Ch. 7 Cells Vocabulary (quiz Wednesday)
advertisement

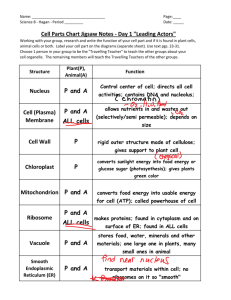
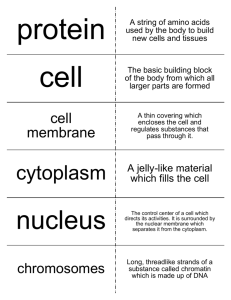
Ch. 7 1. Introduction to Cells Cell theory Cell size Cell shape Cell features CELL THEORY • All living things are made up of one or more cells (living = cells) • Cells are the basic unit of structure & function in organisms (smallest living part = cells) • All cells rise from existing cells (cells come from cells) CELL SIZE ** 200 types of cells** **100 trillion cells = human body** • Cell size limited by surface area-to-volume ratio • Surface area (cell membrane) = big = a lot of places for substances to go in & out Volume (total space cell takes up) = small = a little bit of space to have to travel So. . . A large surface area to volume ratio = can exchange substances more efficiently Ex: 6:1 C E L L S H A P E • A cell’s shape reflects its function • Nerve cells = much longer than they are thick • Shape may increase surface area for exchange • Skin cells = broad & flat • Grow in some ways & remain small in other • Makes surface area to volume larger C E L L F E A T U R E S ALL CELLS HAVE… • 1. Cell membrane ~ outer boundary • 2. Cytoplasm ~ fluid inside cell (cytosol) & all structures suspended C E L L F E A T U R E S ALL CELLS HAVE… • 3. Ribosomes ~ proteins are made here! • 4. DNA ~ instructions, regulates activities, enables reproduction Features of Prokaryotic Cells (single celled) • DNA = a single loop near center • Ribosomes & enzymes = in cytoplasm • Cell wall surrounds membrane – Structure & support – Capsule allows cling to surfaces • Very small • Live in wide range of habitats Features of a Eukaryotic Cell • Single celled or multi cellular • Complex organization = more specialized functions • Contains compartments separated by membranes = organelles (some are connected by channels) • DNA in a nucleus 2. INSIDE the cell: Framework Cytoskeleton Helps cell move, keep its shape, & organize parts Microfilament ~ long, thin, actin, contract to pull in & expand to push out Microtubules ~ thick, hollow, tubulin, info. mol. pass thru Intermediate fibers ~ mod. thick, anchors organelles & enzymes Cytoskeleton INSIDE the cell: Directing activity Nucleus “The Brain” Double membrane (nuclear envelope) which protects & houses DNA Pores to allow passage of RNA & ribosome parts Contains nucleolus, which makes ribosome parts INSIDE the cell: Directing activity Ribosomes Made of protein & RNA “Free” ~makes proteins that remain in cell “Bound” ~makes proteins that leave cell ~attached to organelle INSIDE the cell: protein processing Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) System of internal membranes which move stuff Rough w/ ribosomes modify proteins for export Smooth w/o ribosomes makes lipids, breaks down toxic substances INSIDE the cell: protein processing Golgi apparatus/body Set of flattened sacs Modifies proteins when they come in by vesicle from the ER Modifies, sorts, & packages proteins for export **VESICLES move these substances in & out of ER & golgi** INSIDE the cell: energy production Mitochondrion “Power house” Makes ATP (cellular energy) in inner membrane Smooth outer membrane & folded inner membrane INSIDE the cell: energy production Chloroplast Found in plant cells & some protist Uses light energy to make sugar from carbon dioxide & water ~ photosynthesis Double membrane w/sacs INSIDE the cell: storage & maintenance • Lysosome ~ contains enzymes that break down large molecules. Ex: food, old, damaged cell parts • Central vacuole ~ large compartment of plant cells. Stores water, ions, nutrients & waste. If full, plants stand upright (turgur pressure). If lose water, plants wilt. • Other vacuoles ~ food & contractile 3. Diversity in ________. Vary in . . . • shape • way obtain & use energy • make up of cell walls • Movement flagella long, threadlike pili short, thick, attachment Diversity in ________. Animal cells Plant cells Central vacuole Chloroplasts Cell wall Vary in organelles Specialized function Ex: muscle cells=many mitochondria