Chapter 1: Role of Government
advertisement

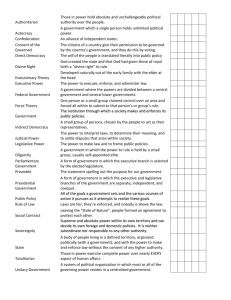
Bueller Anyone, anyone? Cheers--Albania with Coach and Sam Chapter 1: Role of Government Government: an institution with the power to make and enforce rules and regulations for a group of people Rules apply to everyone with the political unit (state) Sovereignty: the exclusive right of an independent state to reign supreme and base absolute power over a geographic region and its people Laws: rules created or recognized by government Public policy: what government decides to do or not do; government laws, rules, or expenditures In past—kings and queens receive power from God Legitimacy: rightful authority any government has over its citizens 1600’s: Thomas Hobbes’ social contract People give up individual sovereignty to the state; in exchange, the state provides peace and order John Locke: government gets its power from the people Natural rights: government should protect natural rights of people; if not, people should revolt OR Basic rights the government can not deny Video • Enforce laws that protect safety and security of people and property • Protect people from unfair business practice 1. • Hiring/firing laws based of race, gender, religion Maintaining • Regulate commerce and trade order • Protect from foreign invasion • Build roads • Inspects food and medicine • Mail 2. Providing • Assists needy services • Builds schools 3. Resolving conflict • politics: the process by which people participating in gov. express opinions about what gov. should or should not do • court system • values: basic principles by which people act and live their lives 4. Promoting • gov. helps promote values by passing laws and setting policies Values • the public interest or the well-being of society as a whole • good gov. pursues policies for the good of the people 5. The Public • what is the common good??? All people have different views and gov. tries to figure it out Good Section 2: Forms of Government Monarchies Theocracies Forms of Government Dictatorships Democracies Form of Definition Government Source of Authority Monarchy a. Absolute: King/queen has absolute power b. Constitutional: King/queen power limited by a Constitution Birth/Passed down Democracy a. 1. 2. 3. Presidential: Executive and legislative branches are separate of each other Chief executive is the president Executive and legislative branches are chosen in separate elections The people /elections b. 1. 2. Parliamentary: Chief executive is prime minister Executive is chose by the legislative branch (parliament) Dictatorship Theocracy Power is with 1 or a small group of people Political power in hands of religious leader Force/secret police/no rights to the people Religion CIA World Factbook Unitary System central gov. holds all power local gov. has no power Federal System National, state, and local gov. share powers Confederate System Each state is represented in a central organization Central gov. carries out policies made by reps Section 3: Democracy Direct democracy Laws are made directly by all citizens Representative democracy People elect representatives to make decisions US gov is representative democracy 1. Allowing Choice • Free Elections • Free Speech 2. Recognizing Individual Worth • All citizens are valued • People have opportunity to succeed or fail 3. Promote Respect for Law • If citizens participate in gov, they will respect the laws • Citizens can challenge the fairness of a law 4. Protecting Minority Rights • Majority rules • Minority rights are respected 5. Promoting the Public Good • If all citizens participate, decisions will be made to promote the public good