Cells
advertisement

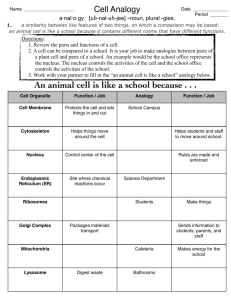
Bellwork 11/2/15 1.What is a cell? A cell is the basic unit (building block) of an organism. 2. What is the largest known cell? The largest know cell is the ostrich egg. On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN Cell Theory Update your Table on contents Materials: -scissors -glue stick -Highlighter History of the Cell • The Cell –The basic unit of an organism –The discovery of the cell was made possible by the invention of the microscope. Glue in your scientists! Anton van Leeuwenhoek Robert Hooke Microscopes and Cells • 1600’s- Anton van Leeuwenhoek first described living cells as seen through a simple microscope. Microscopes and Cells –Robert Hooke used the first compound microscope to view thinly sliced cork cells. • Compound scopes use a series of lenses to magnify in steps. • Hooke was the first to use the term “cell”. Microscopes and Cells • 1830’s - Mathias Schleiden identified the first plant cells and concluded that all plants are made of cells. - Thomas Schwann made the same conclusion about animal cells. Cell Theory- Foldable • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KuJqqiATlqw Jot down some notes about Cell Theory on the back of your foldable as you listen Bellwork 11/3/15 1. What discovery is Robert Hooke responsible for? Robert Hooke observed empty spaces in a slice of cork and called them “cells”. 2. Who identified that all animals are made of cells? Thomas Schwann concluded that all animals are made of animal cells. On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN -Glue Stick -Scissors Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of all organisms. 3. All cells come from other cells already in existence. Two Basic Cell Types 1. Prokaryote – Lacks internal compartments. – No true nucleus. – Most are single-celled (unicellular) organisms. – Examples: bacteria Two Basic Cell Types 2. Eukaryote –Has several internal structures (organelles). –True nucleus. –Either unicellular or multicellular. •unicellular example: yeast •multicellular examples: plants and animals Microscopes Lab- Prokaryote or Eukaryote?? Amphiuma- Liver Gleocapsa Bacteria (three forms) Euglena Scientific Sketching: -Attention to detail -Start with the big stuff and fill in the details. -Use a pencil to sketch lightly, darken as you fill in the details. -Draw your sketch to scale! -Draw your sketch to scale! -Use the highest power Bellwork 11/4/15 1. Draw a picture of a prokaryote (based on the definition in your IAN). 2. Draw a eukaryote (based on the definition in your IAN). On Desk: -Planner -PENCIL -IAN -Scissors Student Feedback Cards • • • • • Red- “I’m Stuck” Yellow- “Getting it” Green- “Good to Go” Blue- “All Done” Orange’ “YOUR name” Scientific Sketching: -Attention to detail -Start with the big stuff and fill in the details. -Use a pencil to sketch lightly, darken as you fill in the details. -Draw your sketch to scale! -Use the highest power Lab- Prokaryote or Eukaryote?? Amphiuma- Liver Gleocapsa Bacteria (three forms) Euglena Scientific Sketching: -Attention to detail -Start with the big stuff and fill in the details. -Use a pencil to sketch lightly, darken as you fill in the details. -Draw your sketch to scale! -Draw your sketch to scale! -Use the highest power Bellwork 11/5/15 1. Is Amphiuma a Prokaryote or eukaryote? 2. Is Gleocapsa a Prokaryote or eukaryote? 3. Is Bacteria a Prokaryote or eukaryote? 4. Is Euglena a Prokaryote or eukaryote? On Desk: -Planner -PENCIL -IAN Lab- Prokaryote or Eukaryote?? Amphiuma- Liver Prokaryote/Eukaryote? Bacteria (three forms) Prokaryote/Eukaryote? Gleocapsa Prokaryote/Eukaryote? Euglena Prokaryote/Eukaryote? Scientific Sketching: -Attention to detail -Start with the big stuff and fill in the details. -Use a pencil to sketch lightly, darken as you fill in the details. -Draw your sketch to scale! -Use the highest power Levels of Organization https://www-brainpopcom.sled.idm.oclc.org/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/cells/ Did you know that you have 75 trillion cells that make up your body?! (that is thousands of times more than the number of people on the planet!) 5 Levels of Organization Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Organism • A living system that has several organ systems that function together. • Examples: Animals, plants, and bacteria Organ System • A group of organs that carries out more generalized set of functions. • Examples: digestive system and circulatory system. Organ • Organs are two or more types of tissues that work together to complete a specific task. • Examples: heart or stomach. Tissue • Groups of cells with similar functions. • Examples: Connective (bone, blood) and muscle tissue. Cells • The smallest unit of life. Cells preform specific functions. • Example: muscle cell or skin cell Levels of Organization Foldable Small Large Bellwork 11/6/15 1. What is the definition of a tissue? A tissue is a group of cells, found within an organism, that share similar functions. 2. What is the definition of an organ system? An organ system is a group of organs that carries out more generalized set of functions. 3. What organism are you going to use in your foldable? On Desk: -Planner -PENCIL -IAN -PED -Colored Pencils Levels of Organization Foldable Small Large Bellwork 11/9/15 1. What is the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote? Prokaryotes lack internal structure whereas eukaryotes have several organelles. 2. What type of cells make up plants? Eukaryotic Cells 3. What type of cells make up animals? Eukaryotic Cells 4. What type of cells make up bacteria? Prokaryotic Cells On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN Cell Organelles-Eukaryotic Cells Cell Parts • Cells – the basic unit of life • Organelles - small structures inside a cell with specific functions. Analogy – City of Palmer A) Cell Membrane/Plasma Membrane Cell membrane 1. Function: Regulates materials entering and exiting the cell. 2. Structure: Two layers of phospholipids, proteins Analogy – Palmer city limits B) Cytoplasm Cytoplasm 1. Function: All cell contents that lie between the cell membrane and the nucleus. (organelles + cytosol) a. Cytosol = liquid portion/non-organelles. 2. Structure: made up of fluid and organelles except for nucleus Analogy – All air, water, life that are in Palmer, except City Hall C) Nucleus Nucleus 1. Function: “Control Center.” Regulates DNA & RNA actions. 2. Structure: membrane bound, contains DNA Analogy – City Hall D) Nuclear Envelope Nuclear Envelope 1. Function: Regulates what enters or exits the nucleus. 2. Structure: Double Layer of Lipids Analogy – Walls & Doors of City Hall E) Nucleolus Nucleolus 1. Function: Produces RNA, which are used to make all proteins. 2. Structure: Inside Nucleus, separate from DNA Analogy – Mayor Johnson of Palmer F) DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA (chromatin) 1. Function: information on how to make proteins. a. Chromatin – unorganized DNA (normal state) b. Chromosomes – organized DNA (present before cell division 2. Structure: Made up of nucleotides, locked in the nucleus Analogy – The Laws or City Code G) Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER Smooth ER 1. Function: Transportation route for proteins. a. Rough ER: has ribosomes b. Smooth ER: no ribosomes 2. Structure: tubes and channels Analogy – Roads & Sidewalks H) Ribosomes Ribosomes Free Ribosomes 1. Function: Makes proteins. 2. Structure: small circular organelles Analogy – Restaurants, Factories, Builders. I) Vacuoles & Vesicles Vesicles 1. Function: Storage for water, nutrients or waste. 2. Structure: small membrane-bound organelle. Analogy – Grocery stores, water tanks. J) Lysosomes Lysosomes 1. Function: packets of enzymes that break down materials in a cell. 2. Structure: Small membrane-bound organelles Analogy – Recycling center K) Mitochondria Mitochondria 1. Function: Produces energy for the cell – site of cellular respiration. “The Powerhouse” 2. Structure: Double membrane-bound, kidney shaped. Analogy – Matanuska Electric Association L) Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus 1. Function: Packages, labels and ships proteins out of the cell. 2. Structure: Pancake-shaped layered organelle Analogy – Post Office M) Cytoskeleton Microfilaments Microtubules 1. Function: Provide support and structure for the cell. a. Microfilaments b. Microtubules 2. Structure: Tubules Analogy – Wood, cement, steel beams N) Centrioles (Animals Only) Centrioles 1. Function: microtubules that help divide the cell during cell division. • Structure: Tubules Analogy – Palmer Jr. MS vs. Colony MS O) Cilia & Flagella Flagella Flagella Cilia 1. Function: provides movement for the cell or objects moving by the cell. 2. Structure: a. Flagella – 1 long fiber b. Cilia – many short fibers Analogy – Cars or bicycles. P) Chloroplasts (Plants only) Chloroplasts 1. Function: site of photosynthesis (converting sun and CO2 into sugar). 2. Structure: Membrane bound organelles that contain chlorophyll Analogy – Solar Panels Q) Cell Wall (Plant cells only) Cell Wall 1. Function: Provides support for the cell and the plant. 2. Structure: Made of cellulose Analogy – ground, rock wall Cell Parts Analogy • Create an analogy (besides the city analogy) for the cell and its parts • Possible ideas: – Stadium – School – Country – Restaurant – House – Mall – Waterpark Stadium Example: • • • • Cell membrane: wall of stadium, gates Cytoplasm: everything inside the stadium. Nucleus: the control room for the stadium. Etc… Glue into IAN! • Input- description of organelles • Output- Your “working” cell https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wRZthGlzEUc Bellwork 11/10/15 1. What cell analogy are you creating for your project? 2. What is the cell membrane of your analogy and how does it function? On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN -Cell Analogy Worksheet Example: Cell Parts Analogy • Create an analogy (besides the city analogy) for the cell and its parts • Possible ideas: – Stadium – School – Country – Restaurant – House – Mall – Waterpark Bellwork 11/12/15 1. What is the nucleus of your analogy and how does it function? 2. What is the mitochondria of your analogy and how does it function? On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN -Cell Analogy Worksheet Continue Working: Cell Parts Analogy Bellwork 11/13/15 1. What is the golgi apparatus of your analogy and how does it function? 2. What is the endoplasmic reticulum of your analogy and how does it function? On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN -Cell Analogy Worksheet Continue Working: Cell Parts Analogy Don’t forget: -Cell Analogy Worksheet and Picture -Label each organelle and structure on your picture -Use color 28 Bellwork 11/16/15 1.Identify the items on the front desk. A. B. 2. Write down some qualitative observations of object “A”. (look back through your notes if you forgot what qualitative observations are ) On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN -Cell Analogy Worksheet Naked Eggs Data Table Tests 11 and 12 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dngsFl2X3nc Bellwork 11/17/15 1. Write down some qualitative observations of the egg. HERE! On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN Naked Eggs Data Table Bellwork 11/18/15 1. Write down some qualitative observations of the egg. HERE! On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN Naked Eggs Data Table 3D Cell Model • Update Table of Contents • Due Wednesday the 25th 3D Cell Model I am making a ______ cell. Materials: ______________ Bellwork 11/18/15 1. Write down some qualitative observations of the egg. HERE! On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN Naked Eggs Data Table Animal Cell Foldable- color Animal Cell Foldable- Cut and Glue Bellwork 11/18/15 1. Write down some qualitative observations of the egg. HERE! On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN Naked Eggs Data Table Colleen.walker@matsuk12.us Let’s finish our Animal Cell Foldable 1. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 3. Ribosome 4. Centrioles 5. Cytoplasm 6. Golgi Apparatus 7. Nucleus 8. Cell membrane 9. Cytoskeleton 10.Mitochondria 11.Lysosome Animal Cell Worksheet Color and label each organelle 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Centrioles Cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Cell membrane Cytoskeleton Mitochondria Lysosome Plant Cell Foldable- Color Bellwork 11/23/15 1. Name two organelles that occur in plant cells but not in animal cells. The cell wall and chloroplasts are only found in animal cells. 2. Grab a plant cell foldable and start coloring. On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN -Glue -Scissors -Colored Pencils Plant Cell Foldable- Cut and Glue 1. 2. 3. 4. Color, cut and glue Glue into IAN Label “Purple” Flaps Check you work (front table) 5. Work on “Plant Cell” worksheet (colored and labeled) HW Plant Cell Organelles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Vacuole Cytoskeleton Ribosome Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell Wall Cell membrane Chloroplast Mitochondria Homework: Plant Cell Worksheet Color and label each organelle 1. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 3. Vacuole 4. Cytoskeleton 5. Ribosome 6. Golgi Apparatus 7. Nucleus 8. Cytoplasm 9. Cell Wall 10. Cell membrane 11. Chloroplast 12. Mitochondria Bellwork 11/24/15 1. Create a Double Bubble thinking map to show the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells. On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN - Plant Cell HW Bellwork Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 9/15/15 #1 11/2/15 #2 11/9/15 #1 11/13/15 #2 Use the following format to receive full credit. Q:_______________________ A:_______________________ Key 1.9/15/15 #1 What are the seven steps of the scientific method? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Choose problem Research problem Develop hypothesis Write procedures Test hypothesis Organize data State conclusions 2.11/2/15 # 2 What is the largest known cell? The largest know cell is the ostrich egg. 3. 11/9/15 #1 What is the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote? Prokaryotes lack internal structure whereas eukaryotes have several organelles. 4. 11/13/15 #2 What is the endoplasmic reticulum of your analogy and how does it function? Bellwork 11/25/15 1.Identify each organelle. A. B. C. D. E On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN CELL-ebration! Bellwork 11/30/15 1.Identify each organelle. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. On Desk: -Planner -Pen/Pencil -IAN Review Day!! • Bingo • Memory • Target Test 10 Online Resources • Flash Cardshttps://quizlet.com/3082892/flashcards • Review Activitieshttp://www.quia.com/jg/65947.html • Who Wants to be a Millionaire http://www.quia.com/rr/445859.html • Jeopardy https://www.superteachertools.us/jeopardyx/je opardy-reviewgame.php?gamefile=398503#.VjAJdrerSmU Plant Cell Model J-E-L-L-O!!!!! 1. Identify which organelles each candy at your table represents. 2. Fill in your cell model and color it. 3. Let’s make jello cells! Jello Cell Model