Brain study guide 2. Cerebrospinal fluid – origin, location and functions
advertisement

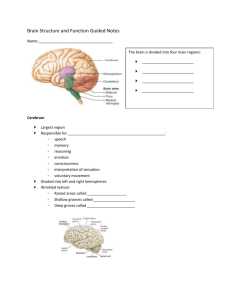
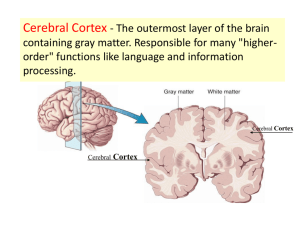
Brain study guide 1. Identify the layers of brain protection - bone and meninges. Identify dura matter folds 2. Cerebrospinal fluid – origin, location and functions External view 1. Identify the parts of the brain: cerebrum, cerebellum. Brain stem, diencephalons (can it be seen from the outside?) 2. Cerebrum – Identify 5 lobes – can they all be seen from the outside? Identify main sulci, fissures and gyri Identify main functional area of the cerebrum 3. Brain stem – Identify the 3 parts of the brain stem: Mid brain (mesencephalon), pos, medulla oblongata 4. Diencephalon – Identify external structure tat are associated with the diencephalons: pituitary gland and infundibulum, mammillary bodies Internal view 1. Open the brain to midsagittal plan and identify the following: - Ventricles and choroids plexus 2. Cerebrum structures and areas: - cerebral cortex (gray matter – what is it made of?), white matter (what is it made of?), Basal nuclei (what are they made of?), what ventricle/s are located in the cerebrum, fornix, corpus callosum 3. Cerebellum structures and areas: - cerebellar cortex (gray matter – what is it made of?), white matter/arbor vitae (what is it made of?), vermis 4. Diencephalon structures and areas – thalamus (lobes, interthalamic adhesion), hypothalamus (what external structures are associated with the hypothalamus?), epithalamus (what structures make the epithalamus?), what ventricle is associated with the diencephalon 4. Brain stem structures and areas – mesencephalon and cerebral peduncles, pons, medulla oblongata, what ventricle is associated with the brain stem, cerebral/mesencephalic aqueduct, Corpora quadrigemina (superior and inferior culliculi Use the table on the website to learn the brain structures’ functions