Chinese Exclusion Act
advertisement

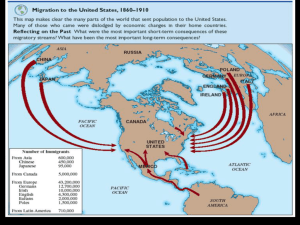
IMMIGRATION Sought to escape difficult conditions Famine, Land shortages Religious/political persecution “Birds of Passage” Immigrate temporary Earn money Return to homelands EUROPEANS 1870-1920- 20 million Europe-180-1900 population doubled (400 million) Image- US had numerous jobs Arrived on east coast (Ellis Island) 1 week journey OLD VS NEW IMMIGRATION New Old 1820-1860 from northern or western Europe [German, English, and Norwegian]. Mostly Protestants Literate and skillful in professions Came to America with money/wealth Experienced in democracy. 1880-1924 from southern or eastern Europe [Italians, Poles, eastern Europe Jews]. Asians Religions were either Catholic, Orthodox, or Jewish Illiterate and unskilled (with some exceptions) They came with little to no money CHINESE West coast California Gold Rush 1848 Helped build rr, farming, mining, and domestic service Chinese immigration limited-1882 Asian immigrants- 3 week journey JAPANESE 1884- Hawaiian planters recruited Japanese workers US annexed Hawaii in 1898 1907- 30,000 Japanese came to US 1920- 200,000 lived on west coast WEST INDIES AND MEXICO Jamaica, Cuba, Puerto Rico (West Indies) Scarce jobs and industrial boom (image of an abundance of jobs in US) Mexican immigration Farm lands in western states 1910- political and social situations in Mexico 700,000 (7% of Mexican population) over 20 years ELLIS ISLAND New York Harbor Main immigration station in US 17 million immigrants Inspection Physical exam: serious health problems, contagious diseases, tuberculosis sent home Government: checked documentation, questioned immigrants to see if met legal requirements (never been convicted of a felony, able to work, had some money) Only 2% were denied entry ANGEL ISLAND San Francisco Bay Primarily Asians (Chinese) 1910-1940- 50,000 Chinese immigrants Processing harsher than Ellis Island Harsh questioning Detained in filthy buildings CULTURE SHOCK When someone feels confused, uncomfortable, nervous, etc. when he or she goes to a place that is unfamiliar to them MELTING POT Native born Americans thought of US as a melting pot Blend of different cultures Many immigrants wanted to keep their customs and cultural identity Strong anti-immigrant feelings Nativism= favoritism towards native-born Americans Push for immigrant restriction NATIVISM Increased the desire for immigration restriction Chinese Exclusion Act- 10 year immigration restriction for Chinese laborers Gentlemen’s Agreement (1907)- Japanese students in San Francisco put in separate schools. Japan raised a protest, Theodore Roosevelt agreed to lift segregation order if Japan would not send unskilled emigrants. PROBLEMS IN URBAN Housing Transportation Tenements Mass transit Water No indoor plumbing Sanitation Crime Fires EMPLOYEE RESPONSES TO STRIKES AND UNIONS Blacklisting- names of people to be barred from employment Lockouts- Company does not let employees come to work Scabs- a person who works despite strike action or against the will of other employees Yellow dog contract- Contract saying the employer will not join a labor union Open Shop- Workers have choice to join labor union. “right to work” states Closed Shop- Workers do not have choice, have to join union