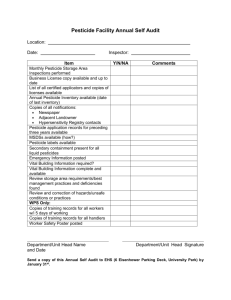
WPS Worker Safety Training - Iowa State University Extension and
advertisement

WPS Handler Safety Training Forest What does the Worker Protection Standard cover? • Pesticides used in production of agricultural plants Forests Greenhouses Farms Nurseries 1. Agricultural Workers 2. Early-entry workers 3. Pesticide Handlers Agricultural workers • Do hand labor, such as planting, watering, and pruning Joe Murray, Treebio.com Early-entry workers • Perform special tasks involving anything that has been treated with a pesticide Pesticide handlers • Mix, load, apply, clean, or repair equipment • Perform other tasks in direct contact with pesticides WPS safety concept: the label • Format and meaning of information contained on pesticide labels and in labeling, including safety information such as precautionary statements about human health hazards Labels and labeling • Information attached to container or referred to on the label or accompanying literature Betsy Buffington, Iowa State University Name of product • Brand name • Common name(s) • Chemical name Active Ingredient: picloram: 4-amino-3,5,6-trichloropicolinic acid, triisopropanolamine salt……….……….……...5.4% 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, triisopropanolamine salt …………….……….20.9% Other Ingredients:…………………….73.7% Total: ……………...…………………………..100.0% Ingredient statement Active Ingredient: picloram: 4-amino-3,5,6-trichloropicolinic acid, triisopropanolamine salt…….……….……...5.4% 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, triisopropanolamine salt ………….…….….20.9% Other Ingredients: …………………...….73.7% Total: …………...…………………………..100.0% EPA registration EPA establishment number number • Used to identify the product EPA Reg. No. 62719-31 • Used to identify where product was produced EPA Est. No. 62719-001 Needed for: Poisoning Claims of misuse Liability claims Restricted use pesticide records Use classification General use • No label statement Restricted use • RUP statement required • Certification Signal words Precautionary statements • Hazards to humans and animals – Ways product may be poisonous Precautionary statements • PPE – Minimum protective equipment that must be worn Max Williamson, USDA Forest Service Precautionary statements • Environmental hazards – What to do to avoid environmental damage Precautionary statements • Physical and chemical hazards – Fire, explosion, or chemical hazards Statement of practical treatment • What to do if poisoning occurs Directions for use 1. Why the pesticide is being used 2. Where the pesticide should be applied 3. How the pesticide is applied 4. When the pesticide should be applied Restricted entry interval • Time that must pass before people can re-enter area without appropriate PPE • Stated on the pesticide label • Most are 4 or 12 hours • Longer for some pesticides AGRICULTURAL USE REQUIREMENTS Use this product only in accordance with its labeling and with the Worker Protection Standard, 40 CFR Part 170. This Standard contains requirements for the protection of agricultural workers on farms, forests, nurseries and greenhouses, and handlers of agricultural pesticides. It contains requirements for training, decontamination, notification, and emergency assistance. It also contains specific instructions and exceptions pertaining to the statements on this label about personal protective equipment (PPE), and restricted entry interval. The requirements in this box only apply to uses of this product that are covered by the Worker Protection Standard. Do not enter or allow entry into treated areas during the restricted entry interval (REI) of 12 hours. PPE required for early entry to treated areas that is permitted under the Worker Protection Standard and that involves contact with anything that has been treated such as plants, soil or water is : coveralls, chemical-resistant gloves such as barrier laminate or butyl rubber or nitrile rubber or viton, shoes plus socks and protective eye wear. Restricted entry interval Do not enter or allow entry into treated areas during the restricted entry interval (REI) of 12 hours. NON-AGRICULTURAL USE REQUIREMENTS The requirements in this box apply to uses of this product that are NOT within the scope of the Worker Protection Standard (WPS) for agricultural pesticides (40 CFR Part 170). The WPS applies when this product is used to produce agricultural plants on farms, forests, nurseries or greenhouses. For ornamental turf uses (golf courses, cemeteries, parks and other turfgrasss areas), do not allow people (other than applicator) or pets on treatment area during application. Do not enter treatment areas until sprays have dried. AGRICULTURAL USE REQUIREMENTS Use this product only in accordance with its labeling and with the Worker Protection Standard, 40 CFR Part 170. This Standard contains requirements for the protection of agricultural workers on farms, forests, nurseries and greenhouses, and handlers of agricultural pesticides. It contains requirements for training, decontamination, notification, and emergency assistance. It also contains specific instructions and exceptions pertaining to the statements on this label about personal protective equipment (PPE), and restricted entry interval. The requirements in this box only apply to uses of this product that are covered by the Worker Protection Standard. Do not enter or allow entry into treated areas during the restricted entry interval (REI) of 12 hours. Early entry workers PPE required for early entry to treated areas that is permitted under the Worker Protection Standard and that involves contact with anything that has been treated such as plants, soil or water is: coveralls, chemicalresistant gloves such as barrier laminate or butyl rubber or nitrile rubber or viton, shoes plus socks and protective eye wear. PPE required for early entry to treated areas that is permitted under the Worker Protection Standard and that involves contact with anything that has been treated such as plants, soil or water is : coveralls, chemical-resistant gloves such as barrier laminate or butyl rubber or nitrile rubber or viton, shoes plus socks and protective eye wear. NON-AGRICULTURAL USE REQUIREMENTS The requirements in this box apply to uses of this product that are NOT within the scope of the Worker Protection Standard (WPS) for agricultural pesticides (40 CFR Part 170). The WPS applies when this product is used to produce agricultural plants on farms, forests, nurseries or greenhouses. For ornamental turf uses (golf courses, cemeteries, parks and other turfgrasss areas), do not allow people (other than applicator) or pets on treatment area during application. Do not enter treatment areas until sprays have dried. Non-agricultural use requirements • If WPS does not apply, then follow these instructions Storage and disposal • How to best store and dispose of product and/or product container WPS safety concept: pesticide hazards • Hazards of pesticides resulting from toxicity and exposure, including: – – – – Acute effects Chronic effects Delayed effects Sensitization Hazard = Exposure x Toxicity • High exposure 90% = 100% x 90 • No exposure 0% = 0% x 90 How can pesticide exposure occur? Mixing/Loading Application Plant residues Three farm workers gave birth to infants with birth defects. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2007, ehponline.org Insecticide: farm worker applied a carbamate insecticide for several days. He became nauseous, dizzy, weak, and had a headache. Michigan pesticide surveillance report, 2005 Herbicide: a worker was spraying glyphosate, the end of the hose came off and some sprayed on his mouth. He became nauseous and vomited. Michigan pesticide surveillance report, 2005 Fungicide: farm worker mixing fungicide rested his arm on a spill, it became red, irritated, and very itchy. Michigan pesticide Surveillance report, 2005 Toxicity is….. • The potential of a chemical to be poisonous • Expressed as LD50 – Lethal dose for 50% of the population Signal words Signal Word Toxicity Oral Lethal Dose (Human, 150 lbs.) Caution Low toxicity 1 ounce to more than a pint Warning Moderately toxic 1 teaspoon to 1 tablespoon Danger Highly toxic Few drops to 1 teaspoon DangerPoison Highly toxic to humans Few drops to 1 teaspoon Acute toxicity • High level, one time exposure Chronic toxicity • Effects are not seen until much later • Result of repeated exposures Chronic toxicity can cause • • • • • • • • • • Cancer Tumors Birth defects Infertility or sterility Impotence Blood disorders Brain damage Paralysis Emphysema, asthma Kidney problems Sensitization • Gradual development of allergic reaction to pesticide WPS safety concept: routes of entry • Routes by which pesticides can enter the body Dermal exposure • Spilling concentrate during mixing and loading • Wind shift during spraying and getting covered with pesticide drift • Most common way applicators are exposed Oral exposure • Accidently drinking pesticide • Not washing hands before eating • Most common route that children are poisoned Inhalation exposure • Mixing and loading in a confined area Ocular exposure • Rubbing eyes with contaminated hands or clothing • Immediate absorption WPS safety concept: signs and symptoms • Signs and symptoms of common types of pesticide poisonings Pesticide poisoning symptoms Mild poisoning • Fatigue • Headache • Nausea • Dizziness Severe poisoning • Excessive sweating • Stomach cramps • Vomiting • Diarrhea • Blurred vision WPS safety concept: first aid & medical care • Emergency first aid for pesticide injuries or poisonings • How to obtain medical care Dermal exposure • Rinse with water • Remove contaminated clothing • Wash with plenty of soap and water Oral exposure • Rinse mouth with water • Do not induce vomiting if – victim is unconscious – having convulsions – petroleum based product – corrosive pesticide – label specifies NOT to induce vomiting Inhalation exposure • • • • Remove to fresh air Loosen tight clothing Keep air passages clear Perform artificial respiration if necessary Eye exposure • Wash eye with a gentle stream of clean water for 15+ minutes • Get medical attention if there is pain or reddening of the eye Obtaining medical care WPS safety concept: obtaining emergency medical care • How to obtain emergency medical care If you suspect poisoning 1. Contact a doctor immediately 2. Tell what pesticides were being used and the EPA registration number 3. Take labels along if medical care is needed Safety poster Employer’s responsibilities • Must provide transportation to hospital • Must provide medical personnel with – Product name, EPA registration number and active ingredient – Product label – Circumstances of application – Circumstances of exposure WPS safety concept: decontamination • Routine and emergency decontamination procedures Everyday decontamination Emergency decontamination • Stop work and leave work area • Remove contaminated clothing • Rinse exposed skin with water right away • Wash with soap and water ASAP • Provide assistance if necessary • Medical attention may be necessary – Provide information Eye flushing technique • Use eye-wash fountain or pour water in eyes • Hold eye open while flushing • Move eye ball and eye lid • Flush for minimum of 15 minutes • Seek medical attention ASAP Rich McColley, Iowa State University WPS safety concept: personal protective equipment • Need for and appropriate use of personal protective equipment Minimize exposure Additional PPE needed during mixing & loading • • • • • Unlined Boots Gloves Apron Goggles Respirator (if required on the label) Hand protection • Types – Nitrile – Neoprene – Butyl – Viton – Latex – Laminate Protection for the body Joyce Hornstein, Iowa State University Eye & face protection Rich McColley, Iowa State University Respiratory protection NIOSH approved Note: Medical approval, fit test and additional training required Rich McColley, Iowa State University Care and maintenance • Inspect before each use • Replace damaged or worn parts • Properly dispose of damaged, contaminated or worn out PPE to prevent reuse Joyce Hornstein, Iowa State University WPS safety concept: heat stress • Prevention, recognition and first aid treatment of heat-related illness Heat exhaustion symptoms • • • • • Sweating or dry skin Headache Fatigue Dry mouth Fast pulse (slow if person has fainted) • • • • • Nausea Dilated (large) pupils Loss of coordination Confusion Fainting (quick recovery) Control heat stress • Drink lots of water • Build up heat tolerance • Take periodic breaks Treatment of heat stress • Get out of the sun • Drink fluids • Loosen or remove clothing • Get help Bill Schall, Florida Grower WPS safety concept: handling pesticides • Safety requirements for handling, transporting, storing and disposing of pesticides, including general procedures for spill cleanup Transporting pesticides • Not inside closed vehicle with people • Not with food or feed • Tied down and secured Joyce Hornstein, Iowa State University Protect sensitive areas from pesticides • Avoid spraying near: – Beehives, water bodies, houses, urban areas, sensitive crops • When spraying: – Not on windy days – Downwind from sensitive areas – Early morning when people & pets are not present Cleaning instructions • Refer to pesticide labels and sprayer manual on how to properly clean sprayer • Check the label for special cleaning instructions and warnings of sensitive crops affected by tank contamination Disposal of excess mixed pesticide and rinsate • Apply on an area listed on the label • May be applied to sprayed area as long as the total of both applications doesn’t exceed label rate Storage of pesticides • Store separately in a locked, labeled, vented cabinet, room, or building • Inform others of pesticide hazards • Maintain a list of your pesticides Betsy Buffington, Iowa State University Storage area safety equipment • • • • • Water supply Soap Eyewash bottle Fire extinguisher Absorbent material • • • • Shovel Broom Dustpan Trash can Store pesticides in their original containers • If a container is broken, leaking, or torn, put the contents into a similar bottle, jug, or bag • Transfer the old container’s label onto the new one or get a replacement label from your dealer • Applies only to end user applicators Pesticide containers • It is unlawful in Iowa to sell or distribute a pesticide except in the registrant’s or manufacturer’s unbroken immediate container that contains the pesticide product label Disposing of surplus pesticides • Contact other possible users – Do not give RUPs to person that is not certified to apply them • If legal, use product up according to label directions Cleaning empty containers • Triple rinse • Pressure rinse: Rinse with specialized nozzle for 30 seconds • Gently tap bags and other dry formulation containers to dislodge remaining product Recycle pesticide containers • DNR landfills or recycling centers – Several across Iowa • Container Services Network – Provides large tote bags, will collect • Cropland Containers – Accepts most containers WPS safety concept: environment concerns • Environmental concerns such as drift, runoff and wildlife hazards Particle drift • Off-target movement of small particles or drops occurring during or after the Wind application Particle drift Solid pesticide particles Vapor drift • Off target movement of vapors produced up to several days after application Vapor drift Surface water contamination Pesticide spray Runoff Soil • Pesticides can move in surface water by either runoff or erosion Surface water Groundwater contamination • Pesticide moves downward in the soil profile with percolating water • Occurs mainly in sandy soils Leaching • Particularly a problem with shallow-dug wells Pesticide spray Soil Groundwater Groundwater advisory Management practices • Prevent backsiphoning and spills Pesticide spill Well Soil Groundwater Pesticide Spill management 1. Control 2. Contain 3. Clean up Lisa Hlavinka, The Gazette Reporting spills Iowa DNR spill reporting • All pesticide spills resulting in hazardous conditions must be reported by phone ASAP, but no later than 6 hours after occurrence • Initial report must be followed by a written report to the DNR w/in 30 days. National Response Center • Federal law requires notification w/in 15 minutes when oil or hazardous substances are discharged and meet or exceed reportable quantities. How can pesticides contact nontarget species? • • • • Direct contact Drift Runoff Residues Your best protection is to Read the Label! WPS safety concept: taking pesticides home • Warnings about taking pesticides or pesticide containers home Do not take pesticides home EPA.gov WPS safety concept: explanation of WPS requirements that handlers must follow • Prohibition against applying pesticides in a manner that will cause contact with workers or others • Requirements to use PPE • Provisions for training and decontamination • Protection against retaliatory acts Central location information TREATED AREA INFORMATION Location of treated area plot 7 Name of pesticide Tordon RTU EPA registration No. 62719-31 Active ingredient picloram Time and date of application 7 am, July 31 Restricted Entry Interval (REI) 48 hours Do not enter until 7 am, August 2 Notification of pesticide application • Employers must post signs around treated areas • Provide oral warnings OR Field signs must be posted • Post at all normal entrances • Post 24 hrs or less before application • Remove within 3 days after REI expires Protections during applications • Handler and Handler Employer shall assure that no pesticide is applied so as to contact any person, either directly or through drift Personal protective equipment • Employers must ensure: – Appropriate PPE is available and used correctly – PPE is inspected before use and is operating correctly – PPE is put on, taken off, cleaned or replaced, and stored correctly Handler training requirements • Must be trained before do any handling task • Training required every 5 years Requirements for training handlers • Certified applicator • Designated trainer by IDALS • Trained WPS Handlers can train WPS Workers Decontamination supplies for handlers • Water – 3 gallons/handler • • • • Soap Single-use towels Coveralls Eye wash Location of decontamination supplies • Workers – Within ¼ mile • Handlers – At mixing site Keep decontamination supplies available • 30 days beyond REI • 7 days, if REI is 4 hours or less Retaliation prohibited… • Employers or supervisors must not prevent or discourage workers or handlers from complying or attempting to comply with the WPS • Employer must not fire or otherwise retaliate against any worker or handler who attempts to comply Resources • Iowa Department of Agriculture & Land Stewardship – http://www.agriculture.state.ia.us • ISU Pest Management & the Environment – http://www.extension.iastate.edu/PME • ISU Extension Online Store – https://www.extension.iastate.edu/store/ Acknowledgements • This project has been funded by the Iowa Department of Agriculture and Land Stewardship through a grant from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency • The contents do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of the Environmental Protection Agency, nor does mention of trade names or commercial products constitute endorsement or recommendation for use