Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
advertisement

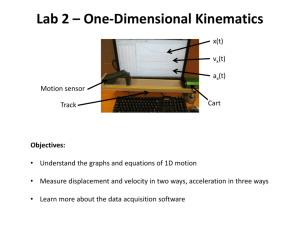
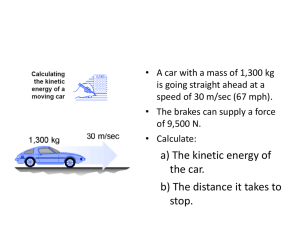
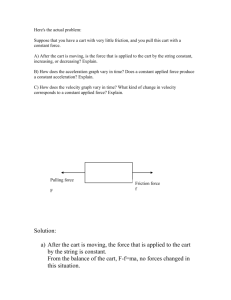
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Balls on a billiard table exhibit collisions that are nearly elastic. Colliding blobs of putty would exhibit perfectly inelastic collisions. Much of the energy in such a collision is converted to internal vibrations or heat. You are to study elastic collision by replicating the following initial conditions and observing the results. You and your lab partners will need to develop a method to obtain the values requested for the initial conditions. You and your lab partners will then need to use your method to determine the velocity of the carts after the collision (event) has occurred. You and your lab partners will need to give an explanation of your method to allow another independent individual to repeat your experiment. Once you have collected your data, you then need to: Calculate the initial momentum of each system prior to the event. Calculate the final momentum of each system after the event. Calculate the initial and final kinetic NRG of each system. Determine a relationship between initial and final momentums for elastic collisions. Determine how Kinetic NRG is part of the determination. Summarize how the data collected demonstrates a relationship between initial and final momentums for each event. Identify the characteristics given the experimental data which define elastic and Inelastic collisions. Scenario #1: Scenario #4: Velcro Stick collision between Carts of Equal Mass Plunger between - One Cart in Motion with equal Mass Cart 1 mass Cart 1 mass Cart 1 initial Velocity 1 kg Cart 2 Mass 1 kg Cart 2 Initial Velocity 0.0 m/s Velcro Stick Mass of Carts are Unequal. Cart 1 initial Velocity 1 kg 1 kg 1.0 kg Cart 2 Mass .5 kg Cart 2 Initial Velocity 0.0 m/s Scenario #3: Velcro Stick - Velcro Stick Mass of Carts are Unequal. .5 kg Cart 1 initial Velocity Cart 2 Initial Velocity 0 Plunger between - One Carts in Motion with Unequal Mass Cart 1 mass Cart 1 initial Velocity .5 kg Cart 1 mass Cart 2 Mass Scenario #5: Scenario #2: Cart 1 mass Cart 1 initial Velocity Cart 2 Mass 1 kg Cart 2 Initial Velocity 0.0 m/s Cart 2 Mass 1 kg Cart 2 Initial Velocity 0 Scenario #6: Plunger between Both Carts in Motion with Unequal Mass Cart 1 mass 1 kg Cart 1 initial Velocity Cart 2 Mass 0.5 kg Cart 2 Initial Velocity Scenario #7: Magnetic Repulsion Mass of Carts are equal. Cart 1 mass Cart 1 initial Velocity 1 kg Cart 2 Mass 1 kg Cart 2 Initial Velocity 0.0 m/s Scenario #8: Magnetic Repulsion - Both Cart in Motion and of Equal Mass Cart 1 mass Cart 1 initial Velocity Cart 2 Mass 1 kg Cart 2 Initial Velocity Scenario #10: TBD Cart 1 mass Cart 1 initial Velocity Cart 2 Mass Cart 2 Initial Velocity Cart 2 Mass Cart 2 Initial Velocity Cart 2 Mass Cart 2 Initial Velocity Scenario #11: TBD Cart 1 mass 1 kg Cart 1 initial Velocity Scenario #9: Magnetic Repulsion - Both Cart in Motion with Unequal Mass Cart 1 mass 1 kg Cart 1 initial Velocity Cart 2 Mass Cart 2 Initial Velocity Scenario #12: TBD Cart 1 mass Cart 1 initial Velocity 0.5 kg Don’t Forget to do the following……………….. Calculate the kinetic NRG for each cart before the collision. Calculate the kinetic NRG of Each Cart after the collision. Determine the total Kinetic NRG before the collision. Determine the total Kinetic NRG After the collision. Compare the total kinetic NRG before the collision to the total kinetic NRG after the collision. What is the nature of an elastic collision? What is the true nature of an inelastic collision? Describe the main ideas learned in this activity regarding initial and final total momentum in elastic collisions.