What is Database Marketing
advertisement

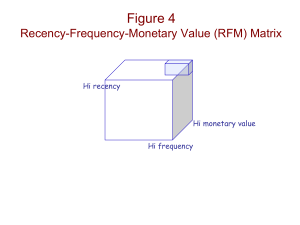
What is Database Marketing? Arthur Middleton Hughes VP Solutions Architect KnowledgeBase Marketing What KnowledgeBase Marketing Does Selected List of Clients How a modern database system works Mail, Email, Phone Customer Transactions Marketing Database Inputs from Retail, Phone, Web Updated several times per day Data Access And Analysis Software Appended Data Marketing Staff Access on the web Compared with newcomers, Long term customers: Buy more per year Buy higher priced options Buy more often Are less price sensitive Are less costly to serve Are more loyal Have a higher lifetime value Retention is the way to measure loyalty 90% 80% 70% Percentage Retained from Previous Year 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 1 2 3 4 Years as a customer 5 Retention pays better than acquisition Annual Profit $48 $60 $40 $20 $0 ($20) ($40) ($60) ($80) ($62) New Customer 3rd Year Customer Two Kinds of Database People Constructors People who build databases Merge/Purge, Hardware, Software Creators People who understand strategy Build loyalty and repeat sales You need both kinds! What doesn’t work: Treating all customers alike 79.67% This 28% lost 22% of the bank’s profits! 80.00% 60.00% 24.82% 40.00% 15.83% 1.52% 20.00% 0.00% -20.00% Bank Customers by Profitability -21.83% -40.00% 5% 11% 28% 28% 28% Marketing to Customer Segments Spend Service Your Best Customers 80% of Revenue Your Best Hope for New Gold Customers 1% of Total Revenue GOLD Move Up These may be losers Dollars Here Spend Marketing Dollars Here Reactivate or Archive Examples of Profitable Strategies Newsletters Surveys and Responses Loyalty Programs Customer and Technical Services Friendly, interesting interactive web site Event Driven Communications What proves that relationship building works? Manufacturer of building products Catalog sent to 45,000 contractors Previous policy: wait for the orders Test: pick 1,200 customers, split into test of 600 and control of 600 Two person pilot program build relationship with test customers to see the results Credit: Hunter Business Direct What did they offer? Follow up on bids and quotes Schedule product training Ask about customer needs New Product information They did not offer discounts Change in the number of orders 112% 120% 82% 100% Change in number of orders 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% 1 2 Control vs Test Groups Change in the Average Order Size 114% 120% 86% 100% 80% Change in average 60% order size 40% 20% 0% 1 2 Control vs Test Group Total revenue gain: $2.6 million dollars 127% 140% 120% 100% Change in total revenue 70% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% 1 2 Control vs Test Group This stuff works! Building a relationship with customers can be highly profitable Using a database to recreate the old family grocer is a winning strategy Business to business relationship marketing is the way to go What is lifetime value? Net present value of the profit to be realized on the average new customer during a given number of years. Lifetime value is “Good Will.” To compute it, you must be able to track customers from year to year. Main use: To evaluate strategy. Lets look at a retail operation Before and after a loyalty program Lets begin with a loyalty building communication Event driven communication: Dear Mr. Hughes: Ridgeway Fashions Leesburg, VA 22069 I would like to remind you that your wife Helena’s birthday is coming up in two weeks on November 5th. We have the perfect gift for her in stock. As you know, she loves Liz Claiborne clothing. We have an absolutely beautiful new suit in blue, her favorite color, in a fourteen, her size, priced at $232.00. If you like, I can gift wrap the suit at no extra charge and deliver it to you next week, so that you will have it in plenty of time for her birthday. Or, I can put it aside so you can come in to pick it up. Please call me at (703) 754-4470 to let me know which you’d prefer. Sincerely yours, Robin Baumgartner Robin Baumgartner, Store Manager LTV Before New Strategies Year 1 40% 200,000 1.4 $50 $14,000,000 Year 2 45% 80,000 1.6 $60 $7,680,000 Year 3 50% 36,000 1.8 $70 $4,536,000 50% Cost Percentage $7,000,000 Costs $6,400,000 Acquisition Cost $32 $13,400,000 Total Costs 49% $3,763,200 48% $2,177,280 $3,763,200 $2,177,280 $600,000 1 $600,000 $600,000 $3.00 $3,916,800 1.12 $3,497,143 $4,097,143 $20.49 $2,358,720 1.32 $1,786,909 $5,884,052 $29.42 Retention Rate Customers Visits Per Year Spending Per Visit Revenue Profit Discount Rate NPV Profit Cum NPV Profie Lifetime Value New Retention Strategies Provide all customers with a card or register their credit cards Birthday Club Communicate with them Give them premiums if they shop a lot Lets see what could happen With New Strategies Retention Rate Customers Visits Per Year Spending Per Visit Revenue Year 1 50% 200,000 1.6 $55 $17,600,000 Year 2 60% 100,000 2 $70 $14,000,000 Year 3 65% 60,000 2.4 $80 $11,520,000 Cost Percentage Costs Acquisition Cost $32 Database Costs Loyalty Program Loyalty Costs Total Costs 50% $8,800,000 $6,400,000 $500,000 $5.00 $1,600,000 $17,300,000 49% $6,860,000 48% $5,529,600 $250,000 $8.00 $1,600,000 $8,710,000 $150,000 $10.00 $1,440,000 $7,119,600 $300,000 1 $300,000 $300,000 $1.50 $5,290,000 1.12 $4,723,214 $5,023,214 $25.12 $4,400,400 1.32 $3,333,636 $8,356,851 $41.78 Profit Discount Rate NPV Profit Cum NPV Profie Lifetime Value Effect of adoption of new strategies Old LTV New LTV Change With 200,000 members Year 1 $3.00 $1.50 -$1.50 -$300,000 Year 2 $20.49 $25.12 $4.63 $926,071 Year 3 $29.42 $41.78 $12.36 $2,472,799 Five Ways to Boost LTV with DB Strategies Increase the retention rate Increase the referral rate Increase the spending rate Decrease the direct costs Decrease the marketing costs Who is going to defect? Besides LTV, you can develop a model that predicts which customers are most likely to leave. Putting that model with LTV you can refocus your entire retention strategy You create a Risk Revenue Matrix Focus on A and B: 44% of your customers. LTV High Medium Low Probability of Leaving Soon High Medium Low Priority A Priority B Priority C Priority B Priority B Priority C Priority C Priority C Priority C AmeriLINK Comprehensive Data on over 230 Million People in the U.S. Compiled on an Individual Level Updated Every 6 Weeks Sources include Drivers License, Voter Registration, multiple purchase transactions, i.e. shopping behavior, Telephone Sources, Children’s Data, Tax Assessor/Property Deeds, Occupational Licenses, Internet Data, Product Registration, Survey Data, Summarized Credit Statistics and Multiple Lifestyle Sources AmeriLINK 58% Mail Order Buyers 34% Multiple Mail Order Buyers 57% Homeowners 65% with Bankcards, 30% with Multiple Bankcards 2000 Census Data Currently Available Quantifiable Verification – 57% Last 12 Months 25% Known On-Line Households AmeriLINK Web Accessible 100 % Exact Age Available 50% Females by First Name 40% Coded with Lifestyle Data from Surveys 100% Coded with Terrestrial Attitudinal Clusters – LWA and MindBase 54% Coded with Internet Behavioral Clusters – Digital Neighborhoods Email Address Coverage on AmeriLink AmeriLink Production Email Coverage 80,000,000 70,000,000 60,000,000 50,000,000 40,000,000 0212 30,000,000 0312 20,000,000 10,000,000 0 Individual Household Online Access Version Individual Household Online Access 0212 7,809,156 23,013,716 55,178,025 0312 21,556,071 45,292,792 75,250,009 Digital Neighborhoods A unique segmentation solution Digital Neighborhoods(SM), a unique segmentation scheme developed jointly by KnowledgeBase Marketing® and its parent company, Wunderman, segments consumers by einvolvement, which measures consumer presence online, relationships with sites and transaction activity. When you understand consumers’ link to the Internet, you can optimize your email marketing efforts by customizing and personalizing your offers and messaging. Digital Neighborhoods Direct Sale Cycle Prudential Agent Step 1 Step 3 Step 2 Pre Qualification Of Prospects Design and Create campaign Email to Prospect or Customer Real Time Reports on Campaign Progress Welcome Arthur to Prudential. To get information on an LTC policy click here. Bob Winslow, Agent Micro-Site Prudential Marketing Staff Step 4 Prizm Cluster Codes 01 Blue Blood Estates 1.18% Elite Privileged Super Rich Families 02 Winner's Circle 2.15% Wealthy Executive Suburban Families 03 Executive Suites 1.32% Affluent Upscale White-Collar Couples 04 Pools & Patios 1.85% Affluent Established Empty Nesters 05 Kids & Cul-de-Sacs 2.93% Affluent Upscale Suburban Families 06 Urban Gold Coast 0.59% Affluent Professional Urban Singles & Couples 07 Money & Brains 1.12% Affluent Sophisticated Townhouse Couples 08 Young Literati 0.94% Upper Middle Upscale Urban Couples & Singles 09 American Dreams 1.40% Upper Middle Established Urban Immigrant Families 10 Bohemian Mix 1.48% Middle Bohemian Singles & Couples 11 Second City Elite 1.89% Affluent Upscale Executive Families 12 Upward Bound 1.83% Upper Middle Young Upscale White-Collar Families More Cluster Codes 13 Gray Power 2.03% Middle Affluent Retirees in Sunset Cities 14 Country Squires 1.33% Wealthy Elite Exurban Families 15 God's Country 2.63% Affluent Executive Exurban Families 16 Big Fish, Small Pond 1.37% Upper Middle Small Town Executive Families 17 Greenbelt Families 1.48% Upper Middle Young Middle-Class Town Families 18 Young Influentials 1.35% Upper Middle Upwardly Mobile Singles & Couples 19 New Empty Nests 2.06% Upper Middle Upscale Suburban Fringe Couples 20 Boomers & Babies 1.11% Upper Middle Young White-Collar Suburban Families 21 Suburban Sprawl 1.50% Middle Young Suburban Townhouse Couples 22 Blue-Chip Blues 1.93% Middle Upscale Blue-Collar Families 23 Upstarts & Seniors 1.28% Middle Middle Income Empty Nesters 24 New Beginnings 1.19% Middle Young Mobile City Singles Gains From Cluster Coding Universe Mailing Responses Response Rate Revenue Mail Cost Cluster Cost Profit Gain 1,005,160 16,083 1.60% $1,222,275 $562,890 $659,385 Good Bad Clusters Clusters 460,445 544,715 14,274 1,809 3.10% 0.33% $1,084,808 $137,466 $257,849 $305,040 $30,155 $796,804 -$167,574 $137,419 Recency Frequency Monetary (RFM) Analysis Used for marketing to customers Always improves response and profits Better than any demographic model The most powerful segmentation method for predicting response How to Apply Recency Codes Put most recent purchase date into every customer record. Sort database by that date - newest to oldest. Divide into five equal parts - quintiles. Assign “5” to top group, “4” next, etc. Put quintile number in customer record. Response Rate Response by Recency Quintile 4.00% 3.50% 3.00% 2.50% 2.00% 1.50% 1.00% 0.50% 0.00% 3.49% 1.25% 1.08% 5 4 0.63% 3 Recency Quintile 2 0.26% 1 How to Compute a Frequency Index Keep number of transactions in customer record Sort recency groups from highest to lowest Divide into five equal groups Number groups from 5 to 1 Put quintile number in customer record Response by Frequency Quintile 2.50% 1.99% 2.00% Response Rate 1.56% 1.50% 1.31% 1.00% 0.92% 0.93% 2 1 0.50% 0.00% 5 4 3 Frequency Quintile How to Compute a Monetary Index Store total dollars purchased in each customer record Sort frequency groups from highest to lowest Divide into 5 equal groups (quintiles) Number quintiles 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 Put quintile number in each record Response by Monetary Quintile 1.80% 1.61% 1.60% 1.45% 1.46% 1.40% 1.22% 1.23% 2 1 1.20% 1.00% 0.80% 0.60% 0.40% 0.20% 0.00% 5 4 3 RFM Code Construction R 5 F 35 4 34 3 33 2 32 31 1 Database One Sort Five Sorts M 335 334 333 332 331 Twentyfive sorts Creating an Nth 300,000 Records Customer Database For Nth by 10, select every tenth record. Nth 30,000 Records Result will be statistical replica of database Result of Test Mailing to 30,000 # 1 2 3 4 5 RFM 555 554 553 552 551 Mailed 240 240 240 240 240 Response 20 16 13 10 11 Rate 8.15% 6.56% 5.62% 4.33% 4.51% 6 7 8 9 10 545 544 543 542 541 240 240 240 240 240 9 12 6 10 7 3.78% 4.98% 2.88% 4.26% 3.10% 11 12 13 14 535 534 533 532 240 240 240 240 10 9 8 6 4.13% 3.83% 3.35% 2.70% Test Response Rate by RFM Cell Index of Response 0 = Break Even 500 400 300 200 100 0 -100 -200 555 455 355 255 111 Test, Full File & RFM Selects Compared Response Rate Responses Net Revenue No. Mailed Mailing Cost Profits Test Full File RFM Select 1.34% 1.17% 2.76% 402 23,412 15,295 $16,080 $936,480 $611,800 30,000 2,001,056 554,182 $16,500 $1,100,581 $304,800 ($420) ($164,101) $307,000 8.00% Test Vs Rollout Response Rates 7.00% 7.00% 6.00% 6.00% 5.00% 5.00% 4.00% 4.00% 3.00% 3.00% 2.00% 2.00% 1.00% 1.00% 0.00% 0.00% 554 553 552 551 545 544 543 542 541 535 534 533 532 531 525 524 523 522 521 515 514 513 512 511 455 451 445 444 443 355 354 351 344 When NOT to Use RFM If you use it all the time, half your customers will never hear from you They will be lost The others will suffer from file fatigue Use it sparingly; When you need a boost Use it to identify your best customers Don’t go hog wild! A few recent case studies Modeling to increase response Auto insurance mailed 1.2MM per mo. Model showed how to pick right HH Total Mailed Cost of Mailing Number of Responses Response Rate Number of Sales Sales Rate Total Revenue Revenue per Sale Profit Return on Promotion Control Group 1,264,571 $547,559 13,366 1.06% 1,599 12.0% $2,605,603 $1,630 $95,896 18% Optimized Group 1,264,571 $547,559 16,090 1.27% 2,323 14.4% $3,158,151 $1,360 $187,851 34% % Change # Change 0% 0 0% 0 20% 2,724 20% 0.22% 45% 724 21% 2.47% 21% $553,208 -17% ($270) 96% $91,955 96% 16.8% Isuzu Post Card Direct To sell their trucks, Isuzu developed 24 different postcards, each with a different case study of truck use such as Gardening, Plumbing, Moving. They set up a web site and used direct mail to get dealers to come to the site and order post cards for prospects developed by Isuzu. Isuzu Results Dealers modeled to determine their likelihood to purchase. The model really worked: Group Companies High Score Medium Score Low Score Control Group Total Totals 1,899 1,855 1,890 520 6,164 Buying 97 32 15 3 144 Buying Rate 5.10% 1.70% 0.80% 0.60% 2.30% Trucks Sold 107 34 16 3 160 HP On Line Survey Hewlett Packard tested an on line survey to promote their network printers. Direct mail drove responders to a web site that contained the survey. Responders received $10 in Pizza Hut coupons. The survey provided a special HP offer for network printing solutions, product links, and e-subscription information. Competitive Advantage Through Advanced Technology Universal Music eMarketing Campaign UMG tested an e-marketing strategy to increase record sales of a new album release for Lucinda Williams The campaign delivered more than a 960% increase to the Lucinda Williams fan base Reached nearly 200,000 fans and prospects with email communications Won DMA Gold Echo Award in 2002 What Works: Email Marketing Where else can you get these results in 3 days? Speech Email Follow Up Results on 3rd Day Delivered Viewed Clicked Do Not Mail 168 131 75 0 Download % Viewed % Clicked % Download 68 78% 45% 40% Get customers to join a club A company sold sporting goods created a member club. When DB was built they learned that: Club members bought 11 times more than non club members. In two years, 81% of club members became multi-buyers. Club members conversion 80.5% 90.0% Conversion to MultiBuyers after two years 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 23.4% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% Goal Club Non Goal Club Cataloger Example Miles Kimball sent 20,000 emails with three different catalogs, and 20,000 with the three catalogs alone. Those who got the emails bought 18% more than those who got the catalogs alone. 118 120 115 110 105 100 100 95 90 Control Test Retailer Example Video retailer sent email newsletters to 170,000 customers for 6 months. Control group of 14,000 got no emails Retail sales to test group was 28% more than to those without emails. 128 140 100 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Control Test Books by Arthur Hughes From McGraw Hill. Order at www.dbmarketing.com Contact Arthur: arthur.hughes@kbm1.com