3.3.2 Nuclear Energy
advertisement

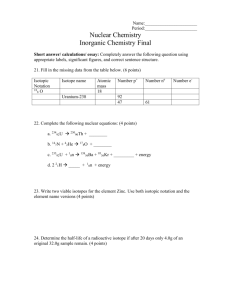
Electricity Production by Fuel 9% Coal Hydroelectric Power Other 23% 56% Nuclear 3% 9% U.S. Department of Energy, Annual Energy Review 1999 Natural Gass Fig 1: Nuclear Reactors in the World Source : AIEA By the end of 2002: 30 countries 441 reactors 16% of electricity production 7% of primary energy 4 Radioactivity • Types • Alpha particles consist of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, and therefore are positively charged • Beta particles are negatively charged (electrons) • Gamma rays have no mass or charge, but are a form of electromagnetic radiation (similar to X-rays) • Sources of natural radiation • • • • • Soil Rocks Air Water Cosmic rays www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt Radioactivity • Radioactivity: Nuclear changes in which unstable (radioactive) isotopes emit particles & energy • Radioactive decay continues until the the original isotope is changed into a stable isotope that is not radioactive www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt Relative Doses from Radiation Sources cstl-cst.semo.edu/bornstein/BS105/ Energy%20Use%20-%203.ppt Effects of Radiation • Genetic damages: from mutations that alter genes • Genetic defects can become apparent in the next generation • Somatic damages: to tissue, such as burns, miscarriages & cancers www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt www.geology.fau.edu/course_info/fall02/ EVR3019/Nuclear_Waste.ppt Half-Life The time needed for one-half of the nuclei in a radioisotope to decay and emit their radiation to form a different isotope Uranium 235 Plutonium 239 Half-time 710 million yrs 24,000 yrs emitted alpha, gamma alpha, gamma During operation, nuclear power plants produce radioactive wastes, including some that remain dangerous for tens of thousands of years www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt Destructive power: [1] Small towns have been leveled by floods and landslides. [2] The same size town could be leveled by 1,000 tons of chemical explosives. [3] Hiroshima (quarter of a million people) was destroyed by releasing the energy in 40 kg of Uranium We know the least about the strong nuclear force. 1945 first large scale use atomic bombs were used by the US to knock Japan out of WWII since then attention has been given to the peaceful uses of atomic energy In a conventional nuclear power plant a controlled nuclear fission chain reaction heats water produce high-pressure steam that turns turbines generates electricity. www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt approximately 20,000 times as much heat and energy is released from uranium fuels as from an equivalent amount of coal when a sufficient amount of fissionable material is brought together, a chain reaction occurs splitting atoms and releasing a tremendous amount of heat Nuclear Fission Controlled Fission Chain Reaction neutrons split the nuclei of atoms such as Uranium or Plutonium release energy (heat) www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt Fusion and Fission are governed by the nuclear strong force. Fusion: two nuclei stick together (or fuse) to form a new, larger nucleus Two separate nuclei One new nucleus Fission: When a single nucleus splits to form two smaller nuclei. Large nucleus Two smaller nuclei Controlled Nuclear Fission Reaction cstl-cst.semo.edu/bornstein/BS105/ Energy%20Use%20-%203.ppt Under appropriate operating conditions, the neutrons given off by fission reactions can "breed" more fuel, from otherwise nonfissionable isotopes, than they consume www.geology.fau.edu/course_info/fall02/ EVR3019/Nuclear_Waste.ppt Fusion is combining together the atoms are fused together rather than split apart possibilities for nuclear fusion are much greater than those for nuclear fission Imagine putting a hydrogen nucleus together instead of pulling it apart. We normally write this in a special way: n + p neutron n proton + 2 H 1 Hydrogen nucleus p This reads: a neutron and a proton fuse together to form a hydrogen nucleus. n + p n + More energy 2 H 1 p Less energy Where did the excess energy from the left-hand-side go? There must be energy released in this process!! It comes in the form of Radiant and Thermal energy Nuclear (fusion) Energy Thermal + Radiant Energy fusion reactors would be fueled by deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen available in almost unlimited supply in sea water Problems: process is so difficult to control that it is questionable whether commercial adaptation will ever be economically feasible fusion requires extreme pressure and temperatures (as high as 100 million degrees) such heat was achieved by the Hydrogen bomb by first setting off a fission explosion Concerns about the safety, cost, and liability have slowed the growth of the nuclear power industry Accidents at Chernobyl and Three Mile Island showed that a partial or complete meltdown is possible Chernobyl • April 26, 1986, reactor explosion (Ukraine) flung radioactive debris into atmosphere • Health ministry reported 3,576 deaths • Green Peace estimates32,000 deaths; • About 400,000 people were forced to leave their homes • ~160,000 sq km (62,00 sq mi) contaminated • > Half million people exposed to dangerous levels of radioactivity • Cost of incident > $358 billion www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt Three Mile Island • March 29, 1979, a reactor near Harrisburg, PA lost coolant water because of mechanical and human errors and suffered a partial meltdown • 50,000 people evacuated & another 50,000 fled area • Unknown amounts of radioactive materials released • Partial cleanup & damages cost $1.2 billion • Released radiation increased cancer rates. www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt evacuation of preschool children and pregnant women within five miles of the plant Photos from : The Yucca Mountain Project: http://www.ymp.gov / Radioactive Waste 1. Low-level radiation (Gives of low amount of radiation) • Sources: nuclear power plants, hospitals & universities • 1940 – 1970 most was dumped into the ocean • Today deposit into landfills 2. High-level radiation (Gives of large amount of radiation) • Fuel rods from nuclear power plants • Half-time of Plutonium 239 is 24000 years • No agreement about a safe method of storage www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt Radioactive Waste 1. Bury it deep underground. • Problems: i.e. earthquake, groundwater… 2. Shoot it into space or into the sun. • Problems: costs, accident would affect large area. 3. Bury it under the Antarctic ice sheet. • Problems: long-term stability of ice is not known, global warming 4. Most likely plan for the US • Bury it into Yucca Mountain in desert of Nevada • Cost of over $ 50 billion • 160 miles from Las Vegas • Transportation across the country via train & truck www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt Yucca Mountain www.geology.fau.edu/course_info/fall02/ EVR3019/Nuclear_Waste.ppt www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.ppt “The odds of an American dying from a nuclear power accident are 300 million to one.” Electricity Electricity & H2 Long-Term Nuclear Energy Depends on an Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle Multiple Nuclear Reactors Reactor Fuel Fabrication Interim Storage Recycle Reprocessing Recycling TRU In Adv. Reactor Enrichment Conversion Uranium Extraction Fissile Resources Encapsulation High Level Waste Fissile Waste 235U/233U/239Pu Intermediate/Low Level Waste Waste Disposal Spent Fuel The Nuclear Fuel Cycle including High level vs. low level Nuclear Waste