Epithelial tissue_2015
advertisement

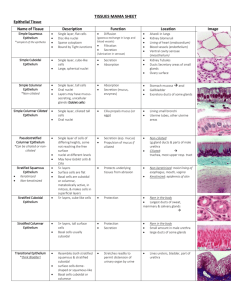
Chapter 1 Introduction zhong jie Li ( 李仲杰 ) School of Medicine, Zhejiang University Email:lizhongjie@zju.edu.cn Reference books • 1. 《组织学与胚胎学》,人民卫生出版社,8年制、7年制和5年制本 科规划教材均可; • 2. 唐军民、李继承. 组织学与胚胎学(Textbook of Histology and Embryology), 北京大学医学出版社, 2011 • 3. William k. Ovalle & Patrick C. Nahirney. Netter’s essential histology, Elsevier Health Sciences,2007 • 4. Gaetner MP, Hlatt JL. Colour Textbook of Histology. Williams & Wilkins, 1997 Final score of Histology & Embryology 1) Attendance and Picture drawing : 5% 2) Quiz: 10% (each quiz 5%) 3) Lab test: 25% 4) Final written exam: 60% Preparation of laboratory work Have the tools ready: 1) Paper 2) Pencils (red-blue pencil) 3) rubber, ruler and so on Course website m-learning.zju.edu.cn Introduction Key points: I. What’s histology? II. Why we study it ? III. How to study it ? ---Histological methods. I. What’s histology? Histology (Greek words): /histo---tissue /logia---study of ,or knowledge of Histology : a science which study the microstructure and the relationship between the structure and function of human being. Cell: smallest unit of structure and function of body (1665年,英国人,Hooke) Tissue: group of cell and extracellular matrix (1801年,法国医生比沙,Bichat) Four basic tissue: ---Epithelial tissue ---Connective tissue ---Muscular tissue ---Nervous tissue Tissue Organ: made up of tissue, have special shape, structure and function --- the cavity organ histology --- parenchymatous organ anatomy System: organs which have related function get together. 组织学内容关系图解 基本组织 器官系统 上皮组织 循环系统 消化系统 结缔组织 呼吸系统 泌尿系统 肌 组 织 生殖系统 免疫系统 神经组织 内分泌系统 感官 II. Why we should study it ? Histology is the meeting-place of anatomy, physiology, pathology and biochemistry . Special structure is related to special function 只有了解正常的机体结构、组成及其基本生命现象, 才能理解机体异常的病理变化。同时也能将生命科学研 究不断引向深入。 III. How to study it histological methods ---Development of histology depends on the development of technique. ---Histology studies the microstructures. So, we should have the aid of microscope to study. Several types of microscopes are available. Light Microscopy The resolution of the light microscope is 0.2 um The procedures of paraffin sectioning and H & E staining. • • • • • • • • 1. Obtaining 2. Fixation 3.Dehydration 4. Clearing 5. Embedding 6. Sectioning 7. Staining 8. Mounting Stain methods Hematoxylin 苏木精 Acidic stucture: Nucleus RER Free ribosome H.E Eosin 伊红 Basic stucture: Cytoplasma lysosome、 Mit.,fibers H&E staining H&E staining TEM: transmission electron microscopy (1932年,Ruska and Knoll) The resolution of the TEM is about 0.1-0.5nm. Basophilic granulocyte (TEM) Basophilic granulocyte (LM) SEM: scanning electron microscopy The resolution of SEM is about 5nm. 激光扫描共聚焦显微镜 Laser scanning confocal microscope Histochemistry & Cytochemistry Immunohistochemistry Cell culture & Tissue engineering Learning methods: • Must think in 3 dimensions • Structure and function • part and whole. longitudinal section Horizontal section oblique section Changes in apparent shape, due to orientation of sections Netter/Ciba Junqueira fig 1-30 Structure and function part and whole relaxation contraction Chapter 2 Epithelial tissue 1.General feature: 1) contain more cells and less extracellular ground substance 2) Polarisaton: ---free surface ---basal surface ---lateral surface 3) Avascularity, but innervation: ---no blood vessels ---rich in nerve terminals 4) Cellular Layer + Basement Membrane 5) Functions: protection secretion absorption sensory reception 2.Classification of Epithelium 1) Covering epithelium: the epithelium which cover body surface or line the inner surface of body cavities, tubes and sac. 2) Glandular epithelium: the epithelium which main function is secretion. 3) Special epithelium * Sensory epithelium: the epithelium which has special sensory function. * Myoepithelial cell 3. Classification of covering epithelium: According to the number of layer and shape of cells Simple epi.: ---simple squamous epi. ---simple cuboidal epi. ---simple columnar epi. ---pseudostratified ciliated columnar epi. Stratified epi.: ---stratified squamous epi. ---stratified columnar epi. ---transitional epi. Cell shape Cell Layers Simple Stratified 1) simple squamous epi: ---structural feature: /one layer flattened cells, cell border are interdigitate closely,polygonal in shape. /with flattened ellipsoid nucleus ---Distribution: • mesothelium: which line the inner surface of body cavities such as pleura, peritoneum and pericardium. • endothelium: which line the inner surface of cardiovascular and lymph vessels. • other place: alveoli, parietal layers of renal capsule. ---function: a) transport of materials b) facilitates movement of viscera endothelium (内皮) mesothelium (间皮) Vascular endothelium 2) simple cuboidal epi.: ---structural feature: • one layer of cells, with same height and width , hexagonal in shape. • spherical centrally-located nucleus ---distribution: /the renal tubule /thyroid /the some ducts of glands ---function: absorption and secretion renal tubule thyroid 3) simple columnar epi.: ---structural features: • one layer of columnar cells, with basally located long ovoid nucleus ---distribution: gastrointestinal tract gall bladder uterus ---function: secretion and absorption * goblet cell: scattered, secreting granules-mucus simple columnar epi goblet cell 4) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epi.: four types of cells ---Structural feature: 1, Four types of cells columnar cell (ciliated); goblet cell fusiform cell; basal cell: pyramid-shaped 2, Every cell locate on basement membrane: Simple epi. ---distribution: inner surface of large duct of respiratory passages trachea bronchi nasal The epithelium of trachea 5) stratified squamous epi.: ---structural features: • deepest (basal) cells: one layer of cuboidal cells • the cells in intermediate regions: several layers of polygonal –shaped cells • to the surface: more and more flattened cells ---distributon: • non-keratinised: mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, urethra and vagina • keratinised: the surface of body, make up the skin non-karatinised karatinised 6)stratified columnar epithelium ---Structural features: suface layer: : one layer of columnal cells deeply regions: several layers of polygonal shaped cells ---Ditribution: Conjunctiva(结膜)、male urethra(男性尿道) 7) transitional epithelium: • Flexible qualities --- Cell shape and the layer variable ---distribution: bladder in the contracted bladder in the distended bladder 4. Epithelial specializations Sides of cells: --- Apical (free) --- Basal --- Lateral 1) Specializations of free surface ① microvilli: ---definition: delicate finger-liked projections of cellmembrane and cytoplasm protruding from the free surface ---structure: • 0.1um in diameter, with different longth. • surface: cell membrane with cell coat • core: longitudinal microfilament-actin filament fixed on terminal web • terminal web: made up of transverse-arranged filament at the apical side of cells ---function: increase the surface areas, thus aid in the processes of secretion and absorption. ---distribution: /striated border: intestinal epi. cell /brush border: proximal renal tubule Striated border ② cell coat: ---definition: a thick layer of extracellular glycoprotein ---function: adherence, supporting, protection, exchange of material and recognize ③ cilia: ---definition: elongated, mobile projections of cell membrane and cytoplasm protruding from free surface ---structure: • 5-10um long, 300-500nm in diameter • surface: cell membrane • core: microtubules, 9X2+2 • basal body: centrioles-connected with microtubules of cilia ---function: beat in a rhythmical manner and produce a forward-moving wave ---distribution: epithelial cells of respiratory tract respiratory tract 2) specializations of the lateral surface ---intercellular connection of adjacent cells: • non-special manner: the minute space and adherent molecules (glycoproteins, proteoglycans, cadherin) • Special manner: junctional structures ① Tight junction (zonula occludens): ---structure: • • • • apical part point-liked fused between adjacent cells arranged in 2-4 thread-liked structures form anastomosing network ---function: seal the space between cells ② intermediate junction (zonula adherens): ---structure: • below the tight junction • a gap of 15-20nm in width with medium electron-density filament material • plaque of electron-dense materials, with attached microfilament-make up of terminal web ---function: /adherens /keep the cell shape /transfer cell contract force ③ desmosome (macula adherens): ---structure: • plate or spot-shaped • a gap of 20-30 nm, with • • low electron-density filaments interdigitate attachment plaque Many tonofilaments are inserted into attachment plaque, each filament make a hairpin loop and then passes back into the cytoplasm ---function: firmly connection ④ gap junction (communication junction): ---structure: • the smallest gap of 2-3 nm • connexons: -consist of protein -7~9nm in diameter -composed of 6-subunits of proteins- connexin -2nm channel: electron-lucid central channel ---function: provide a ions and small molecules pathway between cells connexons junctional complex: at least two types of junctional structures get together. 3) specialization of basal surface ① basement membrane: ---definition: a sheet of membrane-liked amorphous material interposed between epithelium cells and underlying CT. ---structure: • HE: pink colour, hard to see • PAS + • EM: two layers --basal lamina: 20-100 nm, electron-dense, thread-liked and amorphous ground substance, produced by epithelium cell. --reticular lamina: RT+ground substance, produced by CT ---function: • support, connection, fixation • semi-permeable membrane • induce the movement, proliferation and differentiation of epithelium cell ② plasma membrane infolding (basal longitudinal striation): ---definition: the infolding of cell-membrane with many mitochondria at the basal surface of epithelium cell ---function: • increase the basal surface areas • facilitate the passage of water and ions ---distribution: mainly in proximal and distal renal tubule. ③ hemidesmosomes ---is half of desmosome. SUMMARY 1: 上皮类型 单层上皮 单层扁平上皮 主要分布 内皮:循环管道内表面 间皮:胸膜、腹膜、心包膜、 其它:肺泡、肾小囊等 单层立方上皮 肾小管、甲状腺滤泡等 单层柱状上皮 胃肠、胆囊、子宫内膜等 假复层纤毛柱状上皮 呼吸管道 复层上皮 复层扁平上皮 角化型:皮肤表皮 非角化型:口腔、食管、阴道 复层柱状上皮 睑睫膜、男性尿道等 变移上皮 肾盏、肾盂、输尿管、膀胱 SUMMARY 2: 名 称 游离面 侧 面 结 构 特 点 主要功能 微绒毛 细指状,光镜不可见,有微丝 吸收 纤毛 粗指状,光镜下可见,有微管 定向摆动 紧密连接 点状融合 机械连接 中间连接 小盘状融合 机械连接 桥粒 机械连接 斑状融合 缝隙连接 点状,成群,细胞间有通道 基膜 薄膜,分基板和网板,PAS 阳 性,嗜银 基底面 质膜内褶 膜向胞内折叠,线粒体多 半桥粒 桥粒的一半 细胞通讯 连接、支持、 半透膜 吸收 固定 Questions • Describe the characteristics of epithelial • • • tissue. Describe the structural characteristics, distribution and functions of each type covering epithelial. Compare the structure of microvilli with cilia. Compare the structure of intermediate junction with desmosome. Preview: • Connetive tissue. • Cartilage. 5. Glandular epithelium and gland (study yourself ) • • glandular epithelium: are specialized for secretion gland: organs composed mainly of glandular epiithelium 1) Classification: exocrine gland: discharge the secretion through a duct system endocrine gland: release the secretion directly into blood steam 2) structure of exocrine gland: Simple gland compound alveolar gland compound tubulo-alveolar gland ① acinus (secreting unit): according the nature of secretion a. serous acinus: serous secretory cells ---structure: • pyramid-shaped cell • basally-located round nucleus • acidophilic cytoplasm-eosinophilic zymogen granules-contain enzymes • EM: RER, Golgi complex ---function: produce a serous secretion b. Mucous acinus: mucous secreting cells ---structure: • pyramid-shaped cell • flattened dark nucleus against the basal cell membrane • slightly basophilic cytoplasm-large mucigen granules • EM: some RER, Golgi complex ---function: secretes mucus Mucous acinus c. mixed acinus: two types of cells ---structure: • mucous acinus • with several serous cells attach on one sideserous demilune ② ducts: ---from simple squamous epithelium to simple columnar or stratified epithelium ---carry out the secretions ---secrete or absorb water and ions Thank you ! Supplementary material: Preparation of tissue for LM The most routine one is paraffin section stained with hematoxylin and eosin(H&E) The steps: a. Obtaining the specimen: fresh, small pieces tissue block( less than 5mm3) b. Fixation: fixatives: use formalin or Bouin’s to preserve structural organization c. Dehydration: use ethyl alcohol to get rid of water of tissue and cell d. Clearing: use xylene to get rid of alcohol *alcohol and xylene are embedding mediums e. Embedding: firstly, heat the paraffin, make it melt, then put tissue block into melted paraffin, allow paraffin harden, the tissue block is embedded in. f. Sectioning: use microtome to cut the tissue into 3-8um thick sections, then monted them on glass slides g. H&E staining ---Hematoxylin: basic stain, combines with acidic components, make them appear blue colour- basophilic, i.e. cell nucleus, hyaline cartilage ---Eosin: acidic stain, combines with basic components, make them appear pink colouracidophilic (eosinophilic), i.e. cytoplasm Preparation of tissue for EM The steps are same to preparation for LM a. tissue block: more small, less than 1mm3 b. plastic materials for embedding c. ultra-thin sections is about 30-50nm thick( use ultramicrotome) d. heavy metal salts- increase staining contrast ---lead citrate ---uranyl acatate