Unit 5 Cell Energy
advertisement

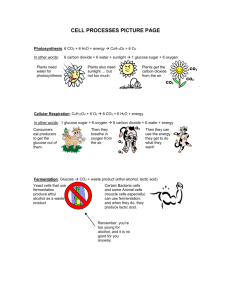
Unit V – Cell Energy The Story of Mitochondria & Chloroplasts How Do Cells Transform Energy? • Background Info: • 1) cells need energy to do work • 2) the food cells eat to make ATP is called glucose • 3) the molecule cells use to store energy is called ATP • 4) heterotrophs must eat food to get glucose, …autotrophs can make their own glucose • Purpose: Fermentation – Make ATP when there is no oxygen present • Who Does It: – Bacteria – Yeast cells – Muscle cells • Site: – Cytoplasm Fermentation • Two Types: 1) Alcoholic Fermentation Glucose CO2 + alcohol + ATP used to make breads & beer 2) Lactic Acid Fermentation Glucose lactic acid + ATP overexerted muscles; dairy products Endosymbiont Theory • Mitochondria & chloroplasts are thought to have come from ancient prokaryotic cells Evidence: Both mitochondria and chloroplasts… • have their own DNA • have their own ribosomes • have membranes similar to bacteria • divide like bacteria (binary fission) Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration • Purpose: – Make energy (ATP) for cells • Site: – Mitochondria • Equation: – C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP (energy – glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + ATP Cellular Respiration • Who Does It: – All eukaryotes • Description: 1) Glycolysis: glucose broken into 2 pieces… makes 2 ATP’s 2) Krebs Cycle & Electron Transport Chain: continue the complete breakdown of the glucose molecule…makes 36 ATP’s Photosynthesis • Purpose: – Make glucose for cells • Site: – Chloroplast • Equation: – carbon dioxide + water + light glucose + oxygen – CO2 + H2O + light (energy) C6H12O6 + O2 Photosynthesis • Who Does It: – Algae, plants, blue-green bacteria • Description 1) Light Reactions: Chlorophylls catch light & use its energy to make ATP & NADPH (O2 as waste) 2) Calvin Cycle: ATP used to change CO2 into glucose molecules (which are then stored as starch) Relationship between Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis • Sketch (& label) the overall plan All actions in an organism ultimately happen on the cellular level! • On the cellular level, why do we need to breathe oxygen? • On the cellular level, why do we need to eat food? All actions in an organism ultimately happen on the cellular level! • On the cellular level, why do plants need light? • On the cellular level, why do plants need carbon dioxide? The End Fake Quiz #1 • 1. Why do cells need energy at all? • 2. Which food molecule do they “burn”? • 3. If that food molecule (from #2 above) is so full of energy, why is ATP made? • 4. Where in the ATP molecule is all of that energy located? • 5. Who “invented” fermentation? • 6. What are 2 “old-fashioned” traits that fermentation exhibits? (hint: location & O2) Lab – Fermentation #1 I. Purpose: How does the amount of sugar affect the amount of CO2 produced? II. Background: glucose CO2 + alcohol + ATP III. Hypothesis: As more sugar is added, the amount of CO2 will ____. IV. Procedure: (Copy picture on board) Lab – Fermentation #1 V. Data Amt of Sugar (mL) Amt of CO2 (ppm) 0 5 20 Net CO2 Produced (ppm) Lab – Fermentation #1 V. Data Amt of CO2 (ppm) Amount of Sugar (mL) Lab – Fermentation #1 VI. Conclusion 1. The data shows that as more sugar is added, the CO2 levels… 2. This supports/does not support my hypothesis. 3. This lab relates to fermentation because… 4. A source of error in this experiment is… Lab – Fermentation #2 I. Purpose: Which sugar do yeast prefer? II. Background: Glucose CO2 + alcohol + ATP III. Hypothesis: (write a statement that answers your purpose question) IV. Procedure: (copy diagram from board) V. Data (copy the data table…then graph the data) Lab – Fermentation #2 VI. Conclusion 1. The data shows that yeast cells prefer… We could tell that this was true because… 2. This does/does not support our hypothesis. 3. A source of error in this experiment is… Quiz #1 1. Which of the following would NOT require cells to use ATP? A. Osmosis B. Growing C. Reproducing D. Moving Quiz #1 2. On the cellular level, why is it necessary for us to eat food? A. Our stomachs get hungry B. Our intestines empty C. Our cells need glucose D. Our cells need oxygen Quiz #1 3. Which of these is FALSE? A. Breaking down glucose gives off energy B. Breaking down ATP gives off energy C. Cells use ATP for cell work D. 1 ATP has more energy than 1 glucose Quiz #1 4. The energy in ATP is A. Stored between its phosphate groups B. Stored in the vacuoles C. Not widely used by cells D. Not very useful Quiz #1 5. Which cells can form ATP by breaking down glucose? A. Prokaryotes only B. Animals only C. Plants only D. All cells Quiz #1 6. Fermentation A. Requires oxygen B. Occurs in the cytoplasm C. Is only done by yeast cells D. Does not make ATP Quiz #1 7. The formula for one type of fermentation is Glucose CO2 + alcohol + ATP If yeast cells are given more sugar, then they will - A. B. C. D. Make less CO2 Make more ATP Be poisoned by alcohol Be poisoned by oxygen Quiz #1 • 1. Why do cells need energy at all? • 2. Which food molecule do they “burn”? • 3. If that food molecule (from #2 above) is so full of energy, why is ATP made? • 4. Where in the ATP molecule is all of that energy located? • 5. Who “invented” fermentation? • 6. What are 2 “old-fashioned” traits that fermentation exhibits? (hint: location & O2) Fake Quiz #2 • 1. Which cells invented fermentation? • 2. What is the purpose of fermentation? • 3. Which food molecule is broken down in fermentation? • 4. How many ATP are made in fermentation? • 5. Where in the cell does fermentation occur? • 6. Is fermentation aerobic or anaerobic? …what does that mean? Fake Quiz #2 • • • • • • • • 7. How does PS change life on earth? 8. Which type of cells can do PS? 9. Where in the cell does PS happen? 10. What is the purpose of Part 1 of PS? 11. Does Part 1 of PS need light? 12. What is the purpose of Part 2 of PS? 13. Does Part 2 of PS need light? 14. What is the carbon source for PS? Lab – Photosynthesis Rate I. Purpose: How does the amount of light affect the rate of photosynthesis? II. Background: CO2 + H2O + light (energy) C6H12O6 + O2 III. Hypothesis: The more light plants receive, the ____ photosynthesis will occur. IV. Procedure: (draw pic) Lab – Photosynthesis Rate V. Data Amt Light (%) Start [DO] (mg/L) Amt of Light (%) 0% 25% 50% 75% 100% End [DO] (mg/L) Net [DO] produced (mg/L) Avg Dissolved Oxygen Produced (mg/L) Lab – Photosynthesis Rate VI. Conclusion 1. The data shows that as plants get more light, the rate of photosynthesis… We could tell that this was true because… 2. This does/does not support my hypothesis. 3. A source of error in this experiment is…