sand sampling apparatus - FAMU
advertisement

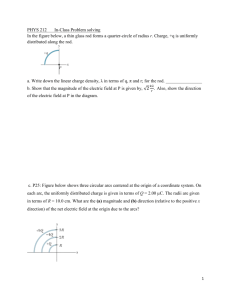
SAND SAMPLING APPARATUS Eglin Air Force Base Gina Teofilak Richard Klimas Dan Mortensen Ruben De Sousa Overview Introduction Current Design Maintenance and Safety Design Specifications Motion Control Motion Control Components Obstacles Cost Analysis Future Plans 2 INTRODUCTION Introduction Projectile Target shot line Fractured sand 3 EGLIN VISIT 10/31/2008 Experimental Changes Newly added forklift straddles 4 CURRENT DESIGN Current Design Uses 2 linear motion actuators for Y and Z motion ¾ inch ACME threaded rod Designed to be a lead screw Each will have an aluminum extrusion frame Y and Z are different sizes ¼ inch aluminum rod stabilizers for support y X z motion to be attained from 2 DC motors Z- actuator is mounted directly to the Y- actuator Legs of Y- actuator mount to wheels to produce X motion 5 CURRENT DESIGN Motion in the X-direction Chain and sprocket motion Wheels fit inside aluminum extrusion grooves DC motor attached to sprocket Chain is clamped to actuator Clamp has teeth of same pitch as the chain Chain mount is adjustable for chain tension 6 Future Considerations for X Axis Instead of wheels, an eight foot long steel rod is considered with linear bearings Steel rod will make it safer for installation than wheel base Prevents tipping when installing onto experiment Wheels might tip Steel rod is cheaper 7 Maintenance and Safety Material are corrosive resistant Threaded rod is hardened stainless steel Will not corrode based on interaction with other materials used Experiment is only ran one time a month When not used it will be stored in indoor atmosphere To keep sand out of moving parts: Bearings with brush guards will used Plastic accordion style rod boots will cover the lead screws Plastic guards will be mounted to keep sand out of x- actuator tracks Lubrication is not required Bearings are shielded ACME lead screw does not require lubrication Safety: Chain guard Safety stickers By all moving parts and electrical components 8 Design Specifications Size: Length 96” Width 27” Height 24” Weight: Mechanism 70 lbs. Vacuum 20 lbs. Electronics5 lbs. Vacuum Power: 6.5 Hp peak Volume: 20 gallons (supplied by Eglin) Mechanism Speed: 2 in/sec Motion Control Motion control 3 DC motors/ controllers microprocessor encoders/ switches y Y axis motion threaded rod aluminum rods for support X z Z axis motion threaded rod vacuum tube rigidly attached Control Sequence z axis ½”-1” y axis 24” x axis 4” 10 Motion Control Schematic X Direction Movement Motor Controller Encoder Motor Z Direction Movement Wall Socket Power Supply Motor Controller Microprocessor Encoder Motor Switches Motor Y Direction Movement Motor Controller Control System Schematic DC Power supply Microprocessor stores code Motor Controllers Distances components Motors Geared motors Required Torque Required Torque Needed (oz*in) X movement 20 Y movement 40 Z movement 20 11 Motion Control Components Why use different distance components? Encoders Convert rotations of shaft to code Encoder Precise measurement of distance Can be used to input exact position Switches Simple short circuit switches Easier to program Cheaper Encoders Switches 12 Motion Control Obstacles Make Screens They are a problem Break and Deform Slightly unequally spaced Removed for simplicity Suggested from the sponsor Projectile Entry Tube Adds safety to the experiment Cannot be removed Mechanism is designed to avoid 13 Cost Analysis Option Total (USD) Machine Shop Wheels and corrosion res.chain 1387.53 Wheels and noncorrosion res.chain 1347.33 Rods and corrosion res.chain 1281.94 Rods and non-corrosion res.chain 1241.74 Current design is more expensive than using the rod Material Cost Shipping Testing Facilities Possible testing table Cost Comparison for X-axis Options Cost(USD) 550.00 500.00 450.00 400.00 Rod Option 350.00 300.00 250.00 200.00 150.00 100.00 50.00 0.00 Rod Option Raw Materials Donations Wheels Option Wheels Option Parts Purchased Control System 14 Future Plans Purchase Parts Machine and Assemble December 2 – January 6 Write the program Test Write Procedures Make modifications Conduct the Experiment Meet the Class Deliverables January 6 – April 24 REFERENCES 1. Cooper, William “Bill”, MSgt Wes Schuler, AFRL/RW Munitions Directorate Air Force Research Laboratory 2. Mortensen, Charles, Owner, Dynatech Associates 3. Dr. Chiang Shih, FAMU-FSU College of Engineering, Mechanical 4. Dr. Daudi Waryoba, FAMU-FSU College of Engineering, Mechanical COST REFERENCES Carbon Stick tape http://www.2spi.com/catalog/spec_prep/cond_adhes-discs.shtml Aluminum Extrusion Dynatech Associates McMASTER-CARR http://www.mcmaster.com/ 16 Questions?