Lab 6: Respiratory System
advertisement

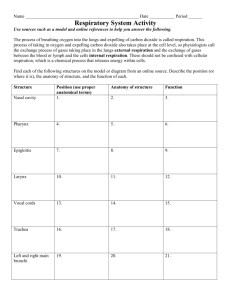
Lab 6: Respiratory System Announcements Extra Credit Assignment Extra Credit Quiz Quick and Painless Review Where is your thymus? What is the difference between lymph nodules and MALT? What is the difference between your lymph nodes and your spleen? Respiration Overview Anatomy of the Respiratory System Mathematics of the Respiratory System How do you evaluate malfunctions in the respiratory system? Respiratory System Respiratory System: Functions? Respiratory System Respiratory System: Functions? 1. Receive air for breathing 2. Exchange gases (O2. CO2) with the blood 3. Expel modified air Schematic of Respiratory System Upper Respiratory Tract Nasal Cavity Guard Hairs Mucous Oral Cavity Pharynx Posterior to Nasal and Oral Cavities Cleans Air Intersection of Respiratory and Digestion Upper Respiratory Tract Epiglottis Flap blocks food from entering the lower respiratory tract Larynx 9 plates of Cartilage Large Chamber Contains vocal cords Anatomy of the Larynx Anatomy of the Larynx Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles in larynx pull the cartilage This causes the cords to move Males have thicker cords Functions of the Upper Respiratory Tract Cleans air Guard hairs Mucus (MALT) Cilia Warms air Moistens air Anatomy of the Lungs Trachea C-shaped cartilage Mucociliary escalator Primary Bronchi Cartilage Right wider than left Secondary Bronchi Tertiary Bronchi More branches on right Mucociliary Escalator Muscus Traps particles Cilia Move particles up toward pharynx Lower Respiratory Tract Bronchioles Small – 1mm or less No longer contain cartilage Continue Branching Terminal Bronchioles Last passages before aveoli Still have Cilia Alveoli – where gas exchange occurs Phagocytosis removes small particles Lower Respiratory Tract Convey air to alveoli Clean air and remove particles by mucociliary elevator Macrophages in aveoli phagocytize foreign particles – last line of defense Dynamic Human Anatomy Airflow in the Lungs 1º Bronchi 2 º Bronchi 3 º Bronchi Bronchioles Terminal Bronchioles Alveolus GAS EXCHANGE with Capillary Bed Mechanism of Airflow Airflow is a result in changes of pressure between two systems System 1: the outer atmosphere System 2: the pressure within the alveoli How does pressure change within the alveoli? Mechanisms of Airflow How does pressure change within the alveoli? Boyles Law: P 1/V (Changes in Volume result in changes in Pressure!!!!!) How does volume change within the alveoli? Mechanism of Airflow How does volume change within the alveoli? Inspiration The diaphragm expands the thoracic cavity during quiet inspiration Deep inspiration is aided by the pectoralis minor, the sternocleidomastoid and the erector spinae muscles (external intercostals) Mechanism of Airflow Expiration Quiet Breathing: Volume changes are not caused by muscular contraction, rather the elasticity of the lungs and ribs Deep expiration: internal intercostals, abdominal muscles Alveolar Gas Exhange O2 loads into RBC; CO2 unloads into the alveoli Factors involved: Concentration gradients Solubility in H2O Membrane thickness Membrane area Alveoli Oxygen Transport and Carbon Monoxide Oxygen is carried through the blood stream by hemoglobin Carbon Monoxide binds to hemoglobin 200x better. Carbon Monoxide Sources? Carbon Monoxide Sources? Car Exhaust Cigarette Smoke Smoking Chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and cancer Over 2000 chemicals in tobacco smoke. What gives the lung at the top its dark color? Carcinogens in Tobacco Carcinogen: substance that increases the potential for tumor growth 50 carcinogens in smoke (2 radioactive) eg.- Nicotine, Formaldehyde Implicated in 90% of lung cancers Dynamic Human Mechanics of Breathing, Gas Exchange, and Carbon Monoxide Spirometry Spirometry Respiratory volumes tidal volume: air inhaled or exhaled in one quiet breath inspiratory reserve volume: air in excess of tidal inspiration that can be inhaled with maximum effort expiratory reserve volume: air in excess of tidal expiration that can be exhaled with maximum effort residual volume: air remaining in lungs after maximum expiration, keeps alveoli inflated Spirometry Exercise Each group is to measure one members tidal and expiratory reserve volume. Record on front board, indicating gender. After all groups are done, average total to get class average tidal and expiratory reserve volume and compare to known averages. Bronchioscopy Flexible tube with camera attached Used to identify blockages in bronchi and to biopsy tumors/growths Dynamic Human Spirometry and Bronchoscopy Asthma Inflammation reaction in the lung caused by and allergen Results in bronchoconstriction and sometimes suffocation Treatments for Asthma Inhalers – daily or rescue Albuterol Vanceril Pills - daily Accolade Singular Injection or Nebulizer - rescue Ephinedrine Gross Anatomy Human/Cow Trachea Primary Bronchi Lungs How many lobes? Larynx Epiglottis Cat Left and right lungs How many lobes? Trachea Primary Bronchi Larynx