TOPIC 2.2-THE LAW OF REFLECTION LAB STATION 1
advertisement

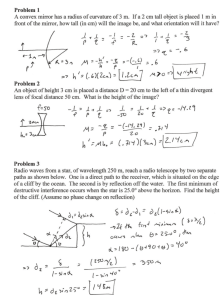
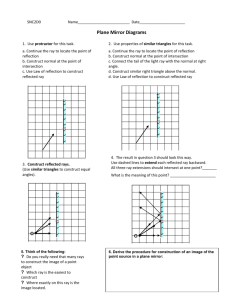
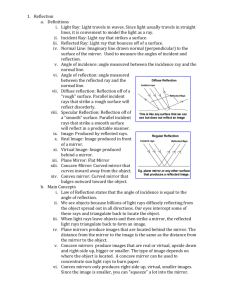
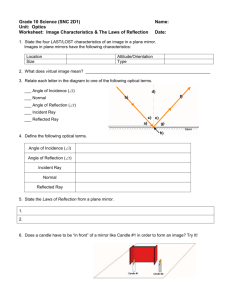
TOPIC 2.2-THE LAW OF REFLECTION LAB STATION 1: REFLECTED LIGHT QUESTION: What material is the best reflector of light? HYPOTHESIS: I THINK …… BECAUSE……… VARIABLES: Manipulated: __________________________________________ Responding: ___________________________________________ Controlled: ____________________________________________ OBSERVATIONS: Material Description Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque Surface type (smooth or rough) Color Qualitative Measurement (good, ave., or poor) Quantitative Measurement (V) ANALYSIS: 1) Which materials reflected the best? Did this agree with your prediction? Why or Why not? 2) Which materials reflected the worst? Did this agree with your prediction? Why or Why not? Ranking 1st, 2nd, etc.. CONCLUSION: LAB STATION 2: TYPES OF REFLECTION: Type of Reflection Ray Diagram Interaction with Light type of surface: _______________ regular bounce off in the _______ ____________ reflected rays stay _______________ to each other image is ________________ type of surface: _____________________ diffuse each ray is reflected at a ____________ angle the light is _________________ LAB STATION 3: WHICH EYE IS WINKING AT YOU: Winking your right eye into a mirror – what happens? With 2 mirrors 90° to each other, when you wink your right eye – what happens? Any possible explanation for this? LAB STATION 4: DESCRIBE IT Classify each of the following objects, as to whether they would give a regular reflection or a diffuse reflection OBJECT – DESCRIBE IT WHAT TYPE OF REFLECTION WOULD YOU GET? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. LAB STATION 5: ANGLES – THE LAW OF REFLECTION: 1. The _________________ ray is the ray that goes into an object and bounces off as a ________________ beam, giving regular reflection. 2. What type of surface gives the best reflections? 3. Examples of objects that allow you to see your image are: still _____________, ____________________, __________________, or even _____________ ______________. The one that gives you the clearest reflection is a _____________ (flat) __________. LAB STATION 6: ANGLES PRACTICE: PROBLEM: What rule can you make that described how light reflects off a flat mirror? HYPOTHESIS: VARIABLES: Manipulated: ______________________________________ Responding: _______________________________________ Controlled: ________________________________________ OBSERVATION DRAWING: Mirror ANAYLYSIS QUESTIONS: a. Label the diagram above using these words: incident ray, angle of incidence, reflecting surface, normal, angle of reflection and reflected ray. b. Using a protractor measure the angle of incidence= _______° c. Using a protractor measure the angle of reflection= _______° d. What happens to the angle of reflection when you increase the angle of incident? CONCLUSION: The “LAW OF REFLECTION” states that…. TOPIC 2.3-REFLECTING LIGHT WITH CURVED MIRRORS LAB STATION 7: CONCAVE MIRRORS 1. A mirror that is curved inwards like a bowl is called a ________________ mirror. 2. Look at the inside of a spoon. Describe what you see. 3. Look at the concave mirror. What does the reflection look like. 4. What happens when you move far away from the mirror? 5. What happens when you move really close to the mirror? 6. Sketch a ray diagram of a concave mirror that has a light source hitting it. Note that the rays follow the Law of Reflection! 7. The place where the light rays all head to a common point is called the __________________ __________________. 8. Because of the shape of a concave mirror they are very good at ___________ ____________ and ________________ it to a ______________ __________________. 9. Explain where concave mirrors are used and why. 10.Make a ray diagram using a light bulb at the focal point of a concave mirror, such as a flashlight or car headlight. 11.Explain what an image looks when the object is outside the focal point and what happens as the object approaches the focal point. 12.When using a concave mirror, explain when you get an image that is upright and enlarged? LAB STATION 8: CONVEX MIRRORS 1. A mirror with the surface curved outwards is called a ____________ ________. 2. Look at the outside of a spoon. Describe what you see. 3. Look at the convex mirror supplied. What does the reflection look like? 4. What happens when you move far away from the mirror? 5. What happens when you move very close to the mirror? 6. Sketch a ray diagram of a convex mirror that has a light source hitting it. Note: the rays follow the Law of Reflection! 7. Describe what type of image you get when using a convex mirror. 8. What warning message do some convex mirrors have on them?