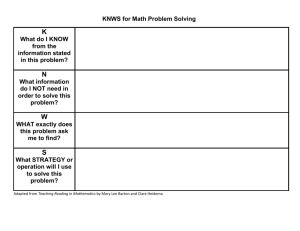
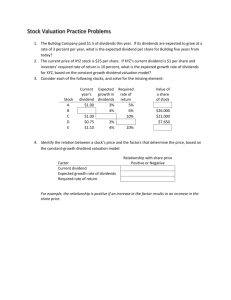
Notes for Chapter 7 (Stocks
advertisement

Stock Valuation Chapter Seven Remaining Topics • Where now – Stock Valuation (Intrinsic and Relative) – Capital Budgeting Tools (NPV, IRR, Payback, etc.) – Capital Budgeting problems with Excel – Return Risk and Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) • This Chapter (Stock Valuation) – What are stocks and why should we care – Stock Book Value vs. Market Value – Intrinsic value price vs. actual market price • Dividend Discount Model of Intrinsic Valuation – Relative Valuation Metrics Barton College 1 Stock Returns • The returns on a stock over one period (Rt) can be divided into capital gains and dividend returns: Pt Pt 1 Dt Rt Pt 1 Pt 1 Pt = stock price at time t Dt = dividends paid over time t – 1 to t (Pt – Pt – 1) / Pt – 1 = capital gain over time t – 1 to t Dt / Pt – 1 = return from dividends paid over time t – 1 to t Suppose an investor buys 10 shares of stock priced at $55.10 and sells the stock one year later for $56.30 after collecting a $0.30 dividend per share. What was the investor’s pre-tax holding period return? Barton College HPR $56.30 $55.10 $0.30 2.18% .54% 2.72% $55.10 $55.10 2 Common Stock • Common stock is the fundamental ownership claim in a public or private corporation • Dividends are discretionary and are thus not guaranteed • Must own before ex-dividend date. • Common stockholders have the lowest priority claim in the event of bankruptcy (i.e., a residual claim) • Limited liability implies that common stockholders can lose no more than their original investment • Common stockholders control the firm’s activities indirectly by exercising their voting rights in the election of the board of directors Barton College 8-3 3 Stock Price Predictions…… Barton College 4 Market WSJ: TODAY'S MARKETS Updated November 8, 2012, 12:52 p.m. ET Stocks edged lower, a day after their steepest tumble in a year for the Dow industrials, as worries about U.S. politicians' ability to strike a budget deal outweighed firm labor-market and export data. Barton College 5 AB InBev, SABMiller Formalize $108 Billion Deal SABMiller agrees to sell stake in MillerCoors to Molson Coors Brewing Barton College 6 Today 3-3-15… In Stocks News drives stock prices Barton College 7 Lumber Liquidators (LL) Today… Barton College 8 LL 3-Year Price Movement Barton College 9 LL Fundamentals look good Barton College 10 Today’s Market “Carpet” 11-11-15 Barton College 11 NYSE Trading Floor Barton College 8-1212 Simple Facts about a Company’s Stock…. Cont… • Stable, sound balance sheets & Income statements typically see less volatile stock price swings. – Consumer Staples: McDonalds (MCD) & Proctor & Gamble (PG) – Earnings sensitive industries generally see more volatile price swings • • Caterpillar (CAT) ---- Sensitive economic data, Capital intensive McDonalds (MCD) and P&G ---- Less sensitive to economic data • In the short run (under a year) stock prices (market) can deviate from it’s true “intrinsic price” • Prices are influenced by macroeconomic data and microeconomic or firm data, .e.g., earnings, company news, etc. Barton College 13 Simple Facts about a Company’s Stock…. • Short term price action is dictated by market “news” surrounding the particular company. NETFLIX (NFLX) Separate DVD from Streaming. P/E = 85 Larger than expected loss of customers ~ 1M 23% better than expected earnings. P/E = 20 Volume of Shares traded… Think Supply & Demand Barton College ~ 66% drop in market price 14 Blue Chips (DOW) Caterpillar (CAT) Industrial Sector Price: $115-$70 ~ 40% move Barton College Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) Health Care Sector ~ %5 – 10% 15 Small Capitalization (S-CAP) Applied Micro (AMCC) Semiconductors Barton College AFFYMAX INC COM (BIO Tech Company) 16 Book Topics • Common Stock Valuation – Dividend Growth Model • • • No Growth Constant Growth Non-constant Growth • Some Features of Common and Preferred Stocks • Fundamental Analysis vs. Technical Analysis – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kpMJEBMUWo4 • The Stock Markets – How does the market for stocks work – Exchanges – Etc.. Barton College 17 Main Formulas for Stocks (Dividend Discount Model) Table 7.1 Page 217 Barton College 18 Characteristics of Common Stock • Common Stock can last for ever • No maturity date as with bonds • You can still loose all of you investment however, e.g., Bear Sterns Example • Factors that affect Stock Prices – Firm Specific Unsystematic: Earnings, growth rates, cost of capital (WACC) – Market Specific Systematic: competition, geo-political, Economic, market interest rates • These variables are captured in the firms financial statements and through stock valuation metrics Barton College 19 More on Stock Price Movers • Almost everything…. can impact or not impact the price…. • Earnings Events or Outside impacts to Earnings – Earnings growth rates or changes in growth rates – Positive or negative impacts to future earnings • M & A, disasters, product launches, financial leverage (gearing), CEO comments, • Sector sell-offs, tactical reallocation, Hedge fund redemptions, • Macro-economic indicators (GDP, unemployment), interest rates, firmspecific indicators. • Liquidity of the stock (velocity of change ….) – Microsoft is more liquid than Fuqi – Fuqi vs. MS or Google • Basically, any type of fear and uncertainty can cause prices to change (short term events…… or noise) • Eventually, prices will regress to their intrinsic value however Barton College 20 S & P 500 moving towards historical P/E Ratios Historical (median) P/E Ratio close to 15 Barton College 21 PE Ratio and Dividend Yield Barton College 22 Historical P/E (S&P 500) and Interest Rates Barton College 23 Cash Flow Model (Intrinsic Value…) Cash Flow to Creditors The cash flow identity Cash Flow from Assets = Cash flow to creditors + Cash flow to owners Cash flow to creditors = Interest – net new debt = Interest – (Ending LTD – Beg LTD) 1. Cash Flow of Assets (Firm) Cash flow from Assets = OCF – NCS – change NWC Cash Flow to Stockholders (owners) OCF = EBIT + Depreciation – tax Cash to owners = Dividends – net new equity (includes common stock and paid in capital) NCS = Ending NFA – Beg NFA + Depreciation Change NWC = Ending NWC – Beg NWC Retained Earnings Plowback $ OCF – change NWC True Cash Flow From Operations Barton College $ Assets (Firm) $ NCS Creditors CFFA (Free Cash Flow) Investments & Other non-operating Income Stockholders (Owners) 24 Industry Lifecycle Barton College 25 The Crossover Point Applied Material, Chipotle or Allergan Barton College P0 D 0 (1 g) D1 R -g R -g Apple ATT, Johnson & Johnson, P&G, Colgate, PepsiCo, YUM Kodak 26 Cash Flows for Stockholders • If you buy a share of stock, you can receive cash in two ways – The company pays dividends – You sell your shares, either to another investor in the market or through a buy-back of shares by the company • As with bonds, the price of the stock is the present value of these expected cash flows • Cash flow from Stock Dividends & capital appreciation of stock P0 = D1/(1+r)1 + D2/(1+r)2 + …Dt/(1+r)t + (Pt)/(1+r)t Where D1, D2, Dn are dividend cash flows, t = number of periods and r = discount rate. Pt = future value of stock at period t. Barton College 27 Developing The Model • You could continue to push back when you would sell the stock • You would find that the price of the stock is really just the present value of all expected future dividends • So, how can we estimate all future dividend payments? • There are basically three different models for valuing stocks…. Barton College 28 Estimating Dividends: Special Cases • Constant dividend (No Growth..) – The firm will pay a constant dividend forever – This is like preferred stock – The price is computed using the perpetuity formula • Constant dividend growth – The firm will increase the dividend by a constant percent every period – Diversified company with constant and steady increases in profit: Proctor and Gamble • Supernormal (non-constant) growth – Dividend growth is not consistent initially, but settles down to constant growth eventually Barton College 29 One Period Example • Suppose you are thinking of purchasing the stock of Moore Oil, Inc. and you expect it to pay a $2 dividend in one year and you believe that you can sell the stock for $14 at that time. If you require a return of 20% on investments of this risk, what is the maximum you would be willing to pay? Pt = $14 r = 20% D = $2.00 – Compute the PV of the expected cash flows – FV = Div in one year plus the Capital appreciation – Price = FV/(1+r)t = (14 + 2) / (1 + .2)1 = $13.33 Calculator – FV = 16; I/Y = 20; N = 1; PV = -13.33 Very similar to PV of a Bond P0 = D1/(1+r)1 + D2/(1+r)2 + …Dt/(1+r)t + Pt / (1+r)t Barton College 30 Two Period Example • Now what if you decide to hold the stock for two years? In addition to the dividend in one year, you expect a dividend of $2.10 in and a stock price of $14.70 at the end of year 2. Now how much would you be willing to pay? – PV = 2 / (1.2)1 + (2.10 + 14.70) / (1.2)2 = 13.33 Dividend + Stock Price on final year Calculator – CF0 = 0; C01 = 2; F01 = 1; C02 = 16.80; F02 = 1; NPV; I = 20; CPT NPV = 13.33 P0 = D1/(1+r)1 + D2/(1+r)2 + …Dt/(1+r)t + Pt/(1+r)t Barton College 31 Three Period Example • Finally, what if you decide to hold the stock for three periods? In addition to the dividends at the end of years 1 and 2, you expect to receive a dividend of $2.205 at the end of year 3 and a stock price of $15.435. Now how much would you be willing to pay? – PV = 2 / (1.2)1 + 2.10 / (1.2)2 + (2.205 + 15.435) / (1.2)3 = 13.33 Last year considers Dividend and Capital Calculator – CF0 = 0; C01 = 2; F01 = 1; C02 = 2.10; F02 = 1; C03 = 17.64; F03 = 1; NPV; I = 20; CPT NPV = 13.33 P0 = D1/(1+r)1 + D2/(1+r)2 + …Dt/(1+r)t + Pt/(1+r)t Barton College 32 Zero Growth Dividend • If dividends are expected at regular intervals forever, then this is like preferred stock and is valued as a perpetuity • P0 = D / R where D = dividend & R = discount rate • Suppose stock is expected to pay a $0.50 dividend every quarter and the required return is 10% with quarterly compounding. What is the price? – P0 = .50 / (10% / 4) = $20 Barton College 33 Dividend Growth Model (Constant Growth) • Dividends are expected to grow at a constant percent per period. – P0 = D1 /(1+R) + D2 /(1+R)2 + D3 /(1+R)3 + … – P0 = D0(1+g)/(1+R) + D0(1+g)2/(1+R)2 + D0(1+g)3/(1+R)3 + … • Where g = growth rate • With a little algebra, this reduces to: D0 (1 g) D1 P0 R -g R -g Barton College 34 DGM – Example 1 (Constant Growth Dividend) • Suppose Big D, Inc. just paid a dividend of $.50. It is expected to increase its dividend by 2% per year. If the market requires a return of 15% on assets of this risk, how much should the stock be selling for? • D0 = $.50, g=2%, R=15% • P0 = D0(1+g) / (R - g) • P0 = .50(1+.02) / (.15 - .02) = $3.92 Barton College 35 DGM – Example 2 • Suppose TB Pirates, Inc. is expected to pay a $2 dividend in one year. If the dividend is expected to grow at 5% per year and the required return is 20%, what is the price. Constant Growth Formula – P0 = D1 / (R- g) – P0 = 2 / (.2 - .05) = $13.33 P0 D0 (1 g) D 1 R -g R -g – Why isn’t the $2 in the numerator multiplied by (1.05) in this example? • • Barton College Because D1 is the next dividend one year later, not the current dividend D1 = D0(1+g) 36 Stock Prices are sensitive to Earnings P0 D0 (1 g) D 1 R -g R -g Barton College 37 Growth Stocks with volatile Earnings can be risky… Barton College 38 Stock Price Sensitivity to Dividend Growth, g 250 D1 = $2; R = 20% Stock Price 200 Price volatility accompanies high growth rates 150 100 50 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 Growth Rate D0 (1 g) D1 P0 R -g R -g Barton College As g gets larger the denominator gets smaller (as long as g < R) 39 Blue Nile Growth Warning… • October 12, 2007, 2:44PM EST text size: TT • CITIGROUP CUTS BLUE NILE TO SELL FROM HOLD • Citigroup analyst Mark Mahaney downgraded Blue Nile (NILE) on his belief that near-term market expectations have gotten ahead of fundamentals. Proprietary Web Traffic Conversion Tracking suggests third quarter units could be 30,000-34,000 vs. his 35,000 estimate. He notes he has very limited visibility into average order size, but sensitivity analysis indicates in-line revenue quarter at best; He thinks the Street's $0.16 EPS is intact. • Mahaney says his $88 target remains based on U.S. specialty retailer average 3.7% 2008 free cash flow yield, which implies 10% downside from current price levels (pre-open). He notes that Blue Nile shares are up 19% since its major second quarter beat, implying expectations for another very strong quarter. He keeps $0.99 2007, $1.35 2008 EPS estimates. D0 (1 g) D1 P0 R -g R -g http://www.bluenile.com Barton College 40 Stock Price Sensitivity to Required Return, R 250 D1 = $2; g = 5% Stock Price 200 150 100 P0 50 D0 (1 g) D 1 R -g R -g 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 Required Return WSJ Prime Rate Barton College This week Month ago Year ago 3.25 3.25 3.25 41 Example 8.3 Gordon Growth Company - I • Gordon Growth Company is expected to pay a dividend of $4 next period and dividends are expected to grow at 6% per year. The required return is 16%. • What is the current price? – Given: D1 = $4, g = 6%, R = 16% – P0 = D1 / (R-g) – P0 = 4 / (.16 - .06) = $40 – Remember that we already have the dividend expected next year, so we don’t multiply the dividend by 1+g or ….. D1 = D0(1+g) Barton College 42 Example 8.3 – Gordon Growth Company - II • What is the price expected to be in year 4? – P4 = D4(1 + g) / (R – g) = D5 / (R – g) – P4 = 4(1+.06)4 / (.16 - .06) = 50.50 Constant Growth…. D0 (1 g) D1 P0 R -g R -g • What is the implied return given the change in price during the four year period? – 50.50 = PV(1+R) 4 = 40(1+R)4; R = 6% – PV = -40; FV = 50.50; N = 4; CPT I/Y = 6% • The price grows at the same rate as the dividends Barton College 43 Non-constant Growth Problem Statement • Suppose a firm is expected to increase dividends by 20% in one year and by 15% in two years. After that dividends will increase at a rate of 5% per year indefinitely. If the last dividend was $1 and the required return is 20%, what is the price of the stock? • Remember that we have to find the PV of all expected future dividends. Barton College 44 Nonconstant Growth – Example Solution G1 = 20% G2 = 15% G3 = 5% • Compute the dividends until growth levels off – D1 = 1(1.2) = $1.20 – D2 = 1.20(1.15) = $1.38 – D3 = 1.38(1.05) = $1.449 • Find the expected future price (price at year 3) – P2 = D3 / (R – g) = 1.449 / (.2 - .05) = 9.66 • Find the present value of the expected future cash flows – P0 = 1.20 / (1.2) + (1.38 + 9.66) / (1.2)2 = 8.67 P0 = D1/(1+r)1 + D2/(1+r)2 + …Dt/(1+r)t + Pt/(1+r)t Barton College 45 Problems • What is the value of a stock that is expected to pay a constant dividend of $2 per year if the required return is 15%? – This is a zero-growth dividend stock – P0 = D / R = 2/.15 = $13.3 • What if the company starts increasing dividends by 3% per year, beginning with the next dividend? The required return stays at 15%. – Constant Growth Dividend stock – P0 = D0(1+g) / (R-g) = 2(1+.03) / (.15-.03) = $17.17 Barton College 46 Using the DGM to Find R • Start with the DGM: D 0 (1 g) D1 P0 R -g R -g rearrange and solve for R D 0 (1 g) D1 R g g P0 P0 Barton College 47 Finding the Required Return - Example • Suppose a firm’s stock is selling for $10.50. They just paid a $1 dividend and dividends are expected to grow at 5% per year. What is the required return? – R = [D0(1+g) / P0] + g – R = [1(1.05)/10.50] + .05 = 15% • What is the dividend yield? – 1(1.05) / 10.50 = 10% • What is the capital gains yield? – g =5% Barton College 48 Table 8.1 - Summary of Stock Valuation Barton College 49 US Car Industry….. Barton College 50 GM Stock Price…. As of 4-16-09 Price of $1.9/Share Barton College 51 Earnings and Growth in Earnings Dividend = 0 Growth Rate < 0 Debt/Asset Ratio ~ 1.45 Barton College 52 Features of Common Stock • Voting Rights – Usually one share one vote – Straight voting (Directors are elected one at a time) • Share holders with large ownerships (50% or more) of the corporation virtually controls the vote – Cumulative Voting (All directors are determined during a single vote and not individually at a time; allows for minority representation on the board, i.e., one person can’t control all elected board members.) • Proxy voting – Allows someone to vote for another person – Mutual Funds do this all the time (i.e., since you will not be voting at the annual meeting) – Carl Ichan uses this method to change or replace company management (Green Card) • Classes of stock – – – – Class B Class C (possibly a non-voting class, etc.) Etc… Examples: • Class B gets dividend distributions before class C, etc. • Stocks used for specific purposes (FCB family classes for example) • Set for specific purposes by the board, e.g., M&A would be one example • Separate class for voting (owners maintain control) and a separate class for raising equity capital • Other Rights of Stock holders – Share proportionally in declared dividends – Share proportionally in remaining assets during liquidation – Preemptive right – first shot at new stock issue to maintain proportional ownership if desired Barton College See Notes Page… 53 Rights Offering Dividend Characteristics • Dividends are not a liability of the firm until a dividend has been declared by the Board • Consequently, a firm cannot go bankrupt for not declaring dividends • Dividends and Taxes – Dividend payments are not considered a business expense, therefore, they are not tax deductible (after Net Income) – Dividends received by individuals are taxed as ordinary income (1099-DIV….)……. Declaring dividends can have tax consequences for stock holders… – Dividends received by corporations have a minimum 70% exclusion from taxable income (i.e., they are taxed on only the remaining 30%.) • Dividends from stock the corporation owns…. Barton College 54 Features of Preferred Stock • Dividends – Stated dividend that must be paid before dividends can be paid to common stockholders – Dividends are not a liability of the firm and preferred dividends can be deferred indefinitely • Dividends paid in arrears – Most preferred dividends are cumulative – any missed preferred dividends have to be paid before common dividends can be paid • Preferred stock generally will not carry voting rights • Unlike debt, preferred dividends do not have to be paid out. Barton College 55 Stock Market • Dealers vs. Brokers – Dealer: maintains an inventory and stands ready to trade at quoted bid (price at which they will buy) and ask (price at which they will sell) prices. Make their profit from the difference between the bid and ask prices, called the bid-ask spread. The smaller the spread the more competition and the more liquid the stock. The move to decimalization allows for a smaller bidask spread. There will be more discussion of this later. – Broker matches buyers and sellers. They perform the search function for a fee (commission). They do not hold an inventory of securities. • New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) – Largest stock market in the world – Members • Own seats (before 2006) on the exchange. NYSE is now public and owners purchase annual license (~$55,000 per year) • Specialists • Floor brokers • Floor traders – Operations – Floor activity – NYSE on YouTube Look at your Book for a host of stories and examples….. Barton College 56 Liquid vs. Illiquid Stocks Stock Price is sensitive to the number of shares transacted or the daily volume. Barton College 57 NASDAQ • Not a physical exchange – computer based quotation system • Multiple market makers • Electronic Communications Networks – EDI • Three levels of information – Level 1 – median quotes, registered representatives – Level 2 – view quotes, brokers & dealers – Level 3 – view and update quotes, dealers only • Large portion of technology stocks Barton College 58 NASDAQ Level I and II Quotes (Shows the Market Makers…. Ask and Bid entity) This is what a level II quote looks like: Barton College 59 US Stock Exchanges (BATS) Barton College 60 Bulletin Board and Pink Sheet Stocks • Bulletin Board: Stocks that do not meet the filing requirements for the NASDAQ or other major exchanges. – Penny Stocks – http://www.otcbb.com/ • Pink Sheets – http://www.otcmarkets.com/otc-pink/home • Both OTCBB and OTC Pink (Pink sheets) should be considered risky companies as each have minimal listing requirements. OTCBB must file statements and report to the SEC, but Pink sheet companies do not. Barton College 61 Reading Stock Quotes • Sample Quote 52 wk hi lo Comp sym 33.25 20.75 Harris HRS P/E Yield volume 87 .7% 3358 last trade price change 29.60 +0.50 • What information is provided in the stock quote? • Click on the web surfer to go to CNBC for current stock quotes. Barton College 62 International Stock Exchanges • Americas – E.g., Toronto, Montreal, Winnipeg – E.g., NYSE, NASDAQ, American (now owned by NYSE) – E.g., Mexico, Brazil, Chile, Argentina • Europe – London Stock Exchange – German Stock Exchange (DAX) – http://www.site-by-site.com/exchanges_europe.htm • Asia/Pacific – Tokyo, Australian, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Bombay, Korea, Singapore, • Africa/Near East – Johannesburg Stock Exchange, Others: http://dir.yahoo.com/Business_and_Economy/Business_to_Business/Financial_Services/Exchanges/Stock_Exchanges/?b=0 Barton College 63 World Markets as of 2-3-15 12:05pm (US Eastern Standard) Barton College 64 Example of the DAX Index that follows The German Stock Exchange or shares trading on that exchange Many companies Will list outside their Home country by issuing ADR’s or American Depository Receipts Barton College 65 Professional Trading Tools • Bloomberg Terminal (Macro, micro and firm specific Indicators and lots… more…) • S&P Compustat (Fundamental Data) • Morningstar Direct (Mutual Funds, ETF’s, hedge funds, etc.) Barton College 66 Bloomberg Terminal (Professionals) Barton College 67