1. Personal 2. Compound personal 3. Indefinite 4. Demonstrative 5. Interrogative 6. Relative Personal Pronouns Takes the place of a person’s name but may also take the place of things. Ex: Monica is a dancer. She has the lead in the school musical. Compound Personal Pronouns Pronouns that are combined with the suffix -self or -selves. Ex: myself, ourselves Indefinite Pronouns These are pronouns that do not refer to a specific person or thing. They sometimes have antecedents. Example: The players practiced in the rain. Some got sick. Players is the antecedent for the indefinite pronoun some. No antecedent example: Everything you say is true. another no one anybody everything anyone either both each many one few several Demonstrative Pronouns This, that, these, those: Pronouns that point to what they are referring to. Example: This is the poem I wrote. (This refers to poem) Interrogative Pronouns Pronouns that are used to ask questions. (Whose, Who, Whom, What, Which) Example: Who won the game? Relative Pronouns Some pronouns are used to relate one idea to another and these are called relative pronouns. Example: Mr. Talbott, who is the history teacher in our community, is an excellent cyclist. 3. Verbs A verb tells what is happening in a sentence. A verb expresses action, condition, or state of being. 2 verb categories ACTION VERBS: - Tell what the subject is doing - May be physical or mental LINKING VERBS: - Link or connect the subject of a sentence with a noun, pronoun, or adjective Action Verbs Examples: - Collide (visible) - Run (visible) - Enjoy (not) - Decide (not) Linking Verbs Can be sensory (like sounds, looks, and tastes), can be verbs of condition (like grew, became, seemed), or can be verbs of being. May have helping verbs with the main verb. Example: This book is now regarded as a classic. Verbs of Being - am - are - were - is - was - be - been - being 2 kinds of action verbs Transitive: Who or what receives the action. Intransitive: Nothing receives the action. Examples (Transitive) He moved the car. Did they pass the law? *Ask who or what receives the action.* Examples (Intransitive) He moved. They passed. *Ask who or what receives the action….in this case, there is nobody/nothing receiving the action. 4. Adjectives Adjectives modify or describe nouns and pronouns. They tell which one, what kind, how many, or how much. Adjectives There is a row of yellow ducks. YELLOW says what kind of ducks so it is the adjective. The Articles A, an, and the are considered adjectives because they modify nouns. 5. Adverbs Modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Adverbs are sort of like adjectives. *Tell where, when, how, or to what extent* Examples: WHERE: They lingered outside. WHEN: The team left early. HOW: The story ended happily. TO WHAT EXTENT: The writing was totally illegible. 6. Prepositions Common way to link and show relationships between words. Prepositions have objects. Example: The doctor went into the house. The preposition song!! About Above Across After Around At Song Before Behind Below Beside By Down During For From In Inside Near Of Off On Song Out Outside Over Through To Under Up With Without 7. The Conjunction A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, and clauses. Conjunctive adverbs connect groups of words that could not stand alone. Examples Conjunctions And But So Or For Yet Conjunctive Adverbs Consequently Hence Also Furthermore However 8. Interjection A word or group of words that expresses strong feeling or emotion. Wow! Help! Oh no! Attention! Source Building English Skills