lab 19 extraction of dna from wisconsin fast plants prelab
advertisement

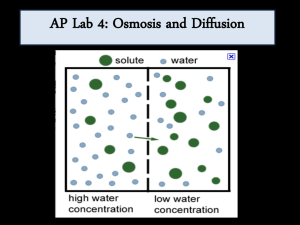
Lab 7: Diffusion and Osmosis Prelab Name: Introduction: Dialysis tubing allows molecules to diffuse through microscopic pores in the tubing. Molecules smaller than the pores can diffuse through the dialysis membrane along their concentration gradients while molecules larger than the pore size are prevented from crossing the dialysis membrane. Go to Biology Place and step through the LabBench Activity on Diffusion. Then answer the questions below. Vocabulary Matching Choose one Choose one Choose one Choose one Choose one Choose one Choose one Choose one 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The net movement of molecules down their concentration gradient. The difference in concentration of solutes in a solution between two regions. Dissolving substance in a solution Substance that is dissolved in a solution Diffusion of water The solution with lower solute concentration The solution with higher solute concentration Two solutions equal in solute concentration Concept 2: Osmosis 9. Water moves from choose oneconcentration of water to a choose one concentration of water. 10. Water moves from choose oneconcentration of solute to a choose one concentration of solute. Concept 3: Movement of Molecules in Solution 11. How will you know whether the iodine solution has crossed the dialysis membrane? Concept 5: Types of Solutions Based on Solute Concentration 12. Will there be a net movement of water between two isotonic solutions? Choose one 13. Water moves from choose one solution to a choose one solution. Concept 6: Water potential 14. Why don’t red blood cells pop in the bloodstream? 15. What happens if an animal cell is placed in distilled water? 16. What happens if a plant cell is placed in distilled water? 17. Why is the outcome different for a plant verses an animal cell? Don’t read Concept 7: Calculating Water Potential or Concept 8: Factors that Affect Water Potential. Exercise 1 18. Which of these substances are expected to pass through the dialysis membrane: Water: choose one IKI: choose one Glucose: choose one Starch: choose one Exercise 2: In the following situations, assume that sucrose cannot diffuse through the dialysis membrane. 19. A dialysis bag containing a 0.20 M solution of sucrose is placed in a beaker of distilled water (the sucrose cannot pass through the membrane). Will the dialysis bag gain or lose mass? choose one Explain why. Exercise 3: Contents of Beaker Initial Mass in grams Final Mass in grams 0.0M 22.0 27.0 0.2M 24.6 26.4 0.4M 23.5 23.2 0.6M 23.7 20.4 0.8M 19.9 15.6 1.0M 21.3 16.2 Percent Change in Mass 3. Calculate the percent change in mass using the equation below and record it in the table above: 𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 − 𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 = 𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 4. Graph the sucrose molarity in the beaker and the percent change in mass of the potatoes using xy scatter plot in Excel. Paste the graph below. 5. At what molarity does the line cross the X axis? 6. What does that number mean?