Parts of Speech Outline
advertisement

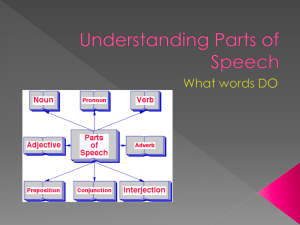
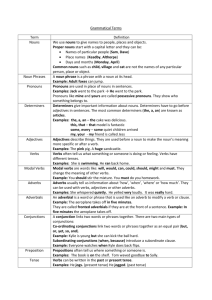
Parts of Speech Outline I. Nouns – person, place or thing A. Proper Nouns – the specific name of a person, place or thing. 1. Always capitalized 2. Example: Mrs. Rogers, Anderson Middle School, Redding, CA B. Common Nouns – any general person, place, thing or idea 1. Example: teacher, school, city II. Pronouns – can take the place of a noun A. Examples: 1. He, She, They 2. Him, Hers, Theirs 3. It, Its, Whose III. Verbs – show what the subject does (predicate) or action. A. Action Verbs – show action (run, jump, sing, dance etc) B. Linking Verbs - To Be Verbs show the state of being and indicate the time of that state of action. (to, be, am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been, has, have, had, would, could, should). C. Infinitive Verbs – are always preceded by the word “TO.” (To run, to jump, to sing, to dance etc) D. Gerund – a verb that ends in – ing but functions as a noun. Example: My singing is not that great. E. Participle – a verb that is used as an adjective and usually ends in –ing/ -ed. IV. Adjectives –describe nouns. They usually specify size, color, shape. A. you can make adjectives out of nouns or verbs (participles) B. Examples: soggy, short, tall, thin, wet, dry, red, round etc. V. Adverbs – describe verbs and usually end with –ly. A. Example: quickly, tiredly, sickly. B. Adverbs can also describe adjectives or other adverbs. 1. Example: Very Pretty or rather quickly. VI. Prepositions – show how nouns or pronouns are related to other words in the Sentence, and usually show the position of the noun. A. Example: over, under, against, behind, of, through, etc. VII. Conjunctions – join words, phrases, or clauses. A. Examples 1. and, but, or 2. if, either, neither, nor VIII. Interjections – are also known as exclamations and are signaled by the use of the Exclamation mark! ! ! !