Chapter 7
advertisement

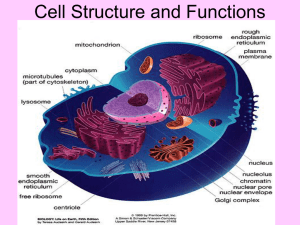
Chapter 7 Cell Discover & Theory • What made the discovery of the cell possible? • Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Dutch scientist (1675) – Used a microscope to view living creatures from pond water. • Mattias Schleiden – German botanist (1838) – Proposed that all plants are made up of cells •Theodore Schwann –German zoologist (1839) –Stated that all animals are made up of cells • Rudolph Virchow – German physician (1858) – Determined that cells come only from other cells and must be like the original cell. Cell Theory • 1. All living things are made up on one or more cells. • 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. • 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Cell Organelles ORGANELLE NAME DESCRIPTION PICTURE Cell Wall • • • • In plants & fungi ONLY Composed of cellulose Used for support and protection Acts as a skeleton for plants Cell (Plasma) Membrane • Controls what moves in and out of the cell, – Selectively permeable membrane – only allows selected substances to move in & out – Structure is a bilayer of phospholipid molecules with proteins embedded in the layers. Proteins can act as channels for molecules to move through membrane & allow communication with environment. Cytoplasm • Clear, thick suspension made up mostly of water, like a nutrient broth • Used to suspend the organelles Nucleus • • • • Control center of the cell Directs cell activities Houses DNA & RNA Membrane - nuclear envelop nucleolus Nuclear envelope Vacuole • Large Central Vacuole in plant cells ONLY • Storage unit for food, water, and waste. Vesicle • Transports substances in cells, like a delivery truck Lysosomes • Contain enzymes that digest & recycle a cell’s used parts; a garbage disposal Cytoskeleton • Microscopic fibers (microfilaments & microtubules) used for support & structure, the internal skeleton of the cell Ribosomes • Protein factories of the cell • Makes proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • A transportation system: internal membranes that move protein & other substances through the cell, – Rough ER: ribosomes attached – Smooth ER: no ribosomes Golgi Apparatus • Packaging & distribution center of the cell, like the Post Office Chloroplast • In plants ONLY • Green structure that stores energy from the sun in sugar molecules. • Converts CO2 and H2O into sugar and O2 • Contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis Mitochondria • Powerhouse of the cell • Converts energy from organic compounds to ATP Centrosome/Centrioles • In animal cells ONLY • Used in cell reproduction, builds microtubules • Form a complex called the centrosome,