Literary Terms Flashcards
advertisement

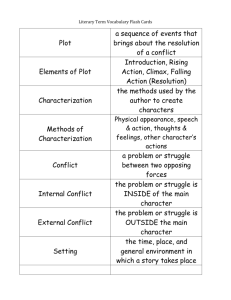
Literary Terms Flashcards This occurs when the reader/ audience knows something that the character(s) in the story do not know. Dramatic Irony The series of related events that make up a story. Plot Literature (along with film and music) is broken down into these different categories. Genre A person, a place, a thing, or an event (a concrete visible object) that has its own meaning AND stands for something beyond itself (an invisible object or idea with a deeper meaning) as well. Symbol A figure of speech in which a nonhuman or nonliving thing or quality is talked about as if it were human or alive. Personification A person or character that is considered to be the main character in a novel, play, story, or poem. Protagonist This is a very broad term and refers to a type of language or writing that does not want the reader to take things literally. It is a word or a phrase that describes one thing in terms of another and is not literally true. Figurative Language The literal dictionary definition of a word. Denotation The repetition of the same or very similar consonant sounds at the beginning of words that are close together. Alliteration A person or character that deceives, frustrates, or somehow works against the main character. Antagonist An interruption in the action of a plot to tell something of importance which happened at an earlier time. Flashback The feelings, emotions, and associations that a word suggests. (positive, negative, or neutral) Connotation A person or animal who takes part in the action of a story, play, or other literary work. (The ways in which the author develops that person or animal in a story.) Character/ Characterization This term is a type of figurative language where one uses an extreme exaggeration for dramatic effect. Hyperbole A struggle or clash between opposing characters or opposing forces. This type is when a character struggles against some outside force. External Conflict An imaginative comparison between two unlike things in which one thing is said to be another thing. A figure of speech. Metaphor A truth about life revealed in a work of literature. Theme An all-knowing perspective from which a story is told. Omniscient Point of View A perspective from which a story is told where the narrator only focuses on one characters thoughts and feelings. 3rd Person Point of View A perspective from which a story is told in which the narrator is telling the story him or herself, using the person pronoun “I”. 1st Person Point of View A story that attempts to explain something about the world or how something was created and typically involves gods or other superhuman beings. Myth Involving a contrast between what is said or written and what is meant: sarcasm. Verbal Irony The use of clues to suggest events that will happen later in the plot. Foreshadowing A struggle or clash between opposing characters or opposing forces. This type is when the struggle is within the character’s own mind. Internal Conflict An example of figurative language in which a comparison between two unlike things is made, using a connecting word such as “like” or “as”. Simile The time and place in which the events of a work of literature take place. Setting An educated guess, a conclusion that makes sense because it is supported by evidence. (What you know + what you read = inference) Inference A reference, found in a story, to a statement a person, a place, or an event from literature, history, religion, mythology, politics, sports, or science. Allusion Occurs when what happens in a story is very different than what was expected to occur. Situational Irony A conversation between two or more characters. Dialogue