Brain Structure and Function Guided Notes Name: The brain is
advertisement

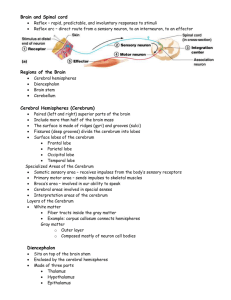
Brain Structure and Function Guided Notes Name:____________________________________ The brain is divided into four main regions: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ Cerebrum Largest region Responsible for _______________________________________________: ◦ speech ◦ memory ◦ reasoning ◦ emotion ◦ consciousness ◦ interpretation of sensation ◦ voluntary movement Divided into left and right hemispheres Wrinkled texture ◦ Raised areas called ___________________ ◦ Shallow grooves called ____________________ ◦ Deep groves called _______________________ The outer part of the cerebrum – called the _________________________________________-is composed of gray matter Gray matter = ________________________ ____________________________________ This is where thought, sensation, etc. occur The inner part of the cerebrum is mostly white matter White matter = ______________________ ____________________________________ This is the connection between different regions of the brain The _________________________________________ is one especially important area of white matter – it’s the connection between the two cerebral hemispheres Diencephalon structure The diencephalon consists of three parts: __________________________ __________________________ (completely enclosed by thalamus) __________________________ Regulation of autonomic functions, including ◦ __________________________________ ◦ __________________________________ ◦ __________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________– emotional / visceral brain (sex, food, thirst, pain, pleasure) Circle the parts that are diencephalon. Square the parts that are brain stem. Brain Stem The brain stem consists of three parts __________________________ __________________________ __________________________________________ Controls many autonomic functions, including: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ Also allows passage of nerves fibers between brain and spinal cord Cerebellum Back of the brain, beneath cerebrum Like cerebrum, it has ◦ ◦ ◦ Two hemispheres Wrinkled surface Outer cortex made of gray matter outside and inner region of white matter Functions _______________________________________ • _______________________________________ You Do Using 4 different colors, label the four major regions of the brain. List the major functions of each section here: Cerebrum: Diencephalon: Brain stem: Cerebellum: Label: gyrus, sulcus, cortex (gray matter), white matter, fissure List three differences between gray matter and white matter. Label the parts: cerebrum, cerebellum, spinal cord, medulla oblongata, mammilary body, thalamus, pineal body, pons, hypothalamus, corpus callosum, midbrain, optic chiasma Questions Following a stroke, a person develops the symptoms listed below. Which part of the brain was damaged? ataxia (an inability to coordinate muscular movement) Drooping left side of face Cerebrospinal Fluid Fluid that surrounds and protects brain and spinal cord Produced by the _________________________ from blood plasma, and drains back into the blood Some diseases can be diagnosed by examining CSF collected during a spinal tap Which glial cells are involved with CSF? What do they do? Blood brain barrier Protects the brain from toxins, most drugs, and fluctuations in other chemicals such as ions Two major barriers ◦ ___________________________________________ ◦ ___________________________ which control flow ofmaterials from blood vessels to neurons Why is the blood brain barrier necessary? Does the blood brain barrier block the passage of alcohol?