Science 8: Unit C – Light and Optics
advertisement

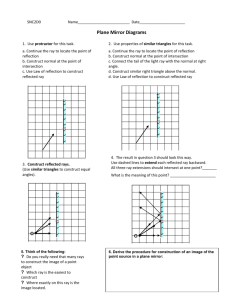
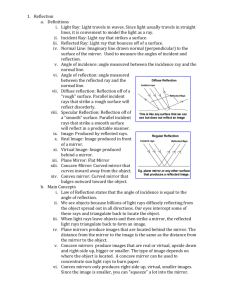
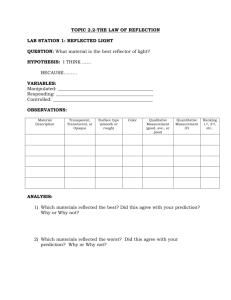
Science 8: Unit C – Light and Optics Topic 2: Reflection What is Reflection? • Reflection is the process when a light ray strikes a surface and bounces off it. Whenever light rays strike an object, some of them are reflected and some are absorbed. Two Types of Reflection • Reflection occurs in smoother surfaces more than rougher surfaces because the light rays are all reflected in the same direction where in a rougher surface the light rays are scattered in all directions, preventing an image from forming. Two Types of Reflection Cont’d • Regular/Specular Reflection – Light rays bounce off the smooth surface at the same angle. • Rough/Diffuse Reflection – Light rays all bounce off the rough surface at different angles. The Incident and Reflected Rays and the Normal • In reflection, the light ray that approaches the surface is called the incident ray and the light ray moving away from the surface is called the reflected ray. • A normal is an imaginary line that is 90° (perpendicular) to the surface of the mirror. The angle that the incident ray makes with the normal is called the angle of incidence, and the angle that the reflection ray makes with the normal is called the angle of reflection. The Law of Reflection • The Law of Reflection – The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. This law applies to all types of reflective surfaces. Concave Mirror • A concave mirror is a mirror whose reflective surface CAVES INWARDS. The advantage of a concave mirror is that it helps focus the light to a focal point, producing an image that can be put on a screen. This image is called a real image. The downside of a concave mirror is that any object that is past its focal point will be upside down. Convex Mirror • A convex image is a mirror whose reflective surface bulges out. The advantage of a convex image is that its reflections are always rightside-up. Also you can see a lot of your surroundings with a convex image which explains why they are used in car mirrors and in convenience stores. The downside of a convex mirror is that you cannot focus its image on a screen. These types of images are called virtual images. Attitude of an Image • The attitude of an image is another word for its orientation. Is it upsidedown (inverted) or right-side-up? Concave vs. Convex Images • Mirror • Draw its shape with Reflective Surface facing the left side. • What type of image is formed? • Attitude of Image formed? • Can image formed be larger than object? • Concave • ) • Real • Usually inverted • Sometimes, depending on position of object • Can be put on a screen? • Yes • Telescopes, • Uses? flashlights. Convex ( Virtual Always right-side up Always smaller than object No Security and car mirrors.