Agent-based modeling in social sciences
advertisement

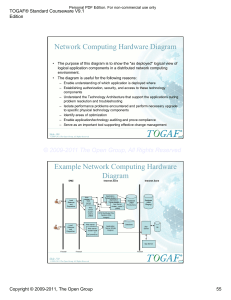
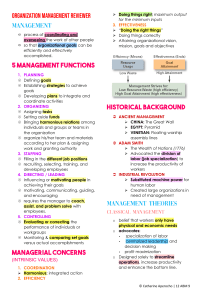
Agent-based modelling in social sciences Andreas Krause School of Management What is ABM? Agent-Based Modeling (ABM) is the computational study of dynamic systems of interacting agents. Here "agent" refers broadly to a bundle of data and behavioral methods representing an entity constituting part of a computationally constructed world. Examples of agents Individuals: consumers, producers, investors Social groupings: families, firms, communities, government agencies Institutions: markets, regulatory systems Biological entities: crops, livestock, fish, insects, forests Physical entities: infrastructure, weather, geographical regions. Examples of applications Investment and trading decisions in financial markets Product market competition Marketing Macroeconomics Traffic flow and road pricing Ethnic conflicts Spread of diseases Opinion dynamics Adoption of new technologies, languages My work Simulating stock markets Formation and evolution of social networks Using simple behavioural rules for traders With realistic market structure rules Investigation of the aggregate behaviour, i.e. stock prices Networks evolve locally following exogenous rules Networks evolving in response to dynamics on the network (Stock) Market Design (started with PhD student) Optimization of markets structures with GAs (maybe GP) Methods used Simulations, usually generation of long time series for a large range of parameter settings Optimization of behavioural rules or institutions, often using Genetic Algorithms (GA) or Probability-Based Incremental Learning (PBIL) Scale of computations Mostly a large number (>1,000) of time series (each easily > 1,000,000 time steps) GAs/PBILs often require more simulations (optimization in high-dimensional spaces means slow convergence) Computing speed is important (simulations often take 2 weeks or longer, GAs could take months) Relatively low computational complexity, but large number of computations Limitations of research Computing power limited access to up-to-date computers (speed, memory, computer lab for parallel computing) Access to software relevant software (MATLAB) not available for desktop, specialist software exists but time consuming to learn Programming skills need to have proficient programmers, e.g. PhD students Funding issues ABM is a new methodology in economics/ finance (about 10 years old), not mainstream or yet generally accepted Funding is difficult to obtain as it falls between areas Most publications are in Physics journals and IEEE Transactions, not truly recognized for promotions/RAE etc. Research at other universities Research Centre in Essex: CCFEA (Economics + Computer Science) Broader Research Centres which include ABM: Santa Fe, Carnegie-Mellon, AI-ECON (Taiwan) Other places have smaller groups, often focussing on special areas, usually centred around a small number of individuals: Cranfield, Cambridge, Oxford, Kiel (Germany), Genoa (Italy), NDA (Japan), … Research in Bath Interests are in various departments mainly in Management and Computer Science, relatively isolated No common forum for exchange of ideas Limited outside and inside visibility of our research Key issues Adequate hardware/software Attraction of funding Visibility within the university and outside Prospects for ABM research Emerging field with a wide range of applications Fast growing community, the main conference covering economics and finance applications started in 1995 and has grown from about 60 participants (1999) to 200 (2006). At present limited competition, chance of taking a pioneering role Interdisciplinary approach Potential key areas of application Market design Carbon trading Road pricing Electricity and gas markets, in future: water markets? Procurement markets Rail franchises Airwave spectrum auctions Modelling of ecosystems and their reaction to environmental/climate change Modelling of ethnic and religious conflicts