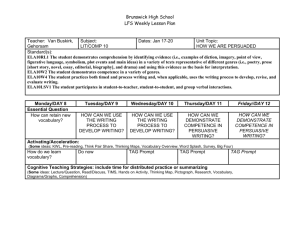
Grammatical Terms - Althorpe and Keadby Primary School
advertisement
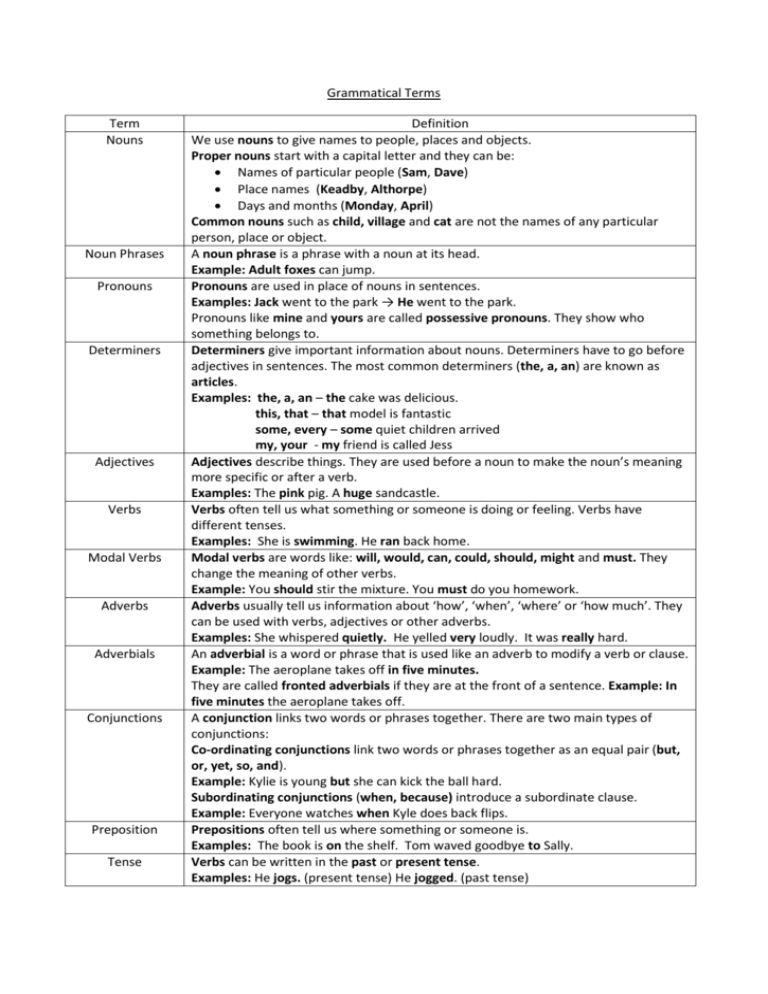
Grammatical Terms Term Nouns Noun Phrases Pronouns Determiners Adjectives Verbs Modal Verbs Adverbs Adverbials Conjunctions Preposition Tense Definition We use nouns to give names to people, places and objects. Proper nouns start with a capital letter and they can be: Names of particular people (Sam, Dave) Place names (Keadby, Althorpe) Days and months (Monday, April) Common nouns such as child, village and cat are not the names of any particular person, place or object. A noun phrase is a phrase with a noun at its head. Example: Adult foxes can jump. Pronouns are used in place of nouns in sentences. Examples: Jack went to the park → He went to the park. Pronouns like mine and yours are called possessive pronouns. They show who something belongs to. Determiners give important information about nouns. Determiners have to go before adjectives in sentences. The most common determiners (the, a, an) are known as articles. Examples: the, a, an – the cake was delicious. this, that – that model is fantastic some, every – some quiet children arrived my, your - my friend is called Jess Adjectives describe things. They are used before a noun to make the noun’s meaning more specific or after a verb. Examples: The pink pig. A huge sandcastle. Verbs often tell us what something or someone is doing or feeling. Verbs have different tenses. Examples: She is swimming. He ran back home. Modal verbs are words like: will, would, can, could, should, might and must. They change the meaning of other verbs. Example: You should stir the mixture. You must do you homework. Adverbs usually tell us information about ‘how’, ‘when’, ‘where’ or ‘how much’. They can be used with verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. Examples: She whispered quietly. He yelled very loudly. It was really hard. An adverbial is a word or phrase that is used like an adverb to modify a verb or clause. Example: The aeroplane takes off in five minutes. They are called fronted adverbials if they are at the front of a sentence. Example: In five minutes the aeroplane takes off. A conjunction links two words or phrases together. There are two main types of conjunctions: Co-ordinating conjunctions link two words or phrases together as an equal pair (but, or, yet, so, and). Example: Kylie is young but she can kick the ball hard. Subordinating conjunctions (when, because) introduce a subordinate clause. Example: Everyone watches when Kyle does back flips. Prepositions often tell us where something or someone is. Examples: The book is on the shelf. Tom waved goodbye to Sally. Verbs can be written in the past or present tense. Examples: He jogs. (present tense) He jogged. (past tense)