File
advertisement

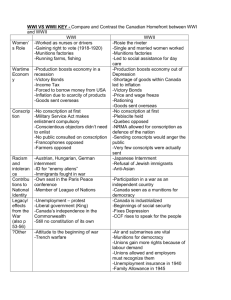
Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: The War Measures Act This was an act passed in August of 1914 What were the consequences of the act???? - Censorship - Economic control - Elimination of democratic rights and civil liberties - Overriding provincial rights What is the War measures Act? The War measures act is a Canadian statute that came into effect on August 4th, 1914. It allowed the federal government emergency powers to govern by decree under circumstances of “war, invasion or insurrection, real or apprehended” IT gave the government the okay to do everything necessary for the “security, defense, peace, order, and welfare of Canada” (Textbook, page 27) Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT HAD NEVER BEEN GRANTED THIS MUCH POWER BEFORE!!!!! What does this mean? Under the act the Cabinet does not have to submit its proposals to parliament for approval Lawmaking process in the legislature can be avoided The government can intervene in the economy of the country Strip ordinary citizens of their civil rights Censored mail Habeus corpus suspended Limited the freedom of “enemy aliens” – recent immigrants from the countries that we were now at war with Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: The Government during WWI Intervention in Canadian society increased dramatically during the war 1916 – War Profit tax 1917 – Personal income tax Temporary 1917 – Nationalization of half of the railroads 1918 – Increased civil service to 40,000 Economics of the war: Financing the war was expensive despite high production levels The cost of the war was 1.3 billion by March of 1919 Public debt in 1911: 350 million dollars vs. Public debt in 1918: 1,175 million dollars Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: Financing the cost of the war: How did Canada finance the cost of the war? 1. Victory bonds 2. Income tax Victory Bonds: In attempts to appeal to patriotism Victory bonds were encouraged Could be cashed in with interest after the war Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: Income Tax: This was supposed to be temporary Well off families and individuals: 3% of their income 4% on business profits Not Enough The money from income tax and victory bond initiaitves was not enough Canada had to borrow money to fund the cost of the war From other countries (USA) Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: Internment of “enemy aliens” During WWI 500,000 people that lived in Canada were from the German, AustroHungarian or Ottoman empires 8579 people into 26 camps performing tasks such as building roads and clearing the land WORK CAMPS They were paid 25 cents per day Propaganda During WWI Canadians were bombarded with war propaganda Used to get people to support the war effort Films, radio, politics, posters, speeches Persuaded young men to volunteer (80% of Canadians were volunteers during WWI) BUT: it often distorts truth Lies about battles on the Western front Lies about enemy casualties and allies successes Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: The Halifax Explosion When: 1917 Where: Halifax, Nova Scotia What: A huge explosion occurred when a French ship (Mont-Blanc) loaded with explosives collided with a Norweigian the Imo in the harbour. Why: The collision was an accident The Numbers: Between 2000-3000 killed, 10,000 injured This was the largest man-made explosion (Before the Atomic bomb) Germans were inaccurately blamed for this Election of 1917 Referred to as a “Khaki Election” A “Khaki Election” is any election that is influenced a great deal by war, wartime, or postwar sentiment In 1917 the Military Voters Act was passed and the vote was granted to all servicemen and women in the Canadian Expeditionary force. Many of these people could now cast their vote in any riding in Canada In 1917 the Wartime Elections Act was also passed This meant that the vote was granted to: wives, sisters, mothers, and daughters of soldiers The Union Government won the election Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: Conscientious Objectors: Mennonites and those from similar churches were exempt from service Many were imprisoned Mennonite and Hutterite immigrants were barred Canadian conscientious objectors were given the option of non-combatant service – medical or dental corps or working in parks under supervision Most chose to work in parks under supervision and were placed in Alternative Service Camps Conscription Conscription divided Canadians Farmer, Quebecois, British loyalists, families of soldiers In January of 1918 conscription was imposed. 400, 000 affected 100, 000 drafted 24, 000 soldiers were sent to France Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: Conscription crisis: 1917: desperate need of soldiers Attempts to recruit and replace soldiers failed conscription was implemented English Canadians were less opposed to conscription because of loyalty and ties to Britain. French Canadians felt no connection to Britain and opposed conscription = Military Voters Act Voters overseas could vote for conscription The Quebecois in WWI The French Canadians did not feel that they needed to serve the British in WWI Conscription was the most hated in Quebec Henri Bourassa and Wilfred Laurier were the leaders of the campaign against conscription They felt that the war was putting Canadians against each other The tension between French and English Canadians that developed here would last for many years Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: Women in WWI WWI affected the role of women and their position in Canadian society They 1. played an essential role in war production 2. They volunteered their time to support troops 3. Served in the Royal Air Force 4. Were nurses 5. Victory gardens, Victory bonds, and rationing programs 6. Kitchen Brigade Women’s Suffrage in WWI Before WWI some women had local and provincial voting rights that were generally dependent upon them owning property By 1900, Nellie McClung and The Famous Five had successfully fought for women’s suffrage in Manitoba provincial elections In 1917, the Wartime Elections Act gave the vote to British Women who were war widows, or had sons husbands or brothers serving overseas In 1918, Prime Minister Sir Robert Borden introduced a bill to extend the franchise to women did not apply to Quebec Quebec women did not gain full suffrage until 1940 Who was the first woman elected to Parliament? Where? When? Agnes Macphail, Ontario, 1921 Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: Women: The Western Front • 2500 medical and field ambulance corps • Nurses “Blue birds” • Hospitals in Britain • Military hospitals in battle zones Minority Enlistment • Those who were not welcomed: Nonwhites and those born in enemy territory • 1915: Aboriginal Canadians were allowed to enlist • Some were accepted into the 114th Battalion • Blacks in Nova Scotia were told “This is not for you fellows, this is a white man’s war!” • One black unit was formed called the No 2. Construction battalion – they were not allowed to fight for their country – they were to build trenches and shelters. • They trained in Pictou, Nova Scotia • They formed their own brass band Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: Minority enlistment: • Won the Boston Marathon in record time in 1907 • He had a professional career as a runner winning several different titles • He was a dispatch runner in WWI and retired after the war • He was married to Lauretta Maracle • Interesting fact: He was mistakenly declared dead during WWI and remarried afterwards • He died of pneumonia in 1949 The End. Summary: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________