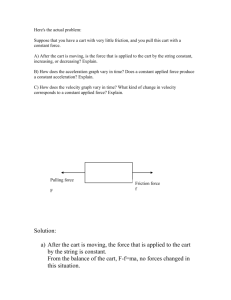
Do Now
advertisement
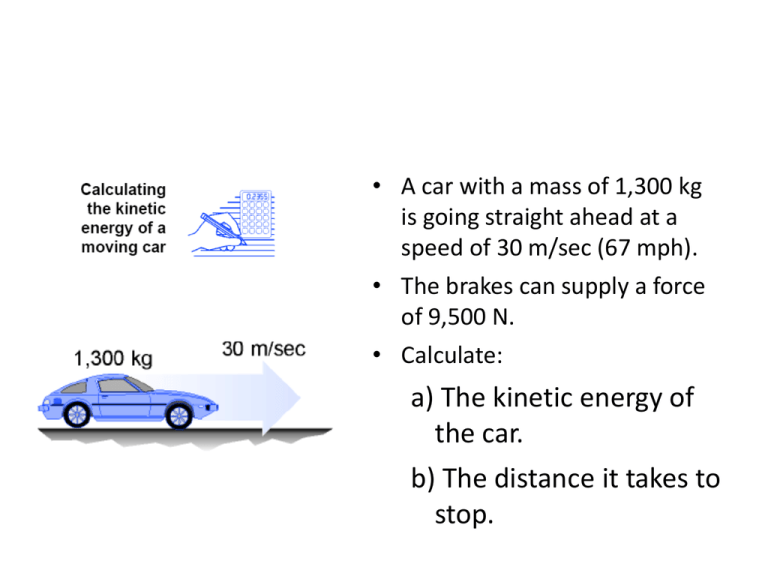
• A car with a mass of 1,300 kg is going straight ahead at a speed of 30 m/sec (67 mph). • The brakes can supply a force of 9,500 N. • Calculate: a) The kinetic energy of the car. b) The distance it takes to stop. Calculate work • A crane lifts a steel beam with a mass of 1,500 kg. • Calculate how much work is done against gravity if the beam is lifted 50 meters in the air. • How much time does it take to lift the beam if the motor of the crane can do 10,000 joules of work per second? Given the force vs. displacement graph below for a net force applied horizontally to an object of mass 100g initially at rest on a frictionless surface, determine the object’s final speed when the net force is 200 N. You may assume the force does not change its direction. In the following diagrams, a force F acts on a cart in motion on a frictionless surface to change its velocity. The initial velocity of the cart and final velocity of each cart are shown. You do not know how far or in which direction the cart traveled. Rank the magnitude of the work done by the force on each cart from greatest to least. A 2kg 2kg B 3kg 3kg V0=5m/s C 5kg V0=5m/s V=2m/s 5kg V=6m/s V0=3m/s D 4kg V0=-1m/s V=-3m/s 4kg V=2m/s A pitcher throws a 143-gram baseball toward the catcher at 45 m/s. If the catcher’s hand moves back a distance of 6 cm in stopping the ball, determine the average force exerted on the catcher’s hand. A chef pushes a 10-kg pastry cart from rest to a distance of 5 meters with a constant horizontal force of 10N. Assuming a frictionless surface, determine the cart’s change in kinetic energy and its final velocity. A 2kg block sliding down a ramp from a height 3meters above the ground reaches the ground with kinetic energy of 50 joules. Find the total work done by the friction on the block as it sliding down the ramp.