personal financial planning
advertisement

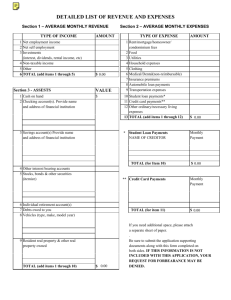
Chapter 1 Key Term personal finance (personal financial planning) 1 personal financial plan 1 per capita debt 1 opportunity cost 1 Financial Planners Standards Council (FPSC) 1 1 1 1 budget planning (budgeting) assets liabilities net worth 1 liquidity 1 money management 1 emergency fund 1 credit management 1 risk 1 risk management 1 insurance planning 1 investment risk Definition The process of planning your spending, financing, and investing activities, while taking into account uncontrollable events such as death or disability, in order to optimize your financial situation over time. A plan that specifies your financial goals, describes the spending, financing, and investing activities that are intended to achieve those goals over time, and the risk management strategies that are required to protect against uncontrollable events such as death or disability. The amount of debt each individual in Canada would have if total debt (consumer debt plus mortgages) was spread equally across the population. What you give up as a result of a decision. A not-for-profit organization that was created to benefit the public through the development, enforcement, and promotion of the highest competency and ethical standards in financial planning. The process of forecasting future income, expenses, and savings goals. What you own. What you owe; your debt. The value of what you own minus the value of what you owe. Access to ready cash, including savings and credit, to cover shortterm or unexpected expenses. Decisions regarding how much money to retain in liquid form and how to allocate the funds among shortterm investment instruments. A portion of savings that you have allocated to short-term needs such as unexpected expenses in order to maintain adequate liquidity. Decisions regarding how much credit to obtain to support your spending and which sources of credit to use Exposure to events (or perils) that can cause a financial loss. Decisions about whether and how to protect against risk. Determining the types and amount of insurance needed to protect your assets. Uncertainty surrounding not only the Sound File 1 risk tolerance 1 retirement planning 1 estate planning 2 2 personal cash flow statement net cash flows 2 budget 2 personal balance sheet 2 liquid assets 2 household assets 2 bonds 2 stocks 2 mutual funds 2 2 real estate rental property 2 current liabilities 2 long-term liabilities 3 excise taxes 3 3 personal income taxes T4 slip potential return on an investment but also its future potential value. A person's ability to accept risk, usually defined as a potential loss of return and/or loss of capital. Determining how much money you should set aside each year for retirement and how you should invest those funds. Determining how your wealth will be distributed before and/or after your death. A financial statement that measures a person's income and expenses. Disposable (after-tax) income minus expenses. A cash flow statement that is based on forecasted cash flows (income and expenses) for a future time period. A summary of your assets (what you own), your liabilities (what you owe), and your net worth (assets minus liabilities). Financial assets that can be easily converted into cash without a loss in value. Items normally owned by a household, such as a car and furniture. Certificates issued by borrowers to raise funds. Certificates representing partial ownership of a firm. Investment companies that sell units to individuals and invest the proceeds in an overall portfolio of investment instruments such as bonds or stocks. Rental property and land. Housing or commercial property that is rented out to others. Personal debts that will be paid in the near future (within a year). Debt that will be paid over a period longer than one year. Special taxes levied on certain consumer products such as cigarettes, alcohol, and gasoline. Taxes imposed on income earned. A document provided to you by your employer that displays your salary and all deductions associated with your employment with that specific employer for the previous year. Your employer is required to provide you with a T4 slip by February 28. 3 Employment Insurance (EI) 3 total income 3 interest income 3 dividend income 3 taxable capital gain 3 capital loss 3 allowable capital loss 3 capital gain 3 deduction 3 T4A slip 3 marginal tax rate 3 tax credits 3 refundable tax credit 3 average tax rate 3 non-refundable tax credits Government benefits that are payable for periods of time when you are away from work due to specific situations. All reportable income from any source, including salary, wages, commissions, business income, government benefits, pension income, interest income, dividend income, and capital gains received during the tax year. Income received from sources outside Canada is also subject to Canadian income tax. Interest earned from investments in various types of savings accounts at financial institutions; from investments in debt securities such as term deposits, GICs, and CSBs; and from loans to other individuals, companies, and governments. Income received from corporations in the form of dividends paid on stock or on mutual funds that hold stock. Dividend income represents the profit due to part owners of the company. The portion of a capital gain that is subject to income tax. The portion included in income is called the inclusion amount and currently stands at 50 percent. Occurs when you sell an asset for a lower price than you paid for it. The portion of a capital loss that you can deduct from taxable capital gains. Money earned when you sell an asset at a higher price than you paid for it. An expense that can be deducted from total income to determine taxable income. A document provided to you when you receive income other than salary income. The percentage of tax you pay on your next dollar of taxable income. Specific amounts used directly to reduce tax liability. The portion of the credit that is not needed to reduce your tax liability (because it is already zero) may be paid to you. The amount of tax you pay as a percentage of your total taxable income. The portion of the credit that is not needed to reduce your tax liability will not be paid to you and cannot be 3 clawback 3 tax planning 3 tax avoidance 3 tax evasion 4 money management 4 depository institutions 4 chartered banks 4 trust and loan companies 4 credit unions/caisses populaires 4 non-depository institutions 4 finance and lease companies 4 mortgage companies 4 investment dealers 4 insurance companies carried forward to reduce your tax liability in the future. Used to reduce (i.e., clawback) a particular government benefit provided to taxpayers who have an income that exceeds a certain threshold amount. Involves activities and transactions that reduce or eliminate tax. A term used to describe the process of legally applying tax law to reduce or eliminate taxes payable in ways that the CRA considers potentially abusive of the spirit of the Income Tax Act. Occurs when taxpayers attempt to deceive the CRA by knowingly reporting less tax payable than what the law obligates them to pay. A series of decisions made over a short-term period regarding income and expenses. Financial institutions that accept deposits from and provide loans to individuals and businesses. Financial institutions that accept deposits and use the funds to provide business and personal loans. These banks are federally incorporated. Financial institutions that, in addition to providing services similar to a bank, can provide financial planning services, such as administering estates and acting as trustee in the administration of trust accounts. Provincially incorporated co-operative financial institutions that are owned and controlled by their members. Financial institutions that do not offer federally insured deposit accounts but provide various other financial services. Non-depository institutions that specialize in providing personal loans or leases to individuals. Non-depository institutions that specialize in providing mortgage loans to individuals. Non-depository institutions that facilitate the purchase or sale of various investments by firms or individuals by providing investment banking and brokerage services. Non-depository institutions that sell insurance to protect individuals or 4 mutual fund companies 4 financial conglomerates 4 cheque register 4 overdraft protection 4 stop payment 4 debit card 4 safety deposit box 4 automated banking machine (ABM) 4 certified cheque 4 money orders and drafts 4 traveller's cheque 4 guaranteed investment certificate (GIC) firms from risks that can incur financial loss. Non-depository institutions that sell units to individuals and use the proceeds to invest in securities to create mutual funds. Financial institutions that offer a diverse set of financial services to individuals or firms. A booklet in your chequebook where you record the details of each transaction you make, including deposits, cheque writing, withdrawals, and bill payments. An arrangement that protects a customer who writes a cheque for an amount that exceeds their chequing account balance; it is a short-term loan from the depository institution where the chequing account is maintained. A financial institution's notice that it will not honour a cheque if someone tries to cash it; usually occurs in response to a request by the writer of the cheque. A card that is not only used for identification for your bank, but also allows you to make purchases that are charged against an existing chequing account. A box at a financial institution in which a customer can store documents, jewellery, and other valuables. It is secure because it is stored in the bank's vault. A machine individuals can use to deposit and withdraw funds at any time of day. A cheque that can be cashed immediately by the payee without the payee having to wait for the bank to process and clear it. Products that direct your bank to pay a specified amount to the person named on them. A cheque written on behalf of an individual that will be charged against a large, well-known financial institution or credit card sponsor's account. An instrument issued by a depository institution that specifies a minimum investment, an interest rate, and a maturity date. 4 Canada Savings Bonds (CSBs) 4 money market funds (MMFs) 5 credit 5 instalment credit 5 revolving open-end credit 5 credit reports 5 5 retail (or proprietary) credit card prestige cards 5 finance charge 5 consumer proposal 5 insolvent 5 trustee in bankruptcy 5 identity theft 5 shoulder surfing 5 dumpster diving 5 skimming Short-term to medium-term, highquality debt securities issued by the Government of Canada. Accounts that pool money from individuals and invest in securities that have short-term maturities, such as one year or less. Funds provided by a creditor to a borrower that the borrower will repay with interest or fees in the future. Credit provided for specific purchases, with interest charged on the amount borrowed. It is repaid on a regular basis, generally with blended payments. Credit provided up to a specified maximum amount based on income, debt level, and credit history; interest is charged each month on the outstanding balance. Reports provided by credit bureaus that document a person's credit payment history. A credit card that is honoured only by a specific retail establishment. Credit cards, such as gold cards or platinum cards, issued by a financial institution to individuals who have an exceptional credit standing. The interest and fees you must pay as a result of using credit. An offer made by a debtor to his or her creditors to modify his or her payments. A person who owes at least $1000 and is unable to pay his or her debts as they come due. A person licensed to administer consumer proposals and bankruptcies and manage assets held in trust. Occurs when an individual uses personal, identifying information unique to you, such as your Social Insurance Number, without your permission for their personal gain. Occurs in public places where you can be readily seen or heard by someone standing close by. Occurs when an identity thief goes through your trash for discarded items that reveal personal information that can be used for fraudulent purposes. Occurs when identity thieves steal your credit or debit card number by copying the information contained in 5 pretexting 5 phishing 5 pharming 6 loan contract 6 amortize 6 maturity or term 6 collateral 6 secured loan 6 6 unsecured loan payday loan 6 annual percentage rate (APR) 6 simple interest 6 add-on interest method 6 home equity loan 6 equity 6 equity of a home 6 second mortgage 6 prime rate the magnetic strip on the card. Occurs when individuals access personal information under false pretenses. Occurs when pretexting happens online. Similar to phishing, but targeted at larger audiences, it directs users to bogus websites to collect their personal information. A contract that specifies the terms of a loan as agreed to by the borrower and the lender. To repay the principal of a loan (the original amount borrowed) through a series of equal payments. A loan repaid in this manner is said to be amortized. With respect to a loan, the life or duration of the loan. Assets of a borrower that back a loan in the event that the borrower defaults. Collateral is a form of security for the lender. A loan that is backed or secured by collateral. A loan that is not backed by collateral. A short-term loan provided in advance of receiving a paycheque. Measures the finance expenses (including interest and all other expenses) on a loan annually. Interest on a loan computed as a percentage of the existing loan amount (or principal). Compounding is not taken into account. A method of determining the monthly payment on a loan; it involves calculating the interest that must be paid on the loan amount, adding together interest and loan principal, and dividing by the number of payments. A loan in which the equity in a home serves as collateral. The market value of your home less any outstanding mortgage balance and/or debts held by others that are secured against your property. The market value of a home minus the debt owed on the home. A secured mortgage loan that is subordinate (or secondary) to another loan. The interest rate a bank charges its 6 student loan 7 Multiple Listing Service (MLS) 7 pre-approval certificate 7 gross debt service ratio (GDSR) 7 total debt service ratio (TDSR) 7 market analysis 7 conventional mortgage 7 high ratio mortgage 7 7 7 vendor take-back mortgage home inspection interest adjustment 7 amortization 7 mortgage term 7 closed mortgage 7 open mortgage 7 fixed-rate mortgage best customers. A loan provided to finance a portion of a student's expenses while pursuing post-secondary education. An information database of homes available for sale through realtors who are members of the service. Provides you with a guideline on how large a mortgage you can afford based on your financial situation. Your mortgage-related debt payments; including mortgage loan repayments, heating costs, property taxes, and any condo fees; divided by your total monthly gross household income. Your mortgage-related debt payments plus all other consumer debt payments divided by your total monthly gross household income. An estimate of the price of a home based on the prices of similar homes in the area. A mortgage where the down payment is at least 25 percent of the home's appraised value. A mortgage where the down payment is less than 25 percent of the home's appraised value. A mortgage where the lender is the seller of the property. A report on the condition of the home. Occurs when there is a difference between the date you take possession of your home and the date from which your lender calculates your first mortgage payment. The expected number of years it will take a borrower to pay off the entire mortgage loan balance. The period of time over which the mortgage interest rate and other terms of the mortgage contract will not change. Restricts your ability to pay off the mortgage balance during the mortgage term unless you are willing to pay a financial penalty. Allows you to pay off the mortgage balance at any time during the mortgage term. A mortgage in which a fixed interest rate is specified for the term of the mortgage. 7 variable-rate mortgage (VRM) 7 mortgage refinancing 8 8 8 premium peril underwriters 8 insurance agent 8 8 captive (or exclusive) insurance agent independent insurance agent insurance policy 8 auto insurance policy 8 third party liability 8 bodily injury liability coverage 8 property damage liability coverage 8 accident benefits coverage 8 uninsured motorist coverage 8 underinsured motorist coverage 8 collision insurance 8 comprehensive coverage 8 A mortgage where the interest charged on the loan changes in response to movements in a specific market-determined interest rate. The rate used is usually referred to as prime. Lenders will add a percentage to prime for the total mortgage rate. Paying off an existing mortgage with a new mortgage that has a lower interest rate. The cost of obtaining insurance. A hazard or risk you face. Employees of an insurance company who determine the risk of specific insurance policies and decide what policies to offer and what premiums to charge. Represents one or more insurance companies and recommends insurance policies that fit customers' needs. Works for one particular insurance company. Represents many different insurance companies. Contract between an insurance company and the policy owner. Specifies the coverage provided by an insurance company for a particular individual and vehicle. A legal term that describes the person(s) who have experienced loss because of the insured. Protects you against liability associated with injuries you cause to others. Protects against losses that result when the policy owner damages another person's property with his or her car. Insures against the cost of medical care for you and other passengers in your car. Insures against the cost of bodily injury when an accident is caused by another driver who is not insured. Insures against the additional cost of bodily injury when an accident is caused by a driver who has insufficient coverage. Insures against costs of damage to your car resulting from an accident in which the driver of your car is at fault. Insures you against damage to your car that results from something other 8 deductible 8 Facility Association 8 exclusion 8 homeowner's insurance 8 all perils coverage 8 named perils coverage 8 cash value policy 8 replacement cost policy 8 home inventory 8 personal property floater 8 tenant's insurance 8 umbrella personal liability policy 9 health insurance 9 medicare 9 Canada Health Act than a collision, such as floods, theft, fire, hail, explosions, riots, vandalism, and various other perils. A set dollar amount that you are responsible for paying before any coverage is provided by your insurer. Ensures that drivers unable to obtain insurance with an individual company are able to obtain the coverage they need to operate their vehicles legally. A term appearing in insurance contracts or policies that describes items or circumstances that are specifically excluded from insurance coverage. Provides insurance in the event of property damage, theft, or personal and third party liability relating to home ownership. Protects the home and any other structures on the property against all events except those that are specifically excluded by the policy. Protects the home and any other structures on the property against only those events named in the policy. Pays you the value of the damaged property after considering its depreciation. Pays you the actual cost of replacing the damaged property. Contains detailed information about your personal property that can be used when filing a claim. An extension of the homeowner's insurance policy that allows you to itemize your valuables. An insurance policy that protects your possessions within a house, condominium, or apartment that you are renting. A supplement to auto and homeowner's insurance that provides additional personal liability coverage. A group of insurance benefits provided to a living individual as a result of sickness or injury. An interlocking system of ten provincial and three territorial health insurance plans provided by the governments, including the federal government. Establishes the criteria and conditions related to insured health care services 9 insured health care services 9 insured person 9 Canada Health and Social Transfer (CHST) 9 disability income insurance 9 indemnification 9 waiting period 9 long-term care insurance 10 life insurance 10 face amount 10 beneficiary 10 life insured 10 policy owner 10 term insurance 10 grace period 10 mortality rate that provinces and territories must meet in order to receive money from the federal government for health care. Medically necessary hospital, physician, and surgical-dental services provided to insured persons. An eligible resident of a province. Does not include someone who may be covered by other federal or provincial legislation. The largest federal transfer of money to the provinces and territories, providing them with cash payments and tax transfers in support of health care, post-secondary education, social assistance, and social services, including early childhood development. A monthly insurance benefit paid to you in the event that you are unable to work as a result of an injury or an illness. The concept of putting an insured individual back into the same position he or she was in prior to the event that resulted in insurance benefits being paid. The period from the time you become disabled until you begin to receive disability income benefits. Covers expenses associated with long-term health conditions that cause individuals to need help with everyday tasks. Insurance that provides a payment to a specified beneficiary when the insured dies. The amount stated on the face of the policy that will be paid on the death of the insured. The named individual who receives life insurance payments upon the death of the insured. The individual who is covered in the life insurance policy. The individual who owns all rights and obligations to the policy. Life insurance that is provided over a specified time period and does not build a cash value. The period the insurance company extends to the policy owner before the policy will lapse due to nonpayment. The number of deaths in a population 10 underwriting 10 creditor insurance 10 creditor 10 decreasing term insurance 10 group term insurance 10 permanent insurance 10 cost of insurance 10 cash value 10 death benefit 10 whole life insurance 10 limited payment policy 10 universal life insurance 10 non-forfeiture options 10 paid-up insurance or in a subgroup of the population. The process of evaluating an insurance application based on the applicant's age, sex, smoking status, driving record, and other health and lifestyle considerations and then issuing insurance policies based on the responses. Term life insurance where the beneficiary of the policy is a creditor. An individual or company to whom you owe money. A type of creditor insurance, such as mortgage life insurance, where the life insurance face amount decreases each time a regular payment is made on debt that is amortized over a period of time. Term insurance provided to a designated group of people with a common bond that generally has lower-than-typical premiums. Life insurance that continues to provide insurance for as long as premiums are paid. The insurance-related expenses incurred by a life insurance company to provide the actual death benefit, sometimes referred to as the pure cost of dying. The portion of the premium in excess of insurance-related and company expenses that is invested by the insurance company on behalf of the policy owner. The total amount paid tax-free to the beneficiary upon the death of the policy owner. A form of permanent life insurance that builds cash value based on a fixed premium that is payable for the life of the insured. Allows you to pay premiums over a specified period but remain insured for life. A form of permanent life insurance for which you do not pay a fixed premium and in which you can invest the cash value portion in a variety of investments. The options available to a policy owner who would like to discontinue or cancel a policy that has cash value. A permanent life insurance policy that results from exercising a non- 10 term to 100 insurance 10 participating policy 10 non-participating policy 10 policy dividend 10 income method 10 budget method (or needs method) 10 reinstatement 10 10 living benefits (accelerated death benefits) renewability option 10 conversion option 10 riders 10 settlement options 10 lump sum settlement 10 instalment payments settlement 10 interest payments settlement forfeiture option on a policy that has accumulated cash value. A form of permanent life insurance designed for the sole purpose of providing a benefit at death. A life insurance policy that is eligible to receive policy dividends. A life insurance policy that is not eligible to receive policy dividends. A refund of premiums that occurs when the long-term assumptions the insurance company made with respect to the cost of insurance, company expenses, and investment returns have changed. Determines how much life insurance is needed based on the policyholder's annual income. A method that determines how much life insurance is needed based on the household's future expected expenses and current financial situation. The process of completing a reinstatement application to restore a policy that is in lapse status. Benefits that allow the policyholder to receive a portion of death benefits prior to death. Allows you to renew your policy for another term once the existing term expires. Allows you to convert your term insurance policy into a whole life policy that will be in effect for the rest of your life. Options that allow you to customize a life insurance policy to your specific needs. The ways in which a beneficiary can receive life insurance benefits in the event that the policyholder dies. A single payment of all benefits owed to a beneficiary upon the death of the policyholder. The payment of life insurance benefits owed to a beneficiary as a stream of equal payments over a specified number of years. A method of paying life insurance benefits in which the insurance company retains the amount owed to the beneficiary for a specified number of years and pays interest to the beneficiary. 11 exchange traded fund (ETF) 11 primary market 11 initial public offering (IPO) 11 secondary market 11 institutional investors 11 individual investors 11 day traders 11 growth stocks 11 value stocks 11 income stocks 11 common stock 11 preferred stock 11 range of returns 11 standard deviation 11 risk premium 11 default 11 asset allocation 11 portfolio 11 insider information A portfolio of securities whose value moves in tandem with a particular stock index. Unlike a mutual fund, these funds trade on an exchange or stock market. A market in which newly issued securities are traded. The first offering of a firm's shares to the public. A market in which existing securities such as debt securities are traded. Professionals responsible for managing large pools of money, such as pension funds, on behalf of their clients. Individuals who invest funds in securities. Investors who buy stocks and then sell them on the same day. Shares of firms with substantial growth opportunities. Stocks of firms that are currently undervalued by the market for reasons other than the performance of the businesses themselves. Stocks that provide investors with periodic income in the form of large dividends. A certificate issued by a firm to raise funds that represents partial ownership in the firm. A certificate issued by a firm to raise funds that entitles shareholders to first priority to receive dividends. Returns of a specific investment over a given period. The degree of volatility in the stock's returns over time. An additional return beyond the riskfree rate you could earn from an investment. Occurs when a company borrows money through the issuance of debt securities and does not pay either the interest or the principal. The process of allocating money across financial assets (such as mutual funds, stocks, and bonds) with the objective of achieving a desired return while maintaining risk at a tolerable level. A set of multiple investments in different assets. Non-public information known by employees and other professionals 11 correlation 11 income trust 11 real estate investment trusts (REITs) 12 equity mutual funds 12 bond mutual funds 12 money market mutual funds 12 marketability 12 liquidity 12 net asset value (NAV) 12 12 net asset value per unit (NAVPU) discount 12 no-load mutual funds 12 front-end load mutual funds 12 back-end load mutual funds 12 declining redemption schedule 12 open-end mutual funds 12 closed-end funds 12 premium that is not known by outsiders. It is illegal to use insider information. A mathematical measure that describes how two securities' prices move in relation to one another. A flow-through investment vehicle that generates income and capital gains for investors. Income trusts that pool investments from individuals and use the proceeds to invest in real estate. Funds that sell units to individuals and use this money to invest in stocks. Funds that sell units to individuals and use this money to invest in bonds. Funds that sell units to individuals and use this money to invest in cash and investments that can be converted to cash quickly (very liquid investments). The ease with which an investor can convert an investment into cash. The ease with which the investor can convert the investment into cash without a loss of capital. The market value of the securities that a mutual fund has purchased minus any liabilities and fees owed. Calculated by dividing the NAV by the number of units in the fund. The amount by which a closed-end fund's unit price in the secondary market is below the fund's NAVPU. Funds that sell directly to investors and do not charge a fee. Mutual funds that charge a fee at the time of purchase, which is paid to stockbrokers or other financial service advisers who execute transactions for investors. Mutual funds that charge a fee if units are redeemed within a set period of time. A fee schedule where the back-end load charge reduces with each year an investor holds the fund. Funds that sell units directly to investors and will redeem those units whenever investors wish to "cash" in. Funds that sell units to investors but will not redeem these units; instead, the fund's units are traded on a stock exchange. The amount by which a closed-end fund's unit price in the secondary market is above the fund's NAVPU. 12 management expense ratio (MER) 12 sector funds 12 index funds 12 global bond funds 12 exchange rate risk 12 market risk 12 hedge funds 12 interest rate risk 12 simplified prospectus 12 investment objective 12 investment strategy 13 balance sheet 13 income statement 13 current ratio 13 times interest earned ratio The annual expenses incurred by a fund on a percentage basis, calculated as annual expenses of the fund divided by the net asset value of the fund; the result of this calculation is then divided by the number of units outstanding. Mutual funds that focus on stocks in a specific industry or sector, such as technology stocks. Mutual funds that attempt to mirror the movements of an existing equity index. Mutual funds that focus on bonds issued by non-Canadian firms or governments. The risk that the value of a bond may drop if the currency denominating the bond weakens against the Canadian dollar. The susceptibility of a mutual fund's performance to general market conditions. Limited partnerships that manage portfolios of funds for wealthy individuals and financial institutions. The risk that occurs because of changes in the interest rate. This risk affects funds that invest in debt securities and other income-oriented securities. A document that provides financial information about a mutual fund, including expenses and past performance. In a prospectus, a brief statement about the general goal of the mutual fund. In a prospectus, a summary of the types of securities that are purchased by the mutual fund to achieve its objective. A financial statement that indicates a firm's sources of funds and how it has invested those funds as of a particular point in time. A financial statement that measures a firm's revenues, expenses, and earnings over a particular period of time. The ratio of a firm's short-term assets to its short-term liabilities. A measure of financial leverage that indicates the ratio of the firm's earnings before interest and taxes to 13 inventory turnover 13 average collection period 13 asset turnover ratio 13 operating profit margin 13 net profit margin 13 return on assets 13 return on equity 13 financial leverage 13 debt ratio 13 economic growth 13 13 gross domestic product (GDP) fiscal policy 13 monetary policy 13 inflation 13 consumer price index (CPI) 13 technical analysis 13 fundamental analysis 13 price–earnings (P/E) method its total interest payments. A measure of efficiency; computed as the cost of goods sold divided by average daily inventory. A measure of efficiency; computed as accounts receivable divided by average daily sales. A measure of efficiency; computed as sales divided by average total assets. A firm's operating profit divided by sales. A measure of profitability that measures net profit as a percentage of sales. A measure of profitability; computed as net profit divided by total assets. A measure of profitability; computed as net profit divided by the owners' investment in the firm (shareholders' equity). A firm's reliance on debt to support its operations. A measure of financial leverage that calculates the proportion of total assets financed with debt. The growth in a country's economy over a particular period. The total market value of all products and services produced in a country. How the government imposes taxes on individuals and corporations and how it spends tax revenues. Techniques used by the Bank of Canada (central bank) to affect the economy of the country. The increase in the general level of prices of products and services over a specified period. A measure of inflation that represents the increase in the prices of consumer products such as groceries, household products, housing, and gasoline over time. The valuation of stocks based on historical price patterns using various charting techniques. The valuation of stocks based on an examination of fundamental characteristics such as revenue, earnings, and/or the sensitivity of the firm's performance to economic conditions. A method of valuing stocks in which a firm's earnings per share are multiplied by the mean industry price– 13 price–sales (P/S) method 13 efficient stock market 13 inefficient stock market 13 stock exchanges 13 venture capital 13 market makers 13 demutualization 13 over-the-counter (OTC) market 13 full-service brokerage firm 13 discount brokerage firm 13 ticker symbol 13 board lot 13 odd lot 13 market order 13 limit order 13 on-stop order 13 buy stop order 13 sell stop order earnings (P/E) ratio. A method of valuing stocks in which the revenue per share of a specific firm is multiplied by the mean industry ratio of share price to revenue. A market in which stock prices fully reflect information that is available to investors. A market in which stock prices do not reflect all public information that is available to investors. Facilities that allow investors to purchase or sell existing stocks. Refers to investors' funds destined for risky, generally new businesses with tremendous growth potential. Securities dealers who are required to trade actively in the market so that liquidity is maintained when natural market forces cannot provide sufficient liquidity. Refers to the transformation of a firm from a member-owned organization to a publicly owned, for-profit organization. An electronic communications network that allows investors to buy or sell securities. A brokerage firm that offers investment advice and executes transactions. A brokerage firm that executes transactions but does not offer investment advice. The abbreviated term used to identify a stock for trading purposes. Shares bought or sold in multiples of typically 100 shares. The size of the board lot depends on the price of the security. Less than a board lot of that particular stock. An order to buy or sell a stock at its prevailing market price. An order to buy or sell a stock only if the price is within limits that you specify. An order to execute a transaction when the stock price reaches a specified level; a special form of limit order. An order to buy a stock when the price rises to a specified level. An order to sell a stock when the price falls to a specified level. 13 on margin 13 margin call 14 bonds 14 par value 14 debentures 14 call feature 14 convertible bond 14 extendible bond 14 put feature 14 yield to maturity 14 discount 14 premium 14 Government of Canada bonds Federal Crown corporation bonds 14 14 provincial bonds 14 municipal bonds 14 corporate bonds 14 high-yield bonds 14 T-Bills 14 banker's acceptances (BAs) Purchasing a stock with a small amount of personal funds and a portion of the funds borrowed from a brokerage firm. A request from a brokerage firm for the investor to increase the cash in the account in order to return the margin to the minimum level. Long-term debt securities issued by government agencies or corporations that are collateralized by assets. For a bond, its face value, or the amount returned to the investor at the maturity date when the bond is due. Long-term debt securities issued by corporations that are secured only by the corporation's promise to pay. A feature on a bond that allows the issuer to repurchase the bond from the investor before maturity. A bond that can be converted into a stated number of shares of the issuer's stock at a specified price. A short-term bond that allows the investor to extend the maturity date of the bond. A feature on a bond that allows the investor to redeem the bond at its face value before it matures. The annualized return on a bond if it is held until maturity. A bond that is trading at a price below its par value. A bond that is trading at a price above its par value. Debt securities issued by the Canadian government. Debt securities issued by corporations established by the federal government. Debt securities issued by the various provincial governments. Long-term debt securities issued by local government agencies. Long-term debt securities issued by large firms. Bonds issued by less stable corporations that are subject to a higher degree of default risk. Short-term debt securities issued by the Canadian government and sold at a discount. Short-term debt securities issued by large firms that are guaranteed by a bank. 14 commercial paper 14 mortgage backed securities 14 strip bonds 14 real return bonds 14 risk premium 14 default risk 14 call (prepayment) risk 14 interest rate risk 14 interest rate strategy 14 passive strategy 14 15 maturity matching strategy pensionable earnings 15 pension assignment 15 defined-benefit pension plan 15 vested 15 defined-contribution pension plan 15 pension adjustment A short-term debt security issued by large firms that is guaranteed by the issuing firm. Represent a pool of CMHC-insured residential mortgages that are issued by banks and other financial institutions. Long-term debt securities issued by the Government of Canada that do not offer coupon payments. Long-term debt securities issued by the Government of Canada that protect you from inflation risk. The extra yield required by investors to compensate for default risk. Risk that the borrower of funds will not repay the creditors. The risk that a callable bond will be called. The risk that a bond's price will decline in response to an increase in interest rates. Selecting bonds based on interest rate expectations. Investing in a diversified portfolio of bonds that are held for a long period of time. Investing in bonds that will generate payments to match future expenses. The amount of income you earn between the year's basic exemption (YBE) and the year's maximum pensionable earnings (YMPE). Occurs when a married or commonlaw couple decides to share their CPP retirement pensions in order to reduce their income taxes. An employer-sponsored retirement plan that guarantees you a specific amount of income when you retire, based on your salary and years of employment. Having a claim to the money in an employer-sponsored retirement account that has been reserved for you upon your retirement, even if you leave the company. An employer-sponsored retirement plan where the contribution rate, not the benefit amount, is based on a specific formula. Calculates the remaining annual contribution room available to an individual after taking into account any employer-sponsored pension 15 normal retirement age 15 registered retirement savings plan (RRSP) 15 spousal RRSP 15 Home Buyers' Plan (HBP) 15 Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) 15 locked-in retirement account (LIRA) 15 term annuity 15 life annuity 15 registered annuities 15 reverse mortgage 16 estate 16 estate planning 16 beneficiaries (heirs) 16 16 intestate preferential share 16 English form will 16 will plan contributions. The age by which employees are entitled to receive 100 percent of the pension income they are eligible for. A type of private pension that enables you to save for your retirement on a tax-deferred basis. A type of RRSP where one spouse contributes to the plan and the other spouse is the beneficiary, or annuitant. A tax-free RRSP withdrawal option that is available to Canadians who would like to buy their first home. A tax-free RRSP withdrawal that is available to full-time students who temporarily would like to use an RRSP to finance their education. A private pension plan that is created when an individual transfers vested money from an employer-sponsored pension plan. A financial contract that provides regular payments until a specified year. A financial contract that provides regular payments for one's lifetime. Annuities that are created using assets from a registered plan, such as an RRSP. A secured loan that allows older Canadians to generate income using the equity in their homes without having to sell this asset. The assets of a deceased person after all debts are paid. The act of planning how your wealth will be allocated on or before your death. The persons specified in a will to receive part of an estate. The condition of dying without a will. The dollar value of estate assets that will be distributed to the surviving spouse before assets are distributed among all potential beneficiaries. A will that contains the signature of the testator and of two witnesses who were present when the testator signed the will. A legal document that describes how your estate should be distributed upon your death. It can also identify a preferred guardian for any surviving minor children. 16 notarial will 16 holograph will 16 executor (personal representative) 16 trustee 16 bequest 16 residue 16 letter of last instruction 16 codicil 16 probate 16 rights or things 16 trust 16 16 settlor inter vivos trust 16 revocable inter vivos trust 16 irrevocable inter vivos trust 16 16 testamentary trust living will 16 limited (non-continuing) A formal type of will that is commonly used in Quebec and is completed in the presence of a notary (lawyer). A will that is written solely in the handwriting of the testator and that does not require the signature of any witnesses. The person designated in a will to execute your instructions regarding the distribution of your assets. An individual or organization that is responsible for the management of assets held in trust for one or more of the beneficiaries of a will. A gift that results from the instructions provided in a will. Refers to the amount remaining in an estate after all financial obligations, such as the payment of debts, expenses, taxes, and bequests, have been fulfilled. A supplement to a will that can describe preferences regarding funeral arrangements and indicate where any key financial documents are stored. A document that specifies changes in an existing will. A legal process that declares a will valid and ensures the orderly distribution of assets. Income that was owed to the deceased taxpayer but not paid at the time of death, but that would have been included in income had the taxpayer not died. A legal document in which one person, the settlor, transfers assets to a trustee, who manages them for designated beneficiaries. The person who creates a trust. A trust in which you assign the management of your assets to a trustee while you are living. An inter vivos trust that can be dissolved. An inter vivos trust that cannot be changed, although it may provide income to the settlor. A trust created by a will. A simple legal document in which individuals specify their preferences if they become mentally or physically disabled. A legal document granting a person power of attorney 16 general power of attorney 16 enduring (continuing) power of attorney 16 durable power of attorney for health care 17 ordinary annuity 17 compounding 17 future value of interest factor (FVIF) 17 discounting 17 present value of interest factor (PVIF) 17 annuity due 17 timelines 17 future value interest factor for an annuity (FVIFA) 17 present value interest factor for an annuity (PVIFA) the power to make specific decisions for you in the event that you are temporarily incapacitated. A legal document granting a person the immediate power to make any decisions and/or commitments for you, with specific limitations. A legal document granting a person the immediate power to make any decisions and/or commitments for you, even when you are mentally incapacitated. A legal document granting a person the power to make specific health care decisions for you. A stream of equal payments that are received or paid at equal intervals in time at the end of a period. The process of earning interest on interest. A factor multiplied by today's savings to determine how the savings will accumulate over time. The process of obtaining present value. A factor multiplied by a future value to determine the present value of that amount. A series of equal cash flow payments that occur at the beginning of each period. Diagrams that show payments received or paid over time. A factor multiplied by the periodic savings level (annuity) to determine how the savings will accumulate over time. A factor multiplied by a periodic savings level (annuity) to determine the present value of the annuity.