Kidney Homeostasis
advertisement
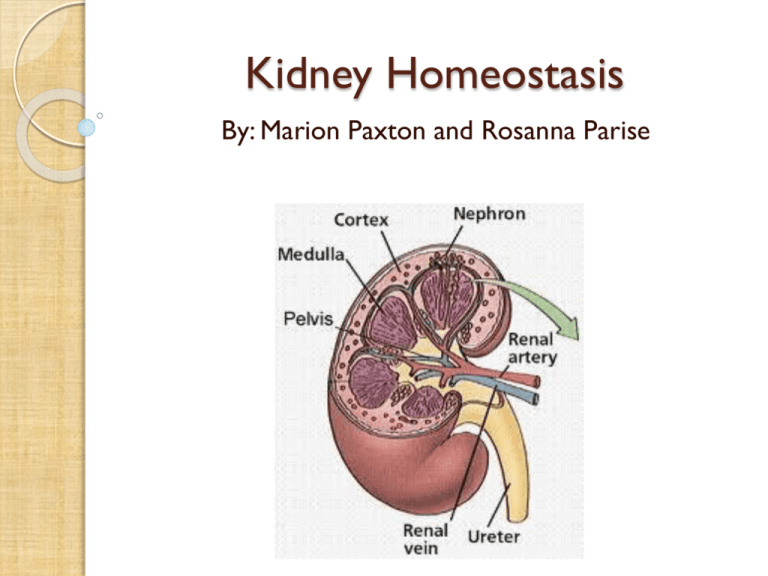
Kidney Homeostasis By: Marion Paxton and Rosanna Parise Lesson Sequence Lesson 1: Kidney Structure and Function Lesson 2: The Nephron: Filtration and Reabsorption Lesson 3: Homeostasis: Feedback Mechanisms Lesson 4: Lab: The Physiological Effects of Coffee Lesson 5: Kidney Transplant Article and Case Study Introduction: The Kidney Main function: to filter the blood to remove waste products and to adjust salt concentrations in the blood Associated with the excretion of cellular wastes (urea, uric acid, creatinine) The Kidney Cont’d Composed of 3 sections: ◦ Outer cortex ◦ Medulla ◦ Inner pelvis Kidney Cont’d In the cortex and medulla, there are about 1,000,000 nephrons – these act as filters and are composed of: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Bowman’s capsule The glomerulus Proximal tubule The loop of Henle Distal tubule Collecting duct Picture of the nephron on next slide The Kidney Nephron The Kidney Cont’d Please go to the following interactive site to learn more about the kidney: http://www.biologymad.com/resources/kidney.swf The Kidney Cont’d Homeostatic mechanisms are in place to control the levels of water and electrolytes in the blood One very important hormone involved in this is called Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Lesson 1: Introduction to the Kidney: Structure and Function KWL Chart – have students fill in KW now and L after lesson 5 (self assessment) Intro Video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qxb2_d9ilEw Group work: ◦ Provide students with basic diagram – have them fill in the name of each structure ◦ Then, they will complete a T chart on the structure and function of the following: kidney, renal veins, renal arteries, urinary bladder, urethra Lesson 2: The Kidney Nephron: Filtration and Re-absorption Lesson 2: The Kidney Nephron: Filtration and Re-absorption Teacher demo on passive transport Youtube video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glu0dzK4dbU Interactive Site: http://www.biologymad.com/resources/kidney.swf • Role play exercise where students are the filtrate and classroom desks are arranged as the nephron • Worksheet: • http://www.biologycorner.com/anatomy/urinary/kidney_coloring.html Lesson 3: Homeostasis: Feedback Mechanisms Lesson 3: Homeostasis: Feedback Mechanisms Quick review of the nephron – quiz Introduce hormone ADH and ADH feedback loop (refer to picture – slide 14) Have students read about this feedback loop in pairs – pg 117 (McGraw Hill Biology 12) Lesson 3: Homeostasis: Feedback Mechanisms Students work in groups to come up with a way to demonstrate the ADH feedback loop to their peers Assign homework questions from textbook – to be taken up next day: Pg 120 Q’s 4-6 Pg 134 Q’s 7, 12 Lesson 4: Lab The Physiological Effects of Coffee For this lab, students will design an experiment that allows them to investigate one physiological effect of consuming coffee (e.g. Effects on blood pressure, urine output, etc.) Refer to Word document for a more detailed description of this lab Lesson 4 Lab: Safety Considerations It may not be appropriate for some students to participate as subjects in the Physiological Effects of Coffee Lab due to health concerns As students design their experiments, be sure to consult with each group to make sure that they don’t exceed their coffee intake Lesson 5: Kidney Transplant Article and Case Study Students use an anticipation guide to read an article about kidney transplants in Canada. 4 corners strategy used to discuss opinions A class debate about steroid use and kidney disease in body builders will follow. Refer to the following article: http://www.nytimes.com/2009/12/10/sports/10stero ids.html?_r=1&scp=2&sq=steroids&st=cse Peer and self assessment Assessment and Evaluation Lesson 1: KWL Chart – diagnostic and form of self assessment Lesson 2: Nephron Worksheet Lesson 3: Group presentations and textbook questions Lesson 4: Lab Report Lesson 5: Anticipation guide; peer and selfassessment Student Difficulties Difficulty: ◦ Students may have difficulty understanding how and why different substances enter and leave the kidney tubule. Rectification ◦ Have students watch the youtube video on the function of the nephron and allow students to use the interactive website to see where different substances enter and leave the nephron. ◦ Youtube video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glu0dzK4dbU ◦ Interactive website: http://www.biologymad.com/resources/kidney.swf **Note: Refer to summary handout for other rectifications.** Student Difficulties cont’d Difficulty: ◦ Some students may have trouble understanding the feedback mechanism involved in controlling urine output. Rectification ◦ Use a flow chart to help students visualize the feedback mechanism. ◦ Group weaker students with stronger students during the problem solving activity. Demonstration Passive Transport Lab ◦ Students will observe passive transport of a substance across a membrane Practical Applications Effects of steroid use on kidney functioning Kidney transplants, dialysis and organ harvesting Effects of alcohol and caffeine on kidney homeostasis Chronic renal diseases Resources Please refer to our summary for a list of the resources used to create this presentation Thank you for being a part of our presentation!








