LS1 PowerPoint Cells ls1.powerpoint.cells
advertisement

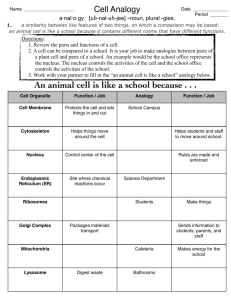
4-23-13 • Do Now: What is the difference between a plant and animal cell? • LT: I can describe the the functions performed by cells. P) Chloroplasts (Plants only) (LS1D) Chloroplasts 1. Function: site of photosynthesis (converting sun and CO2 into sugar). 2. Structure: Membrane bound organelles that contain chlorophyll Analogy – Solar Panels Q) Cell Wall (Plant cells only) (LS1D) Cell Wall 1. Function: Provides support for the cell and the plant. 2. Structure: Made of cellulose Analogy – ground, rock wall Central Vacuole Plants Only (LS1D) Shape (LS1D) Animal Plant Cells-LS1 Definition (LS1A) = Three part theory about cells 1. All living things are made of cells. Part 2 of the Theory (LS1A) 2. The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Part 3 of the Theory (LS1A) 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. yeast cells dividing How big are cells? (LS1B) • Microscopic (mostly) • Measured in microns µm • (micrometers). • A µm is one millionth of a meter = • 10-9 m = one thousandth of 1 mm. How big are cells? (LS1B) • Human red blood cell = 8 µm in diameter How big are cells? • Largest cell on the human body = ovum • Size= • 1000 µm in diameter (1 mm) Cell Parts (LS1A) • Cells – the basic unit of life • Organelles - small structures inside a cell with specific functions. Analogy – City of Tacoma A) Cell Membrane/Plasma Membrane (LS1A) Cell membrane 1. Function: Regulates materials entering and exiting the cell. 2. Structure: Two layers of phospholipids, proteins Analogy – Tacoma city limits B) Nucleus (LS1A) Nucleus 1. Function: “Control Center.” Regulates DNA & RNA actions. 2. Structure: membrane bound, contains DNA Analogy – City Hall C) Nuclear Envelope (LS1A/C) Nuclear Envelope 1. Function: Regulates what enters or exits the nucleus. 2. Structure: Double Layer of Lipids Analogy – Walls & Doors of City Hall E) Cytoplasm (LS1A/C) Cytoplasm 1. Function: All cell contents that lie between the cell membrane and the nucleus. (organelles + cytosol) a. Cytosol = liquid portion/non-organelles. 2. Structure: made up of fluid and organelles except for nucleus Analogy – All air, water, life that are in Tacoma, except City Hall F) DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid (LS1A/C)DNA (chromatin) 1. Function: information on how to make proteins. a. Chromatin – unorganized DNA (normal state) b. Chromosomes – organized DNA (present before cell division 2. Structure: Made up of nucleotides, locked in the nucleus Analogy – The Laws or City Code I) Vacuoles & Vesicles (LS1A/C) Vesicles 1. Function: Storage for water, nutrients or waste. 2. Structure: small membrane-bound organelle. Analogy – Grocery stores, water tanks. J) Lysosomes (LS1A/C) Lysosomes 1. Function: packets of enzymes that break down materials in a cell. 2. Structure: Small membrane-bound organelles Analogy – Recycling center K) Mitochondria (LS1A/C) Mitochondria 1. Function: Produce energy for the cell – site of cellular respiration. “The Powerhouse” 2. Structure: Double membrane-bound, kidney shaped. Analogy – Tacoma Public Utilities M) Cytoskeleton (LS1A/C) Microfilaments Microtubules 1. Function: Provide support and structure for the cell. a. Microfilaments b. Microtubules 2. Structure: Tubules Analogy – Wood, cement, steel beams Cell Types (LS1C) Muscle Cells Stem Cells Nerve Cell Red Blood Cells Cell Types (LS1C) Gametes (sex cells) Skin cells Fat cells Body systems (LS1C) Respiratory system Digestive system Animal classification (LS1E) Pacific salmon classification (Genus: Oncorhynchus) (LS1E)