Kevin SigRist - Florida Government Finance Officers Association
advertisement

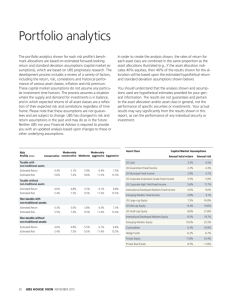
State Board of Administration FRS Pension Plan Risk Management and Asset Allocation FGFOA Meeting May 8, 2012 INVESTING FOR FLORIDA’S FUTURE Presentation Outline • SBA Overview • SBA Enterprise Risk Management • FRS Pension Plan Case Study – Pension Finance – Asset Liability Modeling – Asset Allocation – Implementation and Business Model • Other Management Considerations 2 3 SBA Funds Under Management April 23, 2012 Estimates 4 SBA’s Strategic Risks 1. Investment Management Risk 2. Governance/Management Risk 3. Communication/Public Affairs/Reputational Risk 4. Legislative/Political Risk 5. Compliance Risk 6. Fraud/ Misconduct/ Internal Controls Risk 7. Service Provider Risk 8. Client Relationship Risk 9. Operational Risk 10. Human Capital Risk 11. Security Risk 12. Business Continuity/Infrastructure Risk 13. Legal Risk 5 SBA Risk Management and Compliance Residual Risk Assessment - Aggregated Strategic Risk Level As of 6/30/11 4Highly Likely 3 - Likely 10 4 12. Business Continu 3 2Unlikely 1 13. Legal Risk 2 13 7 9 5 8 11 12 6 1 - Highly Unlikely 1 - Minor 6 2 - Moderate 1. Investment Mana 2. Governance/Mana 3. Communication/P 4. Legislative/Politic 5. Compliance Risk 6. Fraud/ Misconduc 7. Service Provider R 8. Client Relationship 9. Operational Risk 10. Human Capital R 11. Security Risk 3 - Major SBA Investment Risk Components – Policy Risk • • • • – Implementation Risk • • • • • • • • – Policy Design Risk Investment Objective Risk Capital Market Assumption Risk Liability Risk Strategy Risk Portfolio Under Performance Risk Trading Risk Asset Transition Risk Model Risk Due Diligence Risk Leverage Risk Aggregate Issuer/Counterparty Credit Risk Inherent Risk • • Market/Systematic Risk Idiosyncratic/Unsystematic Risk 7 FRS Pension Plan Case Study • Pension Finance • Asset Liability Modeling • Asset Allocation • Implementation and Business Model 8 Millions of 2011 $ Pension Obligations – Future Benefit Cash Flows D C2 B C1 A A = benefits for current retirees B = benefits already accrued/earned for current employees C1+C2 = benefits yet to be earned for current employees (C1 = portion allocated by actuarial method for past service) D = benefits for future employees 9 FRS Pension Plan Investment Policy Objective – … provide investment returns sufficient for the plan to be maintained in a manner that ensures the timely payment of promised benefits to current and future participants and keeps the plan cost at a reasonable level. – To achieve this, a long-term real return approximating 5% per annum (compounded and net of investment expenses) should be attained, consistent with the actuarial investment return assumption of 7.75%. – As additional considerations, the Board seeks to avoid excessive risk in long-term cost trends. – To manage these risks, the volatility of annual returns should be reasonably controlled. 10 Structure Of Asset-Liability Model Economic Simulation Asset Returns Interest Rates Inflation Actuarial Assump. Asset Growth Asset Smoothing Actuarial Methods Plan Cost & Funded Status 11 Liability Growth U.S. Equity Return • For the 2012 asset liability update we used an equity risk premium assumption equal to 4.36%, the average of the assumptions used by the four SBA investment consultants. The resulting expected average compounded return for U.S. equities is equal to 7.4% (the U.S. bond expected return of 3.0% plus the equity risk premium of 4.4%): Price inflation US bond returns Risk premium for US equities HEK Callan Wilshire Mercer Average US equity returns 2010 AL Study 2011 AL Update 2012 AL Update 2.40% 4.60% 2.15% 4.20% 2.10% 3.00% 2.40% 4.00% 3.25% 3.80% 3.36% 7.96% 3.60% 4.25% 3.50% 3.80% 3.79% 7.99% 4.50% 4.50% 4.65% 3.80% 4.36% 7.36% All returns are 15-year geometric average expected returns. 12 FRS Pension Plan Return & Risk Assumptions --- Expected Average Return --Current Policy Targets* Compounded Single Year Standard Deviation Global Equity 52% 8.5% 10.6% 20.8% Private Equity 5% 9.2% 13.2% 28.3% Real Estate 7% 7.1% 8.4% 16.3% Debt-oriented 3% 9.5% 10.1% 10.5% HF - Absolute Return 2% 5.8% 6.3% 9.3% HF - Equity Long/Short 2% 7.7% 8.4% 11.5% HF - Open Mandate 2% 7.3% 7.8% 10.6% Infrastructure 2% 8.5% 10.2% 18.3% 24% 3.0% 3.1% 3.5% 1% 2.2% 2.2% 1.3% Risk Assets Strategic US Bonds Cash Inflation Fixed Income 2.1% Total Portfolio Gross Expenses Net - Nominal Return Net - Real Return 7.5% 8.4% 0.14% 0.14% 7.4% 5.3% 8.3% 13.0% * Allocation targets based on "Expanded Authority" 13 policy, with typical diversification within the "Strategic" class Range of Possible 15-Year Compound Returns -Nominal Percentile: 95th 7.75% actuarial assump. ( 50% probability ) 75th 50th 50% confidence range: from 4.7% to 10.5% 50th %-tile = 7.8% (median value) Best estimate = 7.4% (mean value) 25th 5th 14 90% confidence range: from -0.1% to 13.8% Range of Funded Ratios – Current Asset Allocation Policy 220% 212% 200% 180% 160% 153% 140% 120% 100% 94% 86% 87% 80% 87% 87% 61% 60% Trend line 40% 32% 24% 20% 0% FY12 FY13 FY14 FY15 FY16 FY17 FY18 FY19 FY20 FY21 FY22 FY23 FY24 FY25 FY26 FY27 84% 85% 86% 87% 87% 70% 84% 86% 87% 90% 61% 82% 86% 89% 94% 53% 80% 87% 91% 100% 44% 76% 86% 92% 104% 40% 72% 86% 95% 111% 38% 69% 86% 99% 121% 37% 67% 86% 101% 132% 33% 66% 87% 104% 142% 32% 63% 87% 107% 153% 30% 61% 87% 110% 161% 27% 59% 87% 116% 172% 25% 58% 86% 119% 183% 25% 56% 88% 122% 196% 24% 54% 87% 127% 212% %-tile values: 5% 25% 50% 75% 95% 87% 87% 87% 87% 87% Dark shaded area indicates the 50% probability zone, and light shaded area indicates the 90% probability zone. 15 Range of Employer Contribution Rates (DB Plan Only) – Current Asset Allocation Policy 35% 30.9% 30% 28.0% 25% Trend line 20% 15% 14.6% 10% 5% 10.3% 9.9% 9.3% 7.9% 4.1% 0% FY12 0.0% 0.0% FY13 FY14 FY15 FY16 FY17 FY18 FY19 FY20 FY21 FY22 FY23 FY24 FY25 FY26 FY27 8.7% 8.7% 8.7% 8.7% 8.7% 8.6% 9.0% 9.2% 9.4% 9.9% 7.9% 8.8% 9.3% 9.9% 14.6% 6.9% 8.6% 9.7% 11.0% 18.5% 4.7% 7.6% 9.3% 11.5% 21.2% 4.7% 7.5% 9.8% 13.1% 23.8% 1.3% 6.6% 9.7% 14.3% 25.6% 0.0% 5.6% 9.9% 15.7% 26.5% 0.0% 4.7% 10.0% 16.4% 27.1% 0.0% 4.7% 9.9% 16.8% 28.0% 0.0% 3.8% 9.8% 17.7% 28.8% 0.0% 2.5% 9.9% 18.6% 29.9% 0.0% 0.0% 10.0% 19.3% 30.2% 0.0% 0.0% 10.5% 19.6% 30.7% 0.0% 0.0% 10.3% 20.2% 30.9% %-tile values: 5% 25% 50% 75% 95% 4.1% 4.1% 4.1% 4.1% 4.1% Dark shaded area indicates the 50% probability zone, and light shaded area indicates the 90% probability zone. 16 Risk / Reward Analysis Based On Long-Term Economic Cost Lower cost Current Mix Less risk $0 -$5,000 More risk Diagonal line = 3-to-1 risk/reward benchmark Higher cost Avg. Cost Savings ($MM) (All 500 scenarios) $5,000 -$10,000 -$15,000 -$20,000 -$60,000 -$45,000 -$30,000 -$15,000 Avg. Risk Increase ($MM) (Worst 100 scenarios) Change in cost relative to values using current mix 17 $0 $15,000 2011 Asset Liability Update: Diversification Impact Diversification changes can improve the results. Avg. Cost Savings ($MM) (All 1,000 scenarios) The Recommended policy offers long-term cost savings of $2.3 billion, with no material change in risk profile Recommended Policy (with diversification) Increased diversification shifts curve in favorable direction June 2010 Policy (before diversification) Avg. Risk Increase ($MM) (Worst 200 scenarios) 18 Investment Policy Themes: Enhancing diversification and taking risk more efficiently • Maintain or reduce the overall level of investment risk in the fund – Reduction in the fund’s overall exposure to global stock markets – Decrease in the fund’s use of active management in the public stock and bond markets • Further increase diversification of investments – Greater global diversification within the publicly traded stock investments – Greater diversification into a broader array of investment types (i.e. alternative investments) that do not necessarily fluctuate with stock markets • Increase flexibility to take investment risks more efficiently – Downside protection from volatile markets through bond investments – Participate in worldwide economic growth through stock investments – Generate above market returns, with strong risk controls, through skillful opportunistic investing 19 FRS Pension Plan Asset Allocation Policies Asset Class Pre-July 2010 Policy Current Policy Expanded Authority Policy Global Equity 58% 56% 52% Fixed Income 28 26 24 High Yield Fixed Income 2 – – Real Estate 7 7 7 Private Equity 4 4 5 Strategic Investments – 6 11 Cash 1 1 1 Total 100% 100% 100% *Prior to July 2010, Global Equity was composed of two asset classes, Domestic Equities and Foreign Equities, with target allocations of 38% and 20%, respectively. ** Global Equity asset class includes existing Domestic Equity, Foreign Equity and Global Equity mandates; Strategic Investments includes existing High Yield allocation. *** In recognition of the dynamic nature of this asset class, there is no specific expected weight. Its actual allocation will vary within the policy range depending on the mix of included strategies at any given time. When the actual allocation of Strategic Investments is greater than zero, all other asset class target allocations shall be reduced pro-rata. 20 Strategic Investments Detail Asset Category Recommended (% of Total Fund) Debt-Oriented Funds 3.0% Infrastructure 2.0 Absolute Return Hedge Funds 2.0 Long/Short Equity Hedge Funds 2.0 Open Mandate Hedge Funds 2.0 Commodities -- Timberland -- Total Strategic Investments 11.0% Allocations reflect current expectations for future allocations in Strategic Investments for modeling purposes. Actual allocations, including possible investments in commodities and timberland, will vary dependent on identification of attractive opportunities. 21 FRS Pension Plan Cumulative Performance History Fiscal Years 1976 Through 2011 2000% 1500% Cumulative Net Return on FRS Pension Plan Assets 1000% Actuarial Return Assumption (currently 7.75%) 500% 0% 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 Fiscal Year Ending June 30 Returns are net of investment manager fees for periods after December 1984. 22 FRS Pension Plan Net Managed and Target Returns 18% Managed 16% 7.98% 8.24% 3.15% 3.80% 4% 2.63% 2.93% 6% 5.62% 5.92% 6.68% 8.16% 8.55% 10.40% 8.46% 7.04% 8% 7.60% 10% 8.29% Target 14% 12% 15.87% 16.51% As of March 31, 2012 2% 0% 3 Months 1 Year 3 Years 5 Years 10 Years 15 Years 20 Years 25 Years 30 Years 23 FRS Results Relative to TUCS Top Ten Defined Benefit Plans Periods Ending 12/31/2011 Total FRS (Gross) Top Ten Median Defined Benefit Plan Fund (Gross) 15.0 11.2 11.0 10.0 Rate of Return (%) 5.0 4.5 5.4 5.5 3.9 2.8 2.0 2.2 0.0 -0.3 -5.0 -10.0 -15.0 Quarter 1-Year 3-Year 5-Year Note: The TUCS Top Ten Universe includes $1.1 trillion in total assets. The median fund size was $112.5 billion and the average fund size was $109.7 billion. 24 10-Year Comparison of Asset Allocation As of 12/31/2011 FRS Pension Plan vs. Top Ten Defined Benefit Plans FRS TOTAL FUND Strategic Investments 4.1% TUCS Top Ten Cash 2.1% Cash 0.7% Private Equity 4.9% Alternatives 17.6% Real Estate 7.4% Real Estate 6.3% Global Equity* Global Equity** 46.8% 56.9% Fixed Income 26.0% Fixed Income 27.3% **Global Equity Allocation: 28.9% Domestic Equities; 17.9% Foreign Equities. *Global Equity Allocation: 25.5% Domestic Equities; 28.7% Foreign Equities; 2.8% Global Equities. Percentages are of the Total FRS Fund. Note: The TUCS Top Ten Universe includes $1.1 trillion in total assets. The median fund size was $112.5 billion and the average fund size was $109.7 billion. 25 Hedge Fund Return and Risk Attributes Outperformance Lower Risk Growth of a Dollar Jan 1994 – Dec 2010 Annualized Volatility Jan 1994- Dec 2010 5.0 25% 4.5 4.0 20% 3.5 15% 3.0 2.5 10% 2.0 1.5 5% 1.0 0% 0.5 DJ/CS Hedge Fund Index HFR Fund Weighted Composite S&P 500 Index Dec-10 Dec-09 Dec-08 Dec-07 Dec-06 Dec-05 Dec-04 Dec-03 Dec-02 Dec-01 Dec-00 Dec-99 Dec-98 Dec-97 Dec-96 Dec-95 Dec-94 Dec-93 0.0 Tbill 26 HFR Fund Weighted Index Dow Jones U.S Total Stock Market Index S&P 500 Index MSCI All Country World Index Barclays Aggregate Bond Index Goldman Sachs Commodity Index FRS Pension Plan Cost Comparison to CEM Peer Group 60.0 Cost in Basis Points 50.0 40.0 SBA Total Costs Peer Group Median Total Costs 30.0 20.0 10.0 0.0 2005 2006 2007 2008 Calendar Year 2009 2010 Cost Effectiveness Measurement (“CEM”) maintains a global database of detailed cost information provided by public and corporate pension plans. The SBA’s 2010 CEM Peer Group included 16 U.S. plan sponsors with assets from $22.5 billion to $225.6 billion. 27 27 High Level Investment Guidelines • Public market asset classes shall be well diversified with respect to their benchmarks and have a reliance on low cost passive strategies scaled according to the degree of efficiency in underlying securities markets, capacity in effective active strategies, and ongoing total fund liquidity requirements. • Private Equity, Real Estate and Strategic Investments asset classes shall utilize a prudent process to maximize long-term access to attractive riskadjusted investment opportunities through use of business partners with appropriate: – – – – Financial, operational and investment expertise and resources; Alignment of interests; Transparency and repeatability of investment process; and Controls on leverage. 28 FRS Pension Plan Asset Class Allocations February 2012 29 FRS Pension Plan Active Risk Budget Monitoring Standards Active Risk Active Share Monitoring Standard Current Market Standard Tactical Asset Allocation 0.20% 0.40% -- Global Equity 1.00% 1.50% [40%, 60%]* Fixed Income 0.75% 1.25% [25%, 75%] Real Estate 5.00% 8.00% -- Private Equity (secondary benchmark) 6.00% 10.00% -- Strategic Investments 4.00% 6.00% -- Cash 0.10% 0.20% -- Total Fund 1.00% 1.50% TAA/ Asset Class 30 31 32 Looking Forward: 2012 FRS Pension Plan Asset Liability Update • Supports continuation of the current multi-year implementation of increased allocations to real estate, private equity, and strategic investments, but identifies changes to be considered – Conflicting indicators on best portfolio risk target – some supporting an increase in risk and some supporting a decrease in risk – Growing importance of liquidity management over intermediate-term – Re-emphasizes the value of diversification • The funding policy has a direct impact on some of the investment policy risk-reward analysis – – – – Deferring actuarially recommended contributions (“UAL”) Treatment of 2011 benefit changes Actuarial assumptions Amortization and other actuarial cost methods 33