learning notes
advertisement

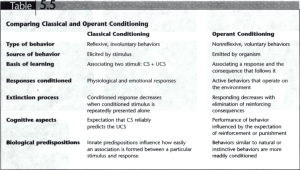
Mrs. Perl AP Psychology-Classical Conditioning Unit 6: Learning Relatively permanent behavior change due to experience Conditioning is the Process of learning associations I. Classical Conditioning: Learn to associate two stimuli and to anticipate an event. A. Acquisition: Initial learning of the stimulus-response relationship. 1. Pavlov-Temporal association UCS UCR NS + UCS CS UCR CR a. Unconditioned Stimulus: Any stimulus that creates an Autonomic, automatic, or reflexive response in an organism. It is unlearned! b. Unconditioned Response: Unlearned response that can be elicited from an organism c. Conditioned Stimulus: Anything that can be learned d. Conditioned Response: Anything that can be an UCR can become a CR if paired with a CS. Becomes a learned stimulus-response association. Come up with an example of classical conditioning: 2. Higher-Order Conditioning (Second-order conditioning) B. Extinction C. Spontaneous Recovery D. Generalization-John Watson (Little Albert) E. Discrimination II. Cognitive Elements to Classical Conditioning A. Predictability B. Learned Helplessness III. Biological elements to classical conditioning A. Taste Aversion-John Garcia Application: Scenarios: Unconditioned Response (UCR): Involuntary, “hard-wired” reaction that does not need to be learned. Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): The event that automatically elicits the involuntary response. Conditioned Response (CR): The new behavior that is acquired through learning Conditioned Stimulus (CS): The event that takes on new meaning through conditioning. 1. After working out Marvin takes a shower in the locker room. During the shower he hears someone flushing a toilet. Suddenly, boiling hot water rushes out of the shower head, causing Marvin discomfort. As he continues the shower, he hears another toilet flush and immediately jumps out from under the shower head. a. What is the unconditioned response? ____________________________ b. What is the unconditioned stimulus? ____________________________ c. What is the conditioned response? ____________________________ d. What is the conditioned stimulus? ____________________________ 2. Jane went with her family to a water show in 100 degree heat. During the performance she became very hot and uncomfortable. During the finale, when “Everybody’s going surfing” was playing over the sound system, Jane became extremely dizzy and actually fainted. After that, whenever Jane heard that song she felt a little dizzy. a. What is the unconditioned response? ____________________________ b. What is the unconditioned stimulus? ____________________________ c. What is the conditioned response? ____________________________ d. What is the conditioned stimulus? ____________________________ e. How did classical conditioning cause Jane’s phobic response? __________________________________________________________ 3. Captain Hook lost his hand to a crocodile who had swallowed an alarm clock. Fortunately for Hook, the loud ticking warned him of the crocodile’s approach. Unfortunately for Hook, any time he hears a ticking clock he now has a full blown anxiety attack. a. What is the unconditioned response? ____________________________ b. What is the unconditioned stimulus? ____________________________ c. What is the conditioned response? ____________________________ d. What is the conditioned stimulus? ____________________________ e. How was generalization a factor in this example?___________________ Write your own scenario and share it with the person sitting next to you. Decide which one to share with the class: II. Operant Conditioning: Learn to associate our behavior (a response) with the consequences of this behavior and thus to repeat acts followed by good results and to avoid acts followed by bad results. III. Observational Learning