2-4 Recording Business Transactions
advertisement

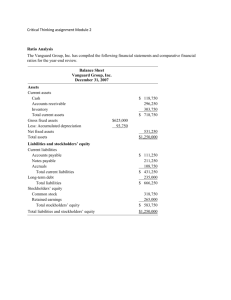
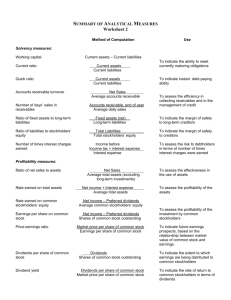
Matakuliah Tahun : V0232 – Akuntansi Keuangan Hotel : 2009 Hospitality Financial Accounting Week 1 Part 1 Hospitality Accounting in Action 1-1 Accounting Process Identification (Select economic events/ transactions) Internal Users Management Managers, supervisors, and company officers Recording (Record, classify, and summarize) Communication (Prepare reports; analyze and interpret) External Users Investors/creditors Present & potential Investors Creditors Other Users Taxing authorities Regulatory agencies Labor unions Economic planners 1-2 Bookkeeping vs. Accounting Bookkeeping Involves only the recording of economic events Just one part of the accounting process Accounting Involves identifying, recording, and communicating economic events Types of Accounting: • Financial • Managerial 1-3 Assumptions Monetary Unit Assumption Only transaction data that can be expressed in terms of money can be included in the accounting records Economic Entity Assumption Activities of the entity must be kept separate from activities of the owner 1-4 The Accounting Equation ASSETS = LIABILITIES + STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY Assets are = Liabilities are resources that creditor claims possess future on the assets and economic represent the debts benefits. and obligations of the entity. TOTAL ASSETS + Creditor claims on assets Stockholder’s claims on assets Stockholders’ equity is the stockholder’s residual claim on total assets. 1-5 The Accounting Cycle Steps in the Accounting Cycle 1. Analyzing Transactions 2. Journalizing 3. Posting 4. Trial Balance 5. Adjustments 6. Adjusted Trial Balance 7. Financial Statements 8. Closing Entries 9. Post Closing Trial Balance 1-6 Uniform Systems Hotels Uniform System of Accounts for the Lodging Industry Clubs Uniform System of Financial Reporting for Clubs Restaurants Uniform System of Accounts for Restaurants Spas Uniform System of Financial Reporting for Spas Hospitality Financial Accounting Part 2 Accounting Principles 2-1 Conceptual Framework CONSTRAINTS Objectives of Financial Reporting Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting Information Elements of Financial Statements Operating Guidelines Assumptions Principles CONSTRAINTS 2-2 Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting Information Useful Financial Information has: Relevance 1. Predictive value 2. Feedback value 3. Timely Reliability Comparability and Consistency 1. Verifiable 2. Faithful representation 3. Neutral 2-3 Operating Guidelines Detailed Guidelines for Solving Practical Problems ASSUMPTIONS PRINCIPLES 1. Economic Entity 1. Revenue Recognition 2. Monetary Unit 2. Matching 3. Time Period 3. Full Disclosure 4. Going Concern 4. Cost CONSTRAINTS and Materiality Conservatism 2-4 Recording Business Transactions A. Review of Selected Transactions Mr. Sam Doty opened and incorporated a hospitality consulting firm during the month of September and provided you with the following data. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Invested $8,000 in his business in exchange for common stock. Purchased $500 of supplies for cash. Purchased $4,000 of equipment on account. Received $3,000 cash for consulting services. Paid salaries of $800 Paid the first month’s rent of $200. Paid $1,000 owned to a creditor. The corporation paid a dividend of $1,500 in cash to Sam Doty, the stockholder. Instructions: Prepare the tabular summary for the transactions above. 2-4 Recording Business Transactions (continued) Summary of Transactions Month of September 2008 Answer: Assets Trans- = SupCash (1) +$8,000 (2) -500 + Equip-ment + Liabilities + Accounts = Stockholders’ Equity Common Retained + +$8,000 Investment +500 (3) +$4,000 +$4,000 (4) +3,000 +3,000 (5) -800 -800 Salary Expense (6) -200 -200 Rent Expense (7) -1,000 (8) -1,500 $7,000 Service Revenue -1,000 -1,500 + $500 + $4,000 = $3,000 + $8,000 $500 Dividends 2-4 Recording Business Transactions (continued) B. Financial Statement Relationship to Transactions and Balances 1. Prepare the Income Statement and Retained Earnings Statement from the Stockholders’ Equity Column of the Summary of Transactions for the month of September. Stockholders’ Equity + $8,000 + 3,000 - 800 (Salary Expense) - 200 (Rent Expense) - 1,500 $8,500 (Investment by Stockholders) (Service Revenue) (Dividends) 2-4 Recording Business Transactions (continued) Answer: Sam Doty Sam Doty Hospitality Consultant Hospitality Consultant Income Statement Retained Earnings Statement For Month Ended September 30, 2008 For Month Ended September 30, 2008 Revenues Service revenue $3,000 Retained Earnings, September 1 $ -0- Expenses Salary expense Rent expense Total expenses Net income Add: Net income $800 2,000 2,000 200 1,000 $2,000 Less: Dividends $1,500 Retained Earnings, September 30 $ 500 2-4 Recording Business Transactions (continued) 2. Prepare the Balance Sheet from the Month-end Balances of the Summary of Transactions. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity Cash + Supplies + Equip. $7,000 + $500 + $4,000 = = Accounts Payable $3,000 + + Common Stock $8,000 + + R.E. $500 2-4 Recording Business Transactions (continued) Sam Doty, Hospitality Consultant Answer: Balance Sheet September 30, 2008 Assets Cash $ 7,000 Supplies 500 Equipment 4,000 Total assets $11,500 Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity Liabilities Accounts payable $ 3,000 Stockholders’ Equity Common stock Retained earnings Total liabilities & stockholders’ equity 8,000 500 $11,500 2-4 Recording Business Transactions (continued) 3. Prepare the Statement of Cash Flows from the Cash Column of the Summary of Transactions for the month of September. Sam Doty, Hospitality Consultant Statement of Cash Flows for Month Ended September 30, 2008 Cash flows from operating activities Cash receipts from customers $3,000 Cash payments for expenses 1,000 Net cash provided by operating activities $2,000 Cash flows from investing activities Purchase of supplies Payment for equipment (500) (1,000) (1,500) Cash flows from financing activities Sale of common stock $8,000 Dividends paid (1,500) Net increase in cash Cash at the beginning of the period Cash at the end of the period 6,500 7,000 0 $7,000 2-5 Analyzing Transactions Identify the various transactions indicated by the information provided: 1. 2. 3. 4. CASH ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE increased………………….. decreased_________________ RENT EXPENSE CASH increased………………….. decreased_________________ SUPPLIES ACCOUNTS PAYABLE increased………………….. decreased_________________ EQUIPMENT CASH increased………………….. decreased_________________ 2-5 Analyzing Transactions (continued) Continue exercise by asking students for a transaction which increases the following: Cash, Accounts Receivable, Supplies, Equipment, Accounts Payable, Common Stock Continue exercise by asking students for a transaction which decreases the following: Cash, Accounts Receivable, Supplies, and Accounts Payable Answer: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 2-5 Analyzing Transactions (continued) Collection of an accounts receivable. Payment of the current month’s rent. Purchase of supplies on account. Purchase of equipment for cash. Rendering of services for a customer on account. The declaration of a cash dividend.