Roles of Women Powerpoint
advertisement

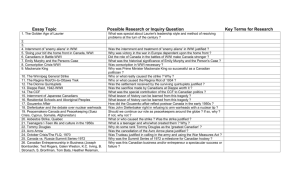
Roles of Women During WWI Roles of Women During WWI • As a guilt tool • In service • On the home front Sympathy A Little Push • This poster sends a message to women, urging them to give their husbands and sons permission to join the war. For much of the war it was against the law for a married man to enlist without the permission of their spouse. Many did refuse to give their husbands permission. A Little Push • In response these posters tried to make women feel guilty for not offering their men to the war. This was common during WWI because of the almost instant respect and honour that a soldier and his family gained by going off to war. • Women were often seen walking through the streets trying to encourage all able bodied men to enlist. Many still saw war as a glorious and heroic event. Nursing • Nursing is the most prominent role that Canadian women played at the front in Europe. Over 2000 women enlisted as nursing sisters in the Canadian Expeditionary Force during WWI. • The role of women at the front was very limited because of army rules and social constraints. Women started an organization called ,"The Canadian Women's Hospital Ship Fund". They raised money by organizing concerts, teas, parties, lectures, and bazaars. Women also raised money for the Red Cross, Belgian Relief, and Canadian Patriotic Fund. Other Services • Canadian women also worked as ambulance drivers and staff officers. • WWI did help suffragist groups break some of these social barriers. As a result, on September 20, 1917 the vote was given to women, whose husbands, sons, and brothers had served in the war. Danger • The dangers of working at the front were not restricted to soldiers. WWI Medical Services used hospital ships to evacuate the sick and wounded back to Canada. • These ships were subject to enemy attack. On the night of 27 June 1917 the Llandovery Castle, a merchant vessel serving as a hospital ship, was torpedoed while returning to England. Of a Canadian crew and medical staff totalling 258, only twenty-four survived. Factories/Farms • Women went to work and took over the occupations previously considered “men’s work.” • In 1917 there were about 35 000 women in munitions factories in Ontario and Québec. • Women also worked as farm assistants. • Paid less / Hostile working conditions. Conservation It became the role of women to preserve food for soldiers – as they were in greater need of hearty food. Women were expected to make their own sacrifices.