Brain Structure and Function: Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brain Stem
advertisement

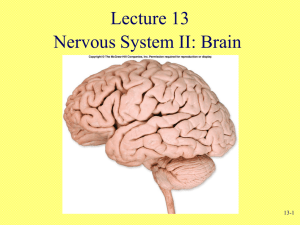
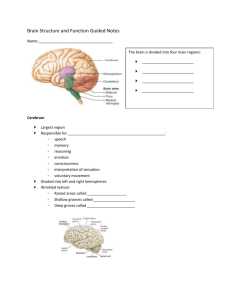
722017-9-1CHP AID: 23739 | 02/06/2017 The brain is the primary site of information processing and response coordination in the central neural system (CNS). It originates from ectoderm of the embryo and remains enclosed in the cranial cavity which is protected by Skull bones. According to functions, for convenience in study, the brain is divided into four following divisions1. Cerebrum The cerebrum occupies about 80% of the total brain hence it is the largest part of the brain. It remains Spread over almost whole brain superiorly. A longitudinal fissure divides the cerebrum into left and right hemispheres. Each hemisphere is subdivided into four visible lobes and one hidden lobe. It is the site of the memory, learning, conscious thought, reasoning, perception, and abstract mental functions. This portion also controls laugh-weep and urinationdefecation. 2. Diencephalon The diencephalon is present between the left and right hemisphere and superior to the brain stem in the center of the brain. The wall of the whole diencephalon is identified into three subparts- Epithalamus, Thalamus, and Hypothalamus. The primary functions of diencephalon are to receive Olfactory and sensory inputs, sending sorted input to particular part of the brain. The hypothalamus of the diencephalon controls olfactory reflexes, autonomic nervous system, pituitary gland, and maintains homeostasis. 3. Brain stem It is located between the diencephalon and spinal cord. Brain stem has three partsSuperior mid Brain, inferior Medulla oblongata, and in middle Pons. There is a smaller part; Midbrain is present in the brain which controls the movement of eye, head, and neck. The medulla oblongata is about 3 cm in length connected with pons in the upper side and spinal cord on the lower side. It contains the center of swallowing, vomiting, coughing, hiccupping, sneezing, taste, and movement of the tongue. Pons controls the respiration process. 4. Cerebellum The cerebellum is found in the posterior region of the brain. It is second bigger part of the brain, situated behind pons, after cerebrum. It receives stimulus from eye, voluntary muscles and maintains posture.