Lymphatic Vessels
advertisement

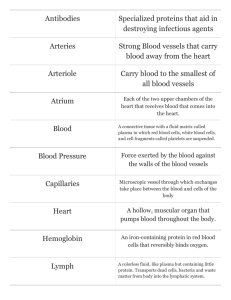
Lymphatic System – Ms Atkinson Leaving Cert Biology Network of lymph vessels -One way system of dead-ends Collect the fluid that surrounds every cell in the body -tissue fluid Tissue fluid is fluid that has been leaked through the walls of blood capillaries as they enter the tissue (due to high blood pressure). This fluid must be returned to the blood. Some of it returns to the capillaries as the blood leaves the tissue. Protein in the tissue fluid does not reenter the blood. Some of it is taken into lymphatic vessels. Lymphatic Vessels Lymphatic capillaries collect the tissue fluid These drain into larger lymphatic ducts Lymphatic vessels contain valves Movement of lymph is as result of surrounding muscles ‘milking’ the vessels contractions in the muscular walls of lymph vessels Lymph Tissue fluid that has entered the lymphatic system is called lymph. Its composition is similar to that of plasma, with lymphocytes, protein and lipids, though contains much less protein than plasma. Many larger proteins do not pass through the leaking capillary walls. Lost protein and fluid is returned to the blood by the thoracic lymph duct into the subclavian vein. Plasma Tissue Fluid Ms Atkinson 2012 Lymph Plasma Formation of Lymph lymphatic some tissue fluid enters the lymphatic tissue fluid cells glucose nitrogenous waste carbon oxygen dioxide blood flow plasma filtered out of capilliary Circulation in the Lymphatic System Ms Atkinson 2012 capilliary tissue fluid enters capilliary Lymph Nodes These are swellings found along lymph vessels Contain large numbers of lymphocytes Form clusters called glands in some parts Eg: thymus, tonsils, spleen, adenoids, armpits, neck, groin Immunity function of lymph nodes 1. Filter microbes and debris from the lymph 2. Maturation and storage of lymphocytes antibody production clean up cancerous cells disable bacteria and viruses Functions of the Lymphatic System 1. Collecting lost tissue fluid. 2. Returning lost fluid and protein to the blood this helps maintains the blood at the right concentration. 3. Defence against pathogens detects and filters out foreign antigens lymphocyte and antibody production 4. Absorption and transport of fats lacteals in the villi of the small intestine 5. Assists in hearing and balance lymph is found in the inner ear Oedema is the swelling of the body (usually lower legs and feet) due to too much tissue fluid. It may be due to a failing circulation system or an unusual blood composition (too much water and salt or too little protein) due to a kidney complaint. Elephantiasis is due to eggs from a parasitic roundworm getting in by mosquito bites. The young worms grow and block the lymph vessels giving an elephantiasis appearance of limbs. Treatment is by removal of worm, drainage of fluid and surgical repair of damaged vessels if necessary Ms Atkinson 2012 Lymphatic system Blood system Open circulatory system Closed c.s. No pump Heart No RBCs and proteins Has both Colourless fluid Red Nodes None Ms Atkinson 2012