WWI VS WWII KEY - Compare and Contrast the Canadian
advertisement
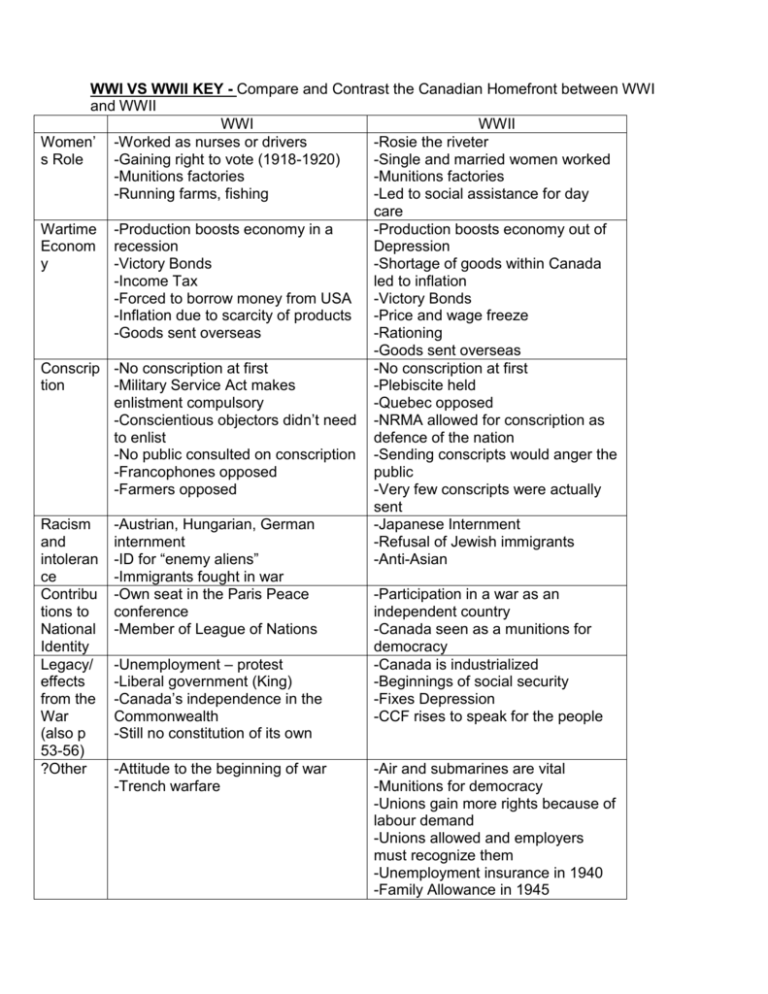
WWI VS WWII KEY - Compare and Contrast the Canadian Homefront between WWI and WWII WWI WWII Women’ -Worked as nurses or drivers -Rosie the riveter s Role -Gaining right to vote (1918-1920) -Single and married women worked -Munitions factories -Munitions factories -Running farms, fishing -Led to social assistance for day care Wartime -Production boosts economy in a -Production boosts economy out of Econom recession Depression y -Victory Bonds -Shortage of goods within Canada -Income Tax led to inflation -Forced to borrow money from USA -Victory Bonds -Inflation due to scarcity of products -Price and wage freeze -Goods sent overseas -Rationing -Goods sent overseas Conscrip -No conscription at first -No conscription at first tion -Military Service Act makes -Plebiscite held enlistment compulsory -Quebec opposed -Conscientious objectors didn’t need -NRMA allowed for conscription as to enlist defence of the nation -No public consulted on conscription -Sending conscripts would anger the -Francophones opposed public -Farmers opposed -Very few conscripts were actually sent Racism -Austrian, Hungarian, German -Japanese Internment and internment -Refusal of Jewish immigrants intoleran -ID for “enemy aliens” -Anti-Asian ce -Immigrants fought in war Contribu -Own seat in the Paris Peace -Participation in a war as an tions to conference independent country National -Member of League of Nations -Canada seen as a munitions for Identity democracy Legacy/ -Unemployment – protest -Canada is industrialized effects -Liberal government (King) -Beginnings of social security from the -Canada’s independence in the -Fixes Depression War Commonwealth -CCF rises to speak for the people (also p -Still no constitution of its own 53-56) ?Other -Attitude to the beginning of war -Air and submarines are vital -Trench warfare -Munitions for democracy -Unions gain more rights because of labour demand -Unions allowed and employers must recognize them -Unemployment insurance in 1940 -Family Allowance in 1945











