Chapter 5 PowerPoint
advertisement

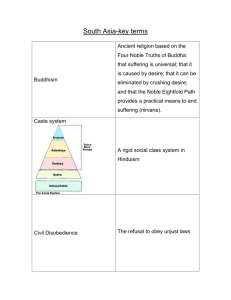
Exploring the Religions of Our World Chapter 5 Hinduism Chapter 5 Hinduism The Basics • 95% of Hindus live in India • Hinduism emerged as a religion, it did not begin with a founder or particular event • Hinduism shares no doctrinal statements • Hindus hold that no one religion can possibly claim knowledge of absolute truth Chapter 5 Hinduism Periods of Hindu History Pages 184-185 Chapter 5 Hinduism History (continued) Major developments of: The Indus Valley Period (3000-1500 BCE) • emphasis on ritual purity • focus on fertility and regeneration • the practice of meditation • emphasis on peacefulness Chapter 5 Hinduism History (continued) Major developments of: The Brahminical Period (1500-300 BCE) • ritual sacrifices by the Brahmins (priests) • home ritual sacrifices • gurus (teachers) train disciples in personal devotion to the gods • the gods Shiva and Vishnu gain in prominence • rise of ascetical practices Chapter 5 Hinduism History (continued) Major developments of: The Classical Period (300-1200 CE) • • • • • • • establishment of Hindu temples growth of home-based rituals the Vedas become the authoritative scripture emphasis shifts from the transcendent to the immanent emphasis on personal transformation the concepts of karma and reincarnation emerge the evolution of the caste system Chapter 5 Hinduism History (continued) Jainism: • founded by Mahavira in the sixth century BCE • contains elements of Hinduism and Buddhism • practice non-violence or non-injury Chapter 5 Hinduism Sacred Stories and Sacred Scriptures Shruti Scriptures (the most sacred) 1. Rig Veda - hymns to various gods The The Holy Vedas Vedasc 2. Soma Veda - hymns chanted at sacrifices 3. Yajur Veda - instructions for priests regarding sacrifices 4. Atharva Veda - hymns, charms, spells and incantations for domestic use Chapter 5 Hinduism Sacred Stories and Sacred Scriptures (continued) Shruti Scriptures – also… The The Upanishads Upanishads concerned with the cycle of rebirth the mystical relationship between Brahman (Ultimate Reality) and atmon (soul) often shared in a dialogue between guru and student Chapter 5 Hinduism Sacred Stories and Sacred Scriptures (continued) Smriti Scriptures Mahabharata Mahabharata Puranas Puranas a Hindu epic poem stories of the gods: Brahma, Vishnu, Shiva Chapter 5 Hinduism Beliefs and Practices Most Hindus hold these beliefs in common: the caste system millions of gods and goddesses the sacredness of life the cycle of rebirth the four stages of life Chapter 5 Hinduism Beliefs and Practices (continued) Brahman = one Ultimate Reality or Absolute Reality which: cannot be grasped by the five senses is manifested in gods and goddesses is transcendent includes everything material and immaterial has no attributes is the lifeforce of the universe Chapter 5 Hinduism Beliefs and Practices (continued) 3 primary forms of Brahman 1. Brahma is the Creator god 2. Vishnu is the Preserving god 3. Shiva is the Destroying god An avatar is the incarnation of a god or goddess e.g. Krishna and Rama Chapter 5 Hinduism Beliefs and Practices (continued) Atman: • is the “real self” (mind, body, and emotions are “maya” or illusions) • Hindus strive for release from maya in order to achieve union with Brahman/atman • Moksha (liberation) is achieved through rigorous physical and mental discipline Chapter 5 Hinduism Beliefs and Practices (continued) Samsara - the cycle of rebirth rebirth breaking the cycle: knowledge birth karma death good deeds devotion Chapter 5 Hinduism Moksha Beliefs and Practices (continued) The major pursuits of life: Artha Dharma one’s duties in life, especially as dictated by caste pursuit of both material and political wealth pursuit of liberation from the cycle of rebirth through actions, thoughts, and devotions Kama pursuit of artistic, recreational, and sensual pleasure Chapter 5 Hinduism Sikhism • a blending of Hinduism and Islam • is monotheistic • beliefs: karma, samsara, moksha, equality • rejects: caste system, idol worship • signs of devotion: unshorn hair, comb, short pants, steel bracelet, short sword • many have a desire to found and establish their own homeland Chapter 5 Hinduism Sacred Places and Sacred Spaces temples home shrines many images of gods/goddesses many images of gods/goddesses Ganges River symbol of life w/o end ritual bathing puja honoring the gods Chapter 5 Hinduism Hinduism through a Catholic Lens Similarities: • toleration of religious diversity • pursuing social issues • honoring Jesus and his teachings • the tradition of depicting and venerating religious images Chapter 5 Hinduism Hinduism through a Catholic Lens (continued) Differences: • karma • reincarnation • the caste system • Jesus as the one and only incarnation of God Chapter 5 Hinduism Vocabulary Brahmins shruti gurus bhakti Sanskrit karma caste system mantra Hare Krishnas Avatar Brahman transcendent Atman maya samsara yoga satyagraha puja iconoclasm devas