Internal Control & Sarbanes-Oxley Act
ERPANET Workshop
Antwerp, April 14, 2004
PwC
© 2000 PricewaterhouseCoopers. PricewaterhouseCoopers refers to the individual member firms of the world-wide PricewaterhouseCoopers organisation. All rights reserved.
Agenda
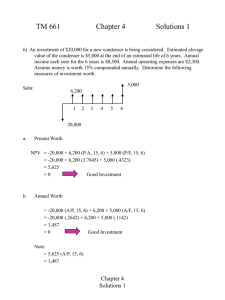
•
Background
•
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act - An Overview
•
Approach to 404 readiness
2
PwC
Background
Reasons for New Legislation
4
PwC
Congressional Votes
Legalizing Marijuana**
Securities Litigation Reform Act
Authorizing Force against Iraq
Yes
93
Yes
387
Yes
373
No
310
No
130
No
156
Not voting
31
Not voting
15
Not voting
12
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
Yes
**House of Representatives only
522
No
3
Not voting
9
5
PwC
Criminal Penalties
Escaping from prison
1 to 2 years
Kidnapping involving ransom
3 to 5 years
Second degree murder
11 to 14 years
Sarbanes-Oxley Certification
10 to 20 years
Air piracy
20 to 25 years
6
PwC
Is all wisdom coming from the US…?
“Americans will always do the right thing…..
after they have exhausted all other options.”
Sir Winston Churchill
7
PwC
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act
An Overview
Titles of the Act
I.
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board
II.
Auditor Independence
III.
Corporate Responsibility
IV.
Enhanced Financial Disclosures
V.
Analyst Conflicts of Interest
VI.
Commission Resources and Authority
VII.
Studies and Reports
VIII.
Corporate and Criminal Fraud Accountability
IX.
White Collar Crime Penalty
X.
Corporate Tax Returns
XI.
Corporate Fraud and Accountability
9
SOX of 2002: An Act to
protect investors by
improving the accuracy
and reliability of
corporate disclosures
………
PwC
SOX: Who will be affected and how?
Executives:
• Responsibility for financial reporting and keeping the markets informed
• Certifications: - 302 “Disclosure controles & procedures”
- 404 “Internal controls for financial reporting”
- 906 “CEO/CFO’s written statement on fairness”
• Implement Code of Ethics and whistleblower procedure
Supervisory Board:
• Enhanced oversight
• Appointment of a “financial expert”
Auditors:
• Independence
• Attestation on internal controls
Definition of “internal control over financial reporting”:
- Encompasses subset of internal controls addressed in the COSO Report that pertains to financial
reporting objectives
- Including controls over safeguarding assets
10
PwC
SOX:
Section 302 certification
Section 302 requires (starting March 2002):
• Quarterly certification by the CEO / CFO regarding the completeness and accuracy of
quarterly reports as well as the nature and effectiveness of disclosure controls and
procedures (DC&P) supporting the quality of information included in such reports
Representations by CEO and CFO as required by Section 302 to include:
• Review of report: no untrue statement or omission of facts & fair presentation of financial
position, results and cash flow
• Responsibility for design and maintenance of controls & controls effective during 90 days
prior to filing
• Disclosure of deficiencies in internal control and fraud to AC and auditor
• Significant changes that affect internal control and management response
Actions:
• Enhance DC&P assessment and turn into consistent and continous process
• Ensure coverage of entire organization (incl. all material subsidiairies)
• Embedding into regular review and monitoring processes
Disclosure controls and procedures need to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the issuer
is recorded, processed, summarized and reported and is accumulated and communicated within the time
periods specified in the Commission’s rules and forms
11
PwC
SOX:
Section 404 certification
Section 404 requires (domestic / foreign as of FY ending 15 November 2004 / 15 April 2005):
• Annual mngt report regarding effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting
and attestation by the company’s auditors as to the accuracy of mngt’s assessment
Representations by CEO and CFO as required by Section 404 to include:
• Management responsibility for adequate internal controls
• Conclusion about management’s evaluation of internal controls for financial reporting
Actions:
• Document of processes & internal controls (process/activity, risk, control, responsibility)
• Management’s evaluation of effectiveness (audits and self assessments)
• Attestation by external auditor
Attestation by the auditor on management’s report on internal control requires:
• Management accepts responsibility and assess internal controls
• Controls are suitable designed and appropriately documented
Internal control is the process, effected by an entity’s board of directors, management and other personnel,
designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of objectives in three categories:
Effectiveness and efficiency of operations
Reliability of financial reporting
Compliance with laws and regulations
12
PwC
SOX:
Section 404 Assessment
• Management’s assessment must be based on procedures sufficient both to
evaluate design and test operating effectiveness
• Management must maintain evidential matter, including documentation, to
provide reasonable support for the assessment (both design and testing) of
effectiveness
• Any material weakness in internal control over financial reporting
precludes management from reporting that internal control is effective
• Reiteration of guidance regarding independence:
– Auditors may assist management in documenting internal controls.
– Management must be actively involved in the process; cannot delegate
assessment responsibility to the auditor
13
PwC
SOX:
Scope of 302 and 404
302:
Disclosure controls and procedures
404:
Internal controls & procedures for financial reporting (COSO & “CobiT”)
Disclosure Requirements
Operations
Financial
Reporting
Compliance
&
Regulatory
Disclosure
Controls and
Procedures
Other aspects of
Compliance and
Operations relate
to DC&P
Internal
Accounting
Controls
Internal Controls
Over Financial
Reporting
14
PwC
SOX:
Meeting SEC Expectations
• Compliance with COSO control standards (or other accepted standards;
IT Governance Institute recently recommended CobiT for general IT
controls assessment)
• Clear documentation of internal controls as well as the testing
processes
• Evidence that management have evaluated the adequacy of the design
and the effectiveness of operation of the procedures and controls
• Evidence that the auditor has adequately evaluated the design and
operation of financial controls
• Evidence that the audit committee and/or disclosure committee have
taken a keen interesting the effectiveness of controls
15
PwC
SOX:
Auditor Responsibility (1)
Independent evaluation of design effectiveness
Independent tests of operating effectiveness
•
•
Use of internal audit and management tests will need to be assessed to
determine how they impact nature, timing and extent of auditor testing
• Requires some re-performance for each significant account, class of
transactions, and disclosure
• Independent testing
Limited use of or inability to use tests performed by others; e.g., internal audit
• Monitoring function may impair objectivity and ability to use in direct
assistance
• Precluded from using internal testing related to certain controls
16
PwC
SOX:
Auditor Responsibility (2)
Auditors’ Report:
•
•
On management’s assertion, if effective internal control
or
Directly on ineffectiveness of internal control over financial reporting
Findings reported include:
•
•
Significant Deficiency – referred to in body of opinion
• A deficiency that could adversely affect an entity’s ability to initiate, record,
process and report financial data
Material Weakness – results in an “except for” qualified report
• A deficiency that precludes the entity’s internal control from reducing to an
appropriately low level the risk that a material misstatement will not be
prevented or detected on a timely basis.
17
PwC
Approach to 404
readiness
Approach to 404 readiness
• Recommend a Sound but Practical approach
• Maximise what has already been achieved and is internally available
• Anticipate on upcoming Changes
• Value Added
Approach
Goals from Sarbanes-Oxley
Efforts
Value Added Approach – seek out operating
improvements and identify best practices
Avoid “process fatigue”
Appropriate Control
Documentation
Formal management process to maintain
compliance throughout organization
Opportunity for ROI
Enabling Technology
Use technology throughout organization to
facilitate assessment and communication
Compliance would add
recurring costs
19
PwC
Considerations
•
Appropriate control documentation:
•
•
•
•
•
Compliance with SOX 404 regulations and proof of compliance
Timely identification of control weaknesses
Facilitation of prioritization of remedial actions and action tracking
Provides basis for attestation by the auditors
Enabling technology:
•
•
•
•
•
•
Consistency and quality of controls documentation
Transparency of weaknesses and improvement areas
Maintenance and improvement of controls documentation
Linkage to other risk and quality initiatives
Auditability of controls
Facilitation of project management
20
PwC
Project Structure
•
Top down: develop at the center, execution by opco’s with support of “Group” teams
•
Development of process and controls standards by corporate & “Group” teams
•
Methodology to be developed by corporate project team and tested and tailored at
pilot site (opportunity: extrapolate best practices)
•
Based on Blueprint Internal Control Framework (guidelines following COSO/CobiT)
and Roadmap (project steering)
Steering Committee
SOX 404 Core Project
Team
Group Team
Group Team
Group Team
21
ICT Team
PwC
Project Responsibilities
•
Corporate project team also responsible for:
•
Communication to divisional teams
•
Monitoring of progress
•
Consolidation/consistency
•
Quality assurance on divisional input
•
Change management and training
•
Coordination with steering committee
•
Quality, progress and consistency of opco activities and deliverables to be
assured by project teams on Group level
•
Execution and addressing control gaps is the responsibility of each opco
•
Decision to be taken on full roll out or selected companies only
22
PwC
Project Steps
Step 0.1
Project setup
– Initial awareness, project owners, resources, budget
– Project team: roles & responsibilities
Step 0.2
Develop Blueprint “Internal Control Framework” (COSO/CobiT)
– Internal control requirements, objectives & components
– Control environment
– Risk assessment
– Control activities
– Monitoring
– Information & communication: guidelines & tools
Step 0.3
Develop Roadmap
– Project time line, organisation & quality assurance
– Project communication, training and information sessions
23
PwC
Next Steps…
Phase 1
Phase 2
Phase 3
Project
Preparation &
Mobilisation
Execution
Evaluation
Step 1
Mobilisation &
Project
Management
Step 3
Setting the Scope for Pilots
Step 6
Evaluating Results & Gap Analysis
Step 4
Pilot Execution & Completion of Templates
Step 7
Assessment & Testing
Step 2
Information
Gathering &
Project
Planning
Step 8
Internal Reporting
Step 5
Roll-out at the Selected Opcos
Step 9
External Audit & Action Planning
24
PwC
Next steps… Phase 1: Preparation & Mobilisation
Step 1:
Mobilisation & project mngt
– Project organisation, project plan and initial communication
– Establishment of communication channels
Step 2:
Information gathering & detailed planning
– Overview of key processes
– Selected Opcos for pilot and full roll out
– Communication and training plan
– Detailed project plan & status reporting template
– Documentation templates
25
PwC
Next steps… Phase 2: Execution
Step 3:
Setting the scope for the pilots
– Key business processes relevant for reporting
– One pilot for each selected process
– Communication to all selected Opcos
Step 4:
Pilot execution and completion of templates
– Templates to be rolled out to all Opcos
– Trained Opco representatives
– Updated control self assessment questionnaire
– Updated detailed roll-out planning
Step 5:
Roll-out at the selected Opcos
– Populated documentation for all selected Opcos
– Updated control self assessment questionnaire
26
PwC
Next steps… Phase 3: Evaluation
Step 6:
Evaluation of results & gap analysis
– Assessment of key controls
– Identification of gaps (internal control weaknesses)
– High level action plan for improvement (closing the gaps)
– Completed and validated documentation on process, risk and controls
Step 7:
Assessment & testing
– Testing plan and execution of internal testing
Step 8:
Internal reporting
– Overview of the assessment process
– Reported conclusions on effectiveness of internal control, weaknesses and
reportable conditions and improvement actions
– Clear process for 302 certification and 404 reporting
– Definition of the text of the 302 certification and 404 reporting in SEC filing
27
PwC
Selecting relevant Business Units
Is location or business unit
individually important?
Yes
Evaluate documentation and test
significant controls at each
location or business unit
Yes
Evaluate documentation and
and test controls over
specific risks
Yes
No further action
required for such units
No
Are there specific
significant risks?
No
Are there locations or business
units that are not important even
when aggregated with others?
No
Evaluate documentation and
test entity
wide controls over group
Yes
Are there documented
entity
wide controls over this group?
No
Some testing of controls at individual
locations or business units required
28
PwC
SOX:
How does IT fit in (1)?
CobiT: Control Objectives for
information and related
Technology
IT RESOURCES
MONITORING
data
application
systems
technology
facilities
people
COSO
CE RA CA IC M
PO1 define a strategic IT plan
PO2 define the information architecture
PO3 determine technological direction
PO4 define the IT organisation and relationships
PO5 manage the investment in IT
PO6 communicate management aims and direction
PO7 manage human resources
PO8 ensure compliance with external requirements
PO9 assess risks
PO10 manage projects
PO11 manage quality
x
x x
x x
x
x
x
x
x x
x
x x x
x
x
x x x
PLANNING &
ORGANISATION
ACQUISITION &
IMPLEMENTATION
DELIVERY &
SUPPORT
29
PwC
SOX:
How does IT fit in (2)?
CobiT:
IT RESOURCES
MONITORING
data
application
systems
technology
facilities
people
COSO
CE RA CA IC M
PLANNING &
AI1 identify solutions
ORGANISATION
ACQUISITION &
IMPLEMENTATION
DELIVERY &
SUPPORT
AI2 acquire and maintain application
software
AI3 acquire and maintain technology
infrastructure
AI4 develop and maintain
procedures
AI5 install and accredit systems
AI6 manage changes
30
x
x
x x
x
x
PwC
SOX:
How does IT fit in (3)?
CobiT:
IT RESOURCES
COSO
CE RA CA IC M
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x x x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x x
x
x
DS1 define service levels
DS2 manage third party services
MONITORING
DS3 manage performance and capacity
DS4 ensure continuous service
DS5 ensure systems security
DS6 identify and attribute costs
DS7 educate and train users
DS8 assist and advise IT customers
DS9 manage the configuration
DS10 manage problems and incidents
DS11 manage data
DS12 manage facilities
DS13 manage operations
31
data
application
systems
technology
facilities
people
PLANNING &
ORGANISATION
ACQUISITION &
IMPLEMENTATION
DELIVERY &
SUPPORT
PwC
SOX:
How does IT fit in (4)?
CobiT:
COSO
CE RA CA IC M
x
x
x
x
x
M1
M2
M3
M4
IT RESOURCES
monitor the processes
assess internal control adequacy
obtain independent assurance
provide for independant audit
data
application
systems
technology
facilities
people
MONITORING
PLANNING &
ORGANISATION
ACQUISITION &
IMPLEMENTATION
DELIVERY &
SUPPORT
32
PwC