Chapter 7.2ST
advertisement

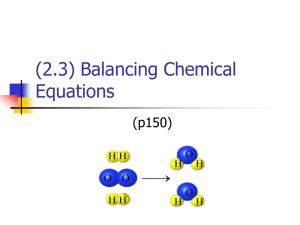
Section 7-2: Chemical Equations A. Describing Reactions 1. chemical equation – representation of a chemical reaction that uses symbols to show the relationship between reactants and products a. many ways to describe a chemical reaction: photograph, videotape, and word equation: methane + oxygen carbon dioxide + water b. chemical rxns are rearrangements of atoms; equations show products and reactants 3. balanced chemical equation – an equation that shows that the number of atoms of each element in the reactants matches those same elements in the products; accounts for the conservation of mass a. unbalanced chemical equation shows simply the symbols for elements and cmpds. b. chemical equations are written the same way worldwide 4. balancing chemical equations a. subscripts must not be changed because the chemical formula would be changed b. coefficient – numeral used to the left of a symbol or formula in a chemical equation to indicate relative amounts of reactants or products; these are changed to balance the equation c. procedure for balancing equations (1) write the chemical equation for the reaction (2) count the number of atoms of each element on each side of the arrow (3) place a coefficient to the left of a symbol or formula so that the number of atoms of that element is the same on each side of the arrow Balance single elements last and H2O next to last d. additional tips for balancing equations (1) balance elements from left to right. (2) balance as single units, polyatomic ions that occur the same on each side (3) balancing one element may unbalance others 7-2b B. Determining Mole Ratios 1. balanced equations show the conservation of mass 2. Law of Definite Proportions – A compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass 3. mole ratio – relative number of moles of the substances required to produce a given amount of product in a chemical reaction: 2H2O → 2H2 + O2 a. determined by the coefficients of the balanced chemical equation: 2: 2: 1 b. relative mass can be calculated from the mole ratios c. multiply the molar mass of each substance by the mole ratio from the balanced equation: 2(18 g/mol) 2(2 g/mol) + 1(32 g/mol)